The dance of molecules how nanotechnology is changing our lives
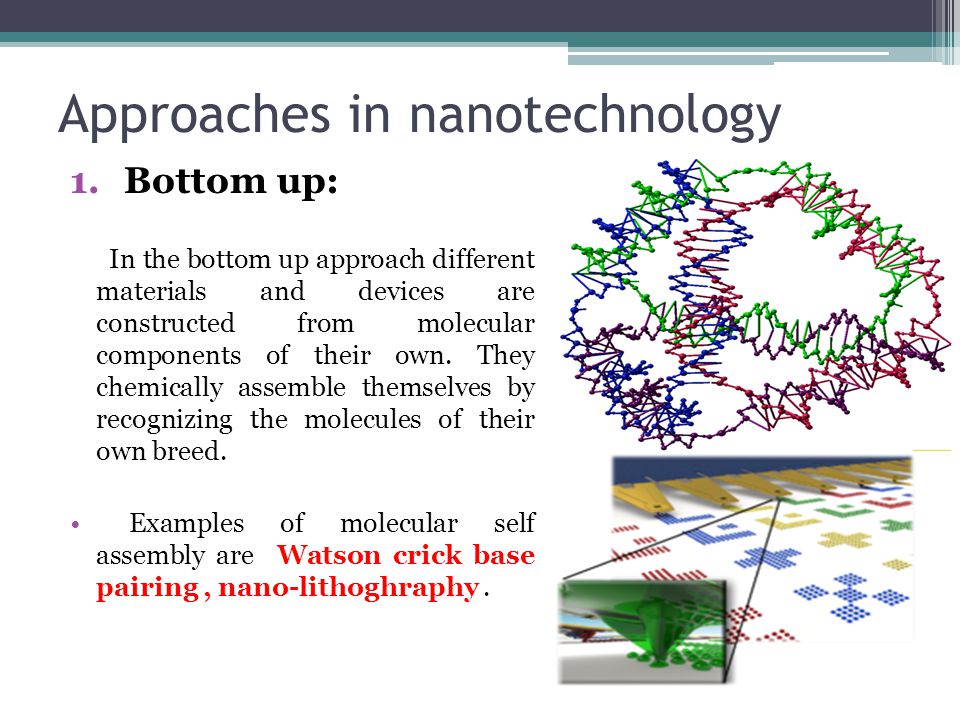
9781560258957: The Dance of the Molecules: How Nanotechnology is Changing Our Lives - Sargent, Ted: 1560258950
What if a doctor could stop cancer by targeting a single malignant cell before it multiplied? Imagine a paper-thin "power suit" that could keep you warm on a winter day? What about a computer that connects directly with your thoughts? In this groundbreaking exploration of the future of nanotechnology, Ted Sargent reveals how all disciplines of science, from medicine to microchips, are converging to create materials using the tiniest scale possible — molecule by molecule. And instead of trying to overcome the natural world, nanotech takes its every move from the perfect, elegant structure of nature itself. Its potential is seemingly endless, with practical implications that will revolutionize the way we live, work, and play. In an age when science often evokes more fear than faith, when the potential for superviruses and diabolical cloning looms in our consciousness, Sargent enthusiastically illuminates nanotech's positive possibilities. By working with the tiniest building blocks in nature, pioneering scientists will drastically improve the quality of life for all of us.
"synopsis" may belong to another edition of this title.
About the Author:
Ted Sargent is visiting professor of nanotechnology at MIT. In 2003, Sargent was named to Technology Review magazine's "TR100": a group of 100 of the world's top young innovators whose work will shape how we live and work in the future. His research breakthroughs have been widely reported in magazines such as Wired, BusinessWeek, and National Geographic. He lives in Cambridge, MA.
From Publishers Weekly:
Sargent, visiting professor of nanotechnology at MIT, persuasively argues that advances in nanotechnology are occurring at a dizzying rate and have the potential to transform almost all aspects of human society, from health care to warfare. The book examines cutting-edge science in health, the environment and communications. Sargent's optimism knows almost no limits. He predicts that with nanotechnology's ability "to design and build matter to order," scientists will soon be able to prescribe nano-size drugs that will identify and kill single cancerous cells long before they can do any harm, and regenerate nerve cells to cure spinal cord injuries. Further, Sargent says, "new technologies may allow ground-based warfare without people." Throw in a limitless energy supply and a fully integrated computer and communications system that will become an integral part of humans, and you have a utopia almost beyond belief. Indeed, with only a few pages devoted to possible negative environmental consequences of runaway nanotechnology, Sargent's utopia is beyond belief. Although his exuberance is somewhat infectious, he tries a bit too hard to make his writing witty, such as describing an optical detector as "a voyeur, a castrato ogling the photon but under-equipped to seduce it." (Jan.)
Sargent's optimism knows almost no limits. He predicts that with nanotechnology's ability "to design and build matter to order," scientists will soon be able to prescribe nano-size drugs that will identify and kill single cancerous cells long before they can do any harm, and regenerate nerve cells to cure spinal cord injuries. Further, Sargent says, "new technologies may allow ground-based warfare without people." Throw in a limitless energy supply and a fully integrated computer and communications system that will become an integral part of humans, and you have a utopia almost beyond belief. Indeed, with only a few pages devoted to possible negative environmental consequences of runaway nanotechnology, Sargent's utopia is beyond belief. Although his exuberance is somewhat infectious, he tries a bit too hard to make his writing witty, such as describing an optical detector as "a voyeur, a castrato ogling the photon but under-equipped to seduce it." (Jan.)
Copyright Reed Business Information, a division of Reed Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.
"About this title" may belong to another edition of this title.
9781560258094: The Dance of Molecules: How Nanotechnology is Changing Our Lives - Sargent, Ted: 1560258098
What if a doctor could stop cancer by targeting a single malignant cell before it multiplied? Imagine a paper-thin “power suit” that could keep you warm on a winter day. What about a computer that connects directly with a person’s thoughts?
In this groundbreaking exploration of the future of nanotechnology, Ted Sargent reveals how all disciplines of science, from medicine to microchips, are converging to create materials using the tiniest scale possible—molecule by molecule. And instead of trying to overcome the natural world, nanotech takes its every move from the perfect, elegant structure of nature itself. Its potential is seemingly endless, with practical implications that will revolutionize the way we live, work, and play.
In an age when science often evokes more fear than faith, when the potential for superviruses and diabolical cloning looms in our consciousness, Sargent enthusiastically illuminates nanotech’s positive possibilities.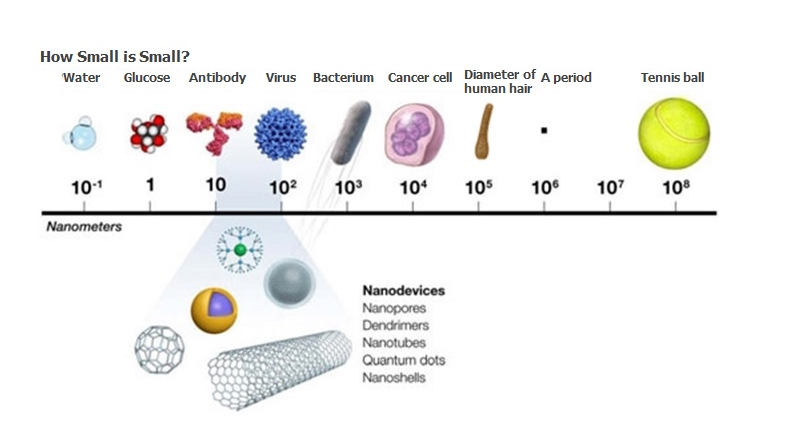 By working with the tiniest building blocks in nature, pioneering scientists will drastically improve the quality of life for all of us.
By working with the tiniest building blocks in nature, pioneering scientists will drastically improve the quality of life for all of us.
"synopsis" may belong to another edition of this title.
About the Author:
Ted Sargent is visiting professor of nanotechnology at MIT. In 2003, Sargent was named to Technology Review magazine's "TR100": a group of 100 of the world's top young innovators whose work will shape how we live and work in the future. His research breakthroughs have been widely reported in magazines such as Wired, BusinessWeek, and National Geographic. He lives in Cambridge, MA.
From Publishers Weekly:
Sargent, visiting professor of nanotechnology at MIT, persuasively argues that advances in nanotechnology are occurring at a dizzying rate and have the potential to transform almost all aspects of human society, from health care to warfare. The book examines cutting-edge science in health, the environment and communications. Sargent's optimism knows almost no limits. He predicts that with nanotechnology's ability "to design and build matter to order," scientists will soon be able to prescribe nano-size drugs that will identify and kill single cancerous cells long before they can do any harm, and regenerate nerve cells to cure spinal cord injuries. Further, Sargent says, "new technologies may allow ground-based warfare without people." Throw in a limitless energy supply and a fully integrated computer and communications system that will become an integral part of humans, and you have a utopia almost beyond belief. Indeed, with only a few pages devoted to possible negative environmental consequences of runaway nanotechnology, Sargent's utopia is beyond belief. Although his exuberance is somewhat infectious, he tries a bit too hard to make his writing witty, such as describing an optical detector as "a voyeur, a castrato ogling the photon but under-equipped to seduce it." (Jan.)
Sargent's optimism knows almost no limits. He predicts that with nanotechnology's ability "to design and build matter to order," scientists will soon be able to prescribe nano-size drugs that will identify and kill single cancerous cells long before they can do any harm, and regenerate nerve cells to cure spinal cord injuries. Further, Sargent says, "new technologies may allow ground-based warfare without people." Throw in a limitless energy supply and a fully integrated computer and communications system that will become an integral part of humans, and you have a utopia almost beyond belief. Indeed, with only a few pages devoted to possible negative environmental consequences of runaway nanotechnology, Sargent's utopia is beyond belief. Although his exuberance is somewhat infectious, he tries a bit too hard to make his writing witty, such as describing an optical detector as "a voyeur, a castrato ogling the photon but under-equipped to seduce it." (Jan.)
Copyright Reed Business Information, a division of Reed Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.
"About this title" may belong to another edition of this title.
Nanotechnologies are changing the world - News - IQ Research and Education Portal - National Research University Higher School of Economics
In a few decades the world may change beyond recognition thanks to the development of nanotechnologies. The world economy will work according to completely different principles, the central place in it will be occupied by a human creator. Catastrophic stories described by science fiction writers can also become a reality. Study by Mikhail Pavlov from Moscow State University
Developments in the field of nanotechnology are already actively used today, for example, in medicine and industry. The leaders in the field of investment in nanotechnology are the United States, the European Union, Japan and China. Russia's share in the global nanotechnology market is minimal.
The development of nanotechnologies is something that with a high degree of probability will determine the future of the world economy. Experts studying the development of nanotechnologies predict maximum information openness and the absence of boundaries between industries and companies in the field of innovation. Inventors will have no problem promoting their inventions on the market, as the demand for them will rise sharply, and the development of information technology will remove the barriers that today exist between innovators and the market. The economy of nanotechnologies will place scientists, inventors, and creative people at the highest levels of the social hierarchy. nine0005
Experts studying the development of nanotechnologies predict maximum information openness and the absence of boundaries between industries and companies in the field of innovation. Inventors will have no problem promoting their inventions on the market, as the demand for them will rise sharply, and the development of information technology will remove the barriers that today exist between innovators and the market. The economy of nanotechnologies will place scientists, inventors, and creative people at the highest levels of the social hierarchy. nine0005
But nanotechnologies also carry many risks for humanity, including those of an existential nature. This is no longer fantasy, but quite real prospects that the governments of a number of countries are afraid of, calling for limiting the development of nanotechnologies. Mikhail Pavlov , Associate Professor of the Faculty of Economics of Moscow State University , spoke about this at the conference "Interdisciplinary Studies of Economics and Society".
Eternal life can become a reality
The basis of nanotechnology is the manipulation of atoms. One nanometer is one billionth of a meter. Nanotechnologies make it possible to create and modify objects with components less than 100 nm in size and integrate them into fully functioning systems. nine0005
One of the areas where nanotechnology can make a real revolution is medicine and biotechnology. The revolution will be possible thanks to the creation of molecular and atomic nanorobots, consisting, as scientists now assume, of carbon and its derivatives. Nanorobots will be able to penetrate into the human body and perform the necessary actions there, which are not available to medicine today. With the help of nanotechnologies, as Pavlov said, it will be possible to cleanse the body at the level of individual cells, restore microdamages inside the body, and in the longer term, correct even rather large damage. nine0005
A number of technologies for the nanomedical industry have already been created in the world today. “These include targeted drug delivery to diseased cells, disease diagnosis using quantum dots, laboratories on a chip, new bactericidal agents,” Pavlov points out in his work “The Economics of Nanotechnology,” a textbook for master’s students prepared during the course of research.
“These include targeted drug delivery to diseased cells, disease diagnosis using quantum dots, laboratories on a chip, new bactericidal agents,” Pavlov points out in his work “The Economics of Nanotechnology,” a textbook for master’s students prepared during the course of research.
As a result, a person's life expectancy can seriously increase, and it will be possible to rejuvenate the body. Mankind, as the scientist notes, can get medicines for all existing diseases, and not only of viral and bacterial origin, but also genetic. nine0005
According to various estimates, such advances in nanomedicine may become a reality in 40-50 years. “But a number of recent discoveries, developments and investments in the nanoindustry have led to the fact that more and more analysts are shifting this date downward by 10-15 years, and perhaps this is not the limit yet,” the author explains.
At the same time, the increase in life expectancy and the victory over old age is not the top of the revolution in the field of nanomedicine. Hypothetically, the development of nanotechnology, scientists predict, can provide humanity with the possibility of an unlimited period of life for a single person, as well as the revival of people frozen by cryonics methods and the restoration of previously extinct species. nine0005
Hypothetically, the development of nanotechnology, scientists predict, can provide humanity with the possibility of an unlimited period of life for a single person, as well as the revival of people frozen by cryonics methods and the restoration of previously extinct species. nine0005
Mercedes-chameleon and grass milk
Nanotechnologies can completely change a person's life and habitual things around him. If today mankind is already accustomed to the rapid progress in the field of Internet technologies, but the main essence, for example, of vehicles is changing rather slowly, then tomorrow the situation may be completely different. Pictures from science fiction films promise to become reality. So the case of the Mercedes of the future "SilverFlow" is a magnetic connection that can restore and change its shape with one click. The choice of color is unlimited. The car runs on mechanical energy, is able to turn around on the spot and park sideways. In its original state, the car is a ferromagnetic ellipsoid in the form of a "puddle" of liquid metal, which requires minimal storage space. nine0005
nine0005
The clothes that people wear today may turn out to be completely different in the future. Already today in the USA models of clothes containing charged nanoparticles in fabric fibers have been created. They protect a person from colds, flu, smog, pollution. These clothes do not require washing. However, while it can not be used in mass industry. One square meter of new fabric costs about $10,000.
Hypothetically, nanotechnologies can solve such global problems of mankind as environmental pollution, lack of food resources and depletion of drinking water. Molecular and atomic robots will be able to produce food, replacing agricultural plants and animals. “For example, it would be theoretically possible to produce milk directly from grass, bypassing the intermediate link – a cow,” writes Pavlov. nine0005
As for improving the ecological state of the planet, it is possible through the development of alternative energy sources, reducing the amount of garbage and its active use in production. Drinking water resources will be replenished through innovative water purification systems.
Drinking water resources will be replenished through innovative water purification systems.
A request for creative work and total openness
In the event that a new technological revolution occurs, every inhabitant of the planet will potentially be able to access the minimum subsistence level, which will be provided through the reproductive labor of nanomachines. nine0005
At the same time, the social hierarchy will undergo a significant transformation. The most important profession, Pavlov notes, will be the creator of new models - the human creator. “Anyone who wants to improve their financial situation and get something in excess of the subsistence minimum and their current level of prosperity will have to use their creative abilities to create a new sample, model, design,” the scientist believes. In the new economy of ubiquity based on nanotechnologies, he notes, two things will have value - creative ideas and energy. nine0005
At the same time, humanity will have to go through a psychologically difficult moment associated with intellectual property. “In particular, it will become impossible to keep anything secret. With the help of “smart dust” created using nanotechnology, it will be possible to track any processes that people can access at all. The appropriate form in such a world would be universal intellectual property,” says the author.
“In particular, it will become impossible to keep anything secret. With the help of “smart dust” created using nanotechnology, it will be possible to track any processes that people can access at all. The appropriate form in such a world would be universal intellectual property,” says the author.
Elevator to space
Hypothetically, nanotechnology can bring the human mind to a whole new level of development. The potential of nanotechnology, as Pavlov notes, contributed to the emergence of a new philosophical direction - transhumanism, according to which the modern human species Homosapiens - Homo sapiens - is not the peak, but one of the links in evolution, which will be followed by stronger and more powerful. New people will be able to explore outer space, populate other planets and gain immortality.
But nanotechnological progress also carries huge threats. For example, a new form of social inequality may emerge - a two-class nanotechnological society - those who have access to new technologies and those who do not. “You can create a new weapon against a person - you can poison, infect with any virus. Finding traces of the use of such weapons is almost impossible. Enormous opportunities are emerging for espionage, theft of information and invasion of privacy. A “world without borders” is emerging for those who have access to the benefits of nanotechnology and total control over others,” says Pavlov. He emphasizes that stratification can occur according to the criteria of health and life expectancy. “The formation of new, extremely powerful elites is possible, potentially capable of holding power for millennia,” he said. nine0005
“You can create a new weapon against a person - you can poison, infect with any virus. Finding traces of the use of such weapons is almost impossible. Enormous opportunities are emerging for espionage, theft of information and invasion of privacy. A “world without borders” is emerging for those who have access to the benefits of nanotechnology and total control over others,” says Pavlov. He emphasizes that stratification can occur according to the criteria of health and life expectancy. “The formation of new, extremely powerful elites is possible, potentially capable of holding power for millennia,” he said. nine0005
But the most serious risks in the development of nanotechnology are associated with nanorobots, which are still under development. Especially dangerous are self-replicating, capable of self-propagation, nanorobots. The American scientist E. Drexler wrote about their danger - "gray slime" in his book "Machines of Creation", recalls Pavlov. It was E. Drexler who introduced the concept of molecular robots. This was in the mid 80s of the last century.
This was in the mid 80s of the last century.
Today, science has advanced a lot. Nanotechnology experts warn that humanity should seriously consider letting the genie out of the bottle. “Even if the three laws of A. Azimov's robotics are put into each nanorobot, there is still a possibility that nanorobots will start creating new copies of themselves without observing these laws. Or it will be done by an evil human genius,” notes Pavlov. nine0005
See also:
Passport of competencies will replace university diploma
Moscow is far from leaders in creativity
Selina Marina Vladimirovna, February 10, 2014
All materials of the author
High tech innovative development science and technology
NANOTECHNOLOGIES IN OUR LIFE | Nauka i Zhizn
Nanostructures will replace traditional transistors. nine0005
The compact training nanotechnological setup "UMKA" allows manipulations with individual groups of atoms.
With the help of the "UMKA" installation it is possible to examine the DVD surface.
A textbook has already been published for future nanotechnologists.
‹
›
View full size
Nanotechnologies that emerged in the last quarter of the 20th century are developing rapidly. Almost every month there are reports of new projects that seemed like an absolute fantasy a year or two ago. By definition, given by the pioneer of this direction, Eric Drexler, nanotechnology is "an expected production technology focused on the cheap production of devices and substances with a predetermined atomic structure." This means that it operates on individual atoms in order to obtain structures with atomic precision. This is the fundamental difference between nanotechnologies and modern "bulk" technologies that manipulate macro objects. nine0005
We remind the reader that nano is a prefix denoting 10 -9 . Eight oxygen atoms can be arranged on a one nanometer long segment.
Nanoobjects (eg, metal nanoparticles) typically have physical and chemical properties that are different from those of larger objects of the same material and from the properties of individual atoms. Let's say the melting point of gold particles 5-10 nm in size is hundreds of degrees lower than the melting point of a piece of gold with a volume of 1 cm 3 .
Research carried out in the nanoscale range lies at the intersection of sciences, often research in the field of materials science affects the fields of biotechnology, solid state physics, and electronics.
The world's leading specialist in the field of nanomedicine Robert Freitas said: "Future nanomachines should consist of billions of atoms, so their design and construction will require the efforts of a team of specialists. Each design of a nanorobot will require the combined efforts of several research teams. The design and construction of the Boeing 777 aircraft involved many teams around the world. The nanomedical robot of the future, consisting of a million (or even more) working parts, will be as complex as an airplane in terms of design complexity." nine0005
The nanomedical robot of the future, consisting of a million (or even more) working parts, will be as complex as an airplane in terms of design complexity." nine0005
NANOPRODUCTS AROUND US
The nanoworld is complex and still relatively little studied, and yet not so far away. from us, as it seemed a few years ago. Most of us regularly use some or other advances in nanotechnology, without even knowing it. For example, modern microelectronics is no longer micro, but nano: transistors produced today - the basis of all chips - lie in the range up to 90 nm. And more is planned miniaturization of electronic components up to 60, 45 and 30 nm. nine0005
Moreover, as representatives of the Hewlett-Packard company recently announced, transistors manufactured using traditional technology will be replaced by nanostructures. One such element is three conductors a few nanometers wide: two of them are parallel, and the third is located at right angles to them.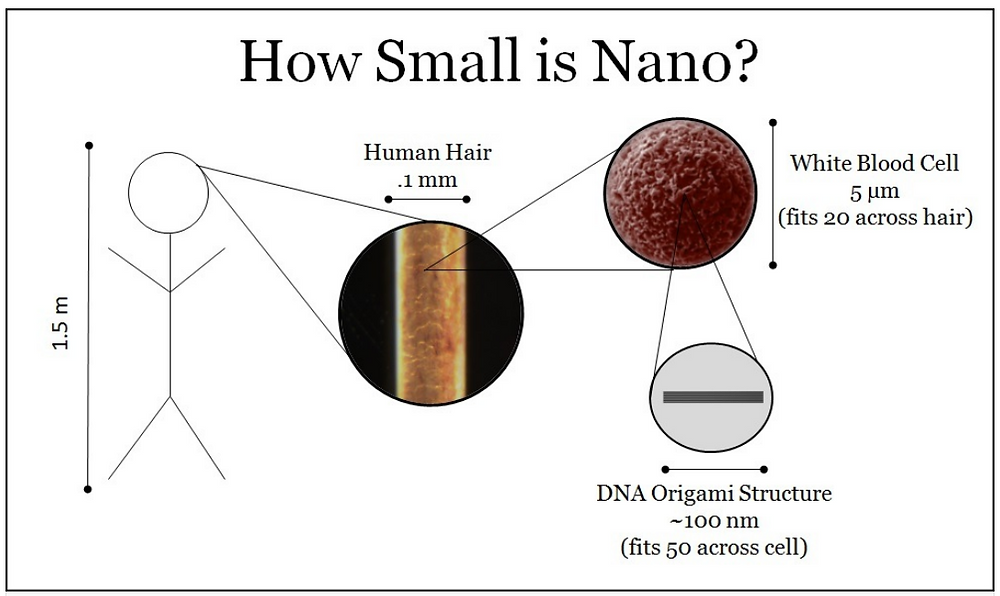 The conductors do not touch, but pass like bridges, one over the other. At the same time, molecular chains formed from the material of nanowires under the influence of voltage applied to them descend from the upper conductors to the lower ones. Circuits built using this technology have already demonstrated the ability to store data and perform logical operations, that is, to replace transistors. nine0005
The conductors do not touch, but pass like bridges, one over the other. At the same time, molecular chains formed from the material of nanowires under the influence of voltage applied to them descend from the upper conductors to the lower ones. Circuits built using this technology have already demonstrated the ability to store data and perform logical operations, that is, to replace transistors. nine0005
With the new technology, the size of microcircuit parts will drop significantly below the bar of 10-15 nanometers, to a scale where traditional semiconductor transistors simply cannot physically work. Probably, already in the first half of the next decade, serial microcircuits (still traditional, silicon) will appear, in which a certain number of nanoelements created using the new technology will be built.
Kodak launched Ultima inkjet paper in 2004. It has nine layers. The top layer consists of ceramic nanoparticles, which make the paper thicker and shinier. The inner layers contain pigment nanoparticles with a size of 10 nm, which improve the quality of printing. And the polymer nanoparticles included in the composition of the coating contribute to the rapid fixation of the paint. nine0005
And the polymer nanoparticles included in the composition of the coating contribute to the rapid fixation of the paint. nine0005
Director of the US Institute of Nanotechnology Chad Mirkin believes that "nanotechnology will rebuild all materials anew. All materials obtained through molecular production will be new, since until now mankind has not had the opportunity to develop and produce nanostructures. Now we use in industry only that "What nature gives us. From trees we make boards, from conductive metal - wire. The nanotechnological approach is that we will process almost any natural resource into the so-called "building blocks" that will form the basis of future industry." nine0005
Now we are already seeing the onset of a nanorevolution: these are new computer chips, and new fabrics that do not leave stains, and the use of nanoparticles in medical diagnostics (see also "Science and Life" Nos. 2, 4, 2005). Even the cosmetics industry is interested in nanomaterials. They can create many new non-standard directions in cosmetics that did not exist before.
In the nanoscale range, almost any material exhibits unique properties. For example, silver ions are known to have antiseptic activity. A solution of silver nanoparticles has a significantly higher activity. If you treat a bandage with this solution and apply it to a purulent wound, the inflammation will go away and the wound will heal faster than with conventional antiseptics. nine0005
The domestic concern "Nanoindustry" has developed a technology for the production of silver nanoparticles that are stable in solutions and in the adsorbed state. The resulting drugs have a wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Thus, it became possible to create a whole range of products with antimicrobial properties with a slight change in the technological process by manufacturers of existing products.
Silver nanoparticles can be used to modify traditional and create new materials, coatings, disinfectants and detergents (including tooth and cleaning pastes, washing powders, soaps), and cosmetics. Coatings and materials (composite, textile, lacquer, carbon, and others) modified with silver nanoparticles can be used as preventive antimicrobial protective equipment in places where the risk of spreading infections increases: in transport, in catering establishments, in agricultural and livestock buildings , in children's, sports, medical institutions. Silver nanoparticles can be used to purify water and kill pathogens in air conditioning filters, swimming pools, showers and other similar public places. nine0005
Coatings and materials (composite, textile, lacquer, carbon, and others) modified with silver nanoparticles can be used as preventive antimicrobial protective equipment in places where the risk of spreading infections increases: in transport, in catering establishments, in agricultural and livestock buildings , in children's, sports, medical institutions. Silver nanoparticles can be used to purify water and kill pathogens in air conditioning filters, swimming pools, showers and other similar public places. nine0005
Similar products are also produced abroad. One company produces coatings with silver nanoparticles for the treatment of chronic inflammation and open wounds.
Another type of nanomaterials is carbon nanotubes with colossal strength (see "Science and Life" No. 5, 2002; No. 6, 2003). These are peculiar cylindrical polymer molecules with a diameter of about half a nanometer and a length of up to several micrometers. They were first discovered less than 10 years ago as by-products of the synthesis of fullerene C 60 . Nevertheless, nanometer-sized electronic devices are already being created on the basis of carbon nanotubes. It is expected that in the foreseeable future they will replace many elements in the electronic circuits of various devices, including modern computers.
Nevertheless, nanometer-sized electronic devices are already being created on the basis of carbon nanotubes. It is expected that in the foreseeable future they will replace many elements in the electronic circuits of various devices, including modern computers.
However, nanotubes are used not only in electronics. There are already commercially available tennis racquets reinforced with carbon nanotubes to limit twisting and provide more punching power. They are also used in some parts of sports bikes. nine0005
RUSSIA ON THE MARKET OF NANOTECHNOLOGIES
The domestic company "Nanotechnology News Network" has recently introduced another novelty in Russia - self-cleaning nanocoatings. It is enough to spray the car glass with a special solution with silicon dioxide nanoparticles, and dirt and water will not stick to it for 50,000 km. A transparent ultra-thin layer remains on the glass, on which water simply has nothing to catch on, and it rolls along with the dirt. First of all, the owners of skyscrapers became interested in the novelty - a lot of money is spent on washing the facades of these buildings. There are such compositions for coating ceramics, stone, wood and even clothing. nine0005
First of all, the owners of skyscrapers became interested in the novelty - a lot of money is spent on washing the facades of these buildings. There are such compositions for coating ceramics, stone, wood and even clothing. nine0005
It must be said that some Russian organizations are already successfully operating on the international nanotechnology market.
Concern "Nanoindustry", for example, has a number of nanotechnological products applicable in various industries. It's restorative "RVS" composition and silver nanoparticles for biotechnology and medicine, industrial nanotechnological installation "LUCH-1,2" and educational nanotechnological installation "UMKA". nine0005
The RVS composition, which can protect against wear and restore almost any rubbing metal surfaces, is prepared on the basis of adaptive nanoparticles. This tool allows you to create a modified high-carbon iron silicate protective layer with a thickness of 0.1-1.5 mm in areas of intense friction of metal surfaces (for example, in friction pairs in internal combustion engines). By pouring such a composition into the crankcase for oil, you can forget about the problem of engine wear for a long time. During operation, mechanical parts are heated by friction, this heating causes metal nanoparticles to adhere to damaged areas. Excessive growth causes more intense heating, and the nanoparticles lose their ability to attach. Thus, equilibrium is constantly maintained in the friction unit, and the parts practically do not wear out. nine0005
By pouring such a composition into the crankcase for oil, you can forget about the problem of engine wear for a long time. During operation, mechanical parts are heated by friction, this heating causes metal nanoparticles to adhere to damaged areas. Excessive growth causes more intense heating, and the nanoparticles lose their ability to attach. Thus, equilibrium is constantly maintained in the friction unit, and the parts practically do not wear out. nine0005
Of particular interest is the UMKA complex of nanotechnological equipment, which is intended for demonstration, research, and laboratory work at the atomic-molecular level in the fields of physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, genetics, and other fundamental and applied sciences. For example, a DVD surface image with a resolution of 0.3 microns was recently obtained on it, and this is not the limit. The unique picoampere current technology allows scanning even weakly conductive biological samples without preliminary metal deposition (usually it is necessary that the top layer of the sample be conductive). "UMKA" has a high temperature stability, which makes it possible to carry out long-term manipulations with individual groups of atoms, and a high scanning speed, which makes it possible to observe fast processes. nine0005
"UMKA" has a high temperature stability, which makes it possible to carry out long-term manipulations with individual groups of atoms, and a high scanning speed, which makes it possible to observe fast processes. nine0005
The main field of application of the UMKA complex is training in modern practical methods of working with nanoscale structures. The UMKA complex includes: a tunnel microscope, a vibration protection system, a set of test samples, sets of consumables and tools. Devices fit in a small case, work in room conditions and cost less than 8 thousand dollars. Experiments can be controlled from a regular personal computer.
In January 2005, the first Russian online store selling nanotechnology products was opened. The permanent address of the store on the Internet is www.nanobot.ru
SAFETY ISSUES
It has recently been found that the spherical molecules C 60 , called fullerenes, can cause serious disease and harm the environment. The toxicity of water-soluble fullerenes when exposed to human cells of two different types was established by researchers from the Universities of Rice and Georgia (USA).
The toxicity of water-soluble fullerenes when exposed to human cells of two different types was established by researchers from the Universities of Rice and Georgia (USA).
Chemistry professor Vicki Colvin of Rice University and his colleagues found that when fullerenes are dissolved in water, C 9 colloids are formed.0131 60 , which, when exposed to human skin cells and liver carcinoma cells, cause their death. At the same time, the concentration of fullerenes in water was very low: ~ 20 molecules of C 60 per 1 billion water molecules. At the same time, the researchers showed that the toxicity of molecules depends on the modification of their surface.
The researchers suggest that the toxicity of simple fullerenes C 60 is due to the fact that their surface is capable of producing superoxide anions. These radicals damage cell membranes and lead to cell death. nine0005
Colvin and his colleagues said that such a negative property of fullerenes can be used for good - for the treatment of cancerous tumors. It is only necessary to elucidate in detail the mechanism of formation of oxygen radicals. Obviously, on the basis of fullerenes it will be possible to create super-effective antibacterial drugs.
It is only necessary to elucidate in detail the mechanism of formation of oxygen radicals. Obviously, on the basis of fullerenes it will be possible to create super-effective antibacterial drugs.
At the same time, the danger of using fullerenes in consumer products seems quite real to scientists.
Apparently, this is why the US Food and Drug Safety Commission (FDA) recently announced the need to license and regulate a wide range of products (food, cosmetics, medicines, apparatus and veterinary medicine) manufactured using nanotechnology and using nanomaterials and nanostructures. nine0005
NANOTECH GOVERNMENT SUPPORT NEEDED
Unfortunately, in Russia there is still no state program for the development of nanotechnologies. (In 2005, the US nanotechnology program, by the way, turned five years old.) Without a doubt, the existence of a centralized state program for the development of nanotechnology would greatly help in the practical implementation of research results. Unfortunately, we learn that there are successful developments in the field of nanotechnologies in the country from foreign sources. For example, in the summer, the US Standards Institute announced the creation of the world's smallest atomic clock. As it turned out, the Russian team also worked on their creation. nine0005
Unfortunately, we learn that there are successful developments in the field of nanotechnologies in the country from foreign sources. For example, in the summer, the US Standards Institute announced the creation of the world's smallest atomic clock. As it turned out, the Russian team also worked on their creation. nine0005
There is no state program in Russia, but there are researchers and enthusiasts: over the past year, the Youth Scientific Society (YNS) united more than 500 young scientists, graduate students and students thinking about the future of their country. For detailed study of the problems of nanotechnology in February 2004, on the basis of the analytical company "Nanotechnology News Network (NNN)", tracking hundreds of open world sources in this area and has processed more than 4500 information messages of foreign and Russian media, articles, press releases and expert comments. The websites www.mno.ru and www.nanonewsnet.ru have been created, with which more than 170,000 citizens of Russia and the CIS have become acquainted. nine0005
nine0005
YOUTH PROJECT COMPETITION
In April 2004, together with the concern "Nanoindustry" with the support of "Uniastrum Bank", the first All-Russian competition of youth projects on the creation of domestic molecular nanotechnology was successfully held, which aroused keen interest of Russian scientists.
The winners of the competition presented outstanding developments: the first place was awarded to a team of young scientists from the Russian Chemical Technical University. D. I. Mendeleev under the guidance of Candidate of Chemical Sciences Galina Popova, who created biomimetic (biomimetic - imitation of structures that exist in nature) materials for optical nanosensors, molecular electronics and biomedicine. The second place was taken by a post-graduate student of the Tashkent State Pedagogical University. Nizami Marina Fomina, who developed a system for targeted delivery of drugs to diseased tissues, and the third - Alexei Khasanov, a schoolboy from Tomsk, the author of the technology for creating nanoceramic materials with unique properties. The winners received valuable prizes. nine0005
The winners received valuable prizes. nine0005
With the support of the bank, a popular science textbook "Nanotechnologies for All" has been developed and is being prepared for publication. It has earned a high appraisal of leading scientists.
In December 2004, NNN, which became the leading analytical agency in the field of nanotechnology, announced the start of the Second All-Russian Competition for Youth Projects in December 2004, the general sponsor of which again was Uniastrum Bank, satisfied with the results of the first competition. In addition, Powercom, an international manufacturer of uninterruptible power supplies, has also become a sponsor this time. The journal "Science and Life" takes an active part in the preparation and coverage of the competition. nine0005
The purpose of the competition is to attract talented young people to the development of nanotechnologies in their own country, and not abroad.
The winner of the competition will receive the UMKA nanotechnological laboratory. The second and third place winners will be awarded modern laptops; the best participants will receive a free subscription to the Science and Life magazine. As prizes, repair and restoration kits for vehicles based on nanoparticles, a subscription to the magazine "Universum" and monthly CDs "The World of Nanotechnologies" are provided. nine0005
The second and third place winners will be awarded modern laptops; the best participants will receive a free subscription to the Science and Life magazine. As prizes, repair and restoration kits for vehicles based on nanoparticles, a subscription to the magazine "Universum" and monthly CDs "The World of Nanotechnologies" are provided. nine0005
The focus of projects is extremely diverse: from promising nanomaterials for the automotive industry and aviation to implants and neurotechnological interfaces. Detailed materials of the contest are available on the website www.nanonewsnet.ru.
In December 2004, the city of Fryazino (Moscow region) hosted the first conference dedicated to the industrial use of nanotechnologies, where scientists presented dozens of developments ready for implementation in production. Among them are new materials based on nanotubes, ultra-strong coatings, anti-friction compounds, conductive polymers for flexible electronics, super-capacitive capacitors, etc.