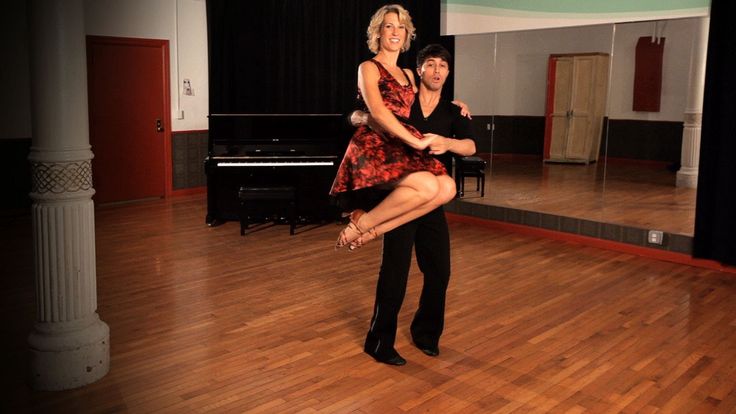
Learn how to swing out dance
Learn Basic Swing Steps
Swing is a lively, non-progressive partner dance that can be danced to a wide variety of music, from blues to rock & roll. Non-progressive means it's mostly performed in one spot, so it's very convenient on a crowded dance floor.
- Basic steps
- Instructions & Diagrams
- Video
- Recommended Video Lessons »
Quick intro
Swing is one of the most versatile partner dances you can learn - very social and beginner friendly. Easily adaptable to a wide range of tempos, it involves movements with lots of swinging, spinning and rhythmic, creative footwork.
There are many different styles of swing, the term actually refers to a group of dances that developed from the swing style of jazz music in the first half of the last century. There's Lindy Hop, Boogie-Woogie, Jitterbug, Shag, Charleston, West Coast and East Coast Swing, just to name a few. Each of these dances has its own distinct flavor.
One of the most popular and very suitable for beginners is the East Coast Swing. It's a bit more social and relaxed than other versions. It's also a formal ballroom dance and the easiest to learn. Perfect for beginners, which is why we'll focus on this version here. It will create a good foundation and is the base for other more complex versions.
East Coast Swing can be danced to a variety of music styles. If it's written in 4/4 time and has a tempo between 135-170 beats per minute, you can swing it.
To dance swing you'll need a partner, a sense of humor, and a bit of endurance. It may seem a bit intimidating at first, especially if you're watching those who really mastered it. But as with all things, you have to start with the basics. And the basics are easy. Once you learn the fundamentals, you'll be swinging in no time. Always remember, wear comfortable shoes. Now let's go swinging.
Basic steps (East Coast Swing)
Beginners usually start with East Coast Swing, because it is the easiest of all swing styles. Here we will show you the basic 6 count step for East Coast Swing.
Here we will show you the basic 6 count step for East Coast Swing.
East Coast Swing has a basic count of 1&2, 3&4, 5,6. It's known as a triple step swing. The basic pattern is triple step, triple step, and a rock step.
When you're starting out you can replace the triple step with a single step. In that case the pattern would be step, step, rock step or rock step, step, step, depending on how you start counting. The overall progression is, of course, the same.
The triple step is really not that difficult to master, it is performed in a chasse-like manner - side step, together, side step.
Instructions & Diagrams:
Basic Steps For Men: The man starts with his left foot.
- 1&2: Triple step (chasse) to the left (left-right-left)
- 3&4: Triple step to the right (right-left-right)
- 5: Step backward with your left foot
- 6: Weight shifts to your right foot
Basic Steps For Women:
The woman starts with her right foot.
- 1&2: Triple step (chasse) to the right (right-left-right)
- 3&4: Triple step to the left (left-right-left)
- 5: Step backward with your right foot
- 6: Weight shifts to your left foot
Remember, keep the steps small.
Video
Leon and Kim will show you the basic steps, how to turn, and more:
more videos »
Now let's have some more fun, let's do some kicking:
Where to go next?
When you're ready for more fun, check out our recommended video lessons. Video is a great way to learn dancing.
Video is a great way to learn dancing.
8 Beginner Tips for Learning Swing Dances
Are you sociable, energetic, and like to move? If so, then swing dancing may be a good fit for you to learn out of all of the dance styles out there. Swing dancing is fun and not that difficult when you compare it to some other dances out there.
But not all swing dances are created equal. There are different types of swing dances that are specific to different musical genres and steps. Before you put on your dance shoes and head out onto the dance floor, it’s important to be familiar with what you’re going to be doing during your swing dance.
If you’re not familiar with swing dancing and the different swing dance styles, don’t worry; we’ve got you covered. We’re going to take a look at the history of swing dancing, the different styles of swing dances, and swing music, as well as give you some beginner tips to get started.
Get your dancing shoes on and let’s go!
What is Swing Dancing?
Swing dancing is known as the group of dances that came about during the Harlem Renaissance in the 1920s. It takes elements from different dances and combines them with contemporary constricted rhythm structures.
It takes elements from different dances and combines them with contemporary constricted rhythm structures.
What are Different Types of Swing Dances?
Swing dancing is not just one type of dance. There are several different types of swing that fall under the general swing umbrella. These types of swing include:
East Coast Swing
East Coast Swing is also known as Triple Step swing because of the rhythm of the basic triple step. It is the base for all swing dances and is a simple dance.
In this dance, there are six-count patterns and eight-count patterns. To start, a man and woman step back. The Triple Step swing is a circular dance that has a bounce. It is not high in the legs and is very grounded. To do this dance, the dancer has to stay very smooth and not jump much. They require a rock step back.
West Coast Swing
You’ll see six-count patterns and eight-count patterns in the West Coast Swing as well. They are done in a slot. Instead of a rock step, the woman walks forward on count one. This swing dance is done to medium tempo music that is slower than East Coast Swing.
This swing dance is done to medium tempo music that is slower than East Coast Swing.
As you get better at this dance, you can do it to fast tempo music. There are no bouncy movements to this dance, and it has a very smooth feel. You won’t see many high kicks or moves that require the dancer to leave the floor.
The Hustle
The Hustle resembles the West Coast Swing pattern. It uses disco-style music and revived partner-style dance among nightclub dancers in the 1970s. The Hustle is a fast, smooth tempo partner dance. The woman spins constantly, while her partner draws her close and then moves her away.
The Jive
The Jive is the European version of East Coast Swing dancing. It consists of six and eight- count patterns, with bouncy movements, and sharp kicks and flicks. Jive is danced to faster tempo music and is often part of competitive style dancing with its intricate footwork.
The Lindy Hop
The Lindy Hop is a member of the swing dance family. It’s frequently referred to as a jazz dance but is a fusion of many dances. The Lindy Hop is an African American dance that originated in Harlem, New York. Legend has it that the name Lindy Hop was inspired by aviator Charles Lindbergh who hopped the Atlantic Ocean in 1927.
It’s frequently referred to as a jazz dance but is a fusion of many dances. The Lindy Hop is an African American dance that originated in Harlem, New York. Legend has it that the name Lindy Hop was inspired by aviator Charles Lindbergh who hopped the Atlantic Ocean in 1927.
There are many other swing dance styles as well. As you learn more, you can discover which types of swing dance styles you prefer and work more on those.
Beginner Tips for Learning Swing Dances
Before you start any type of swing dance, consider these beginner tips:
- Learn the basics
Learn the basics of swing dance and the traditional swing dances if you want to become a swing dance pro. Once you get these down, you can try the more complicated moves. Practice them everywhere and whenever you can!
- Dance with different partners
Swing is a partner dance, so you’ll want to dance with different partners instead of the same one all the time.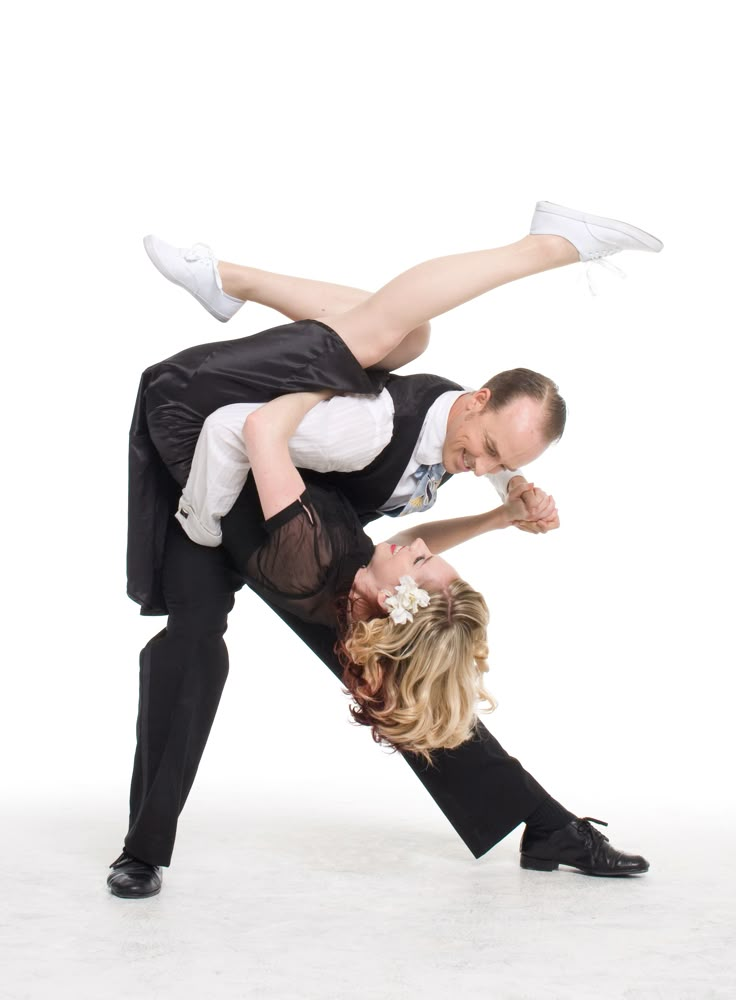 You’ll find that dancing with different people can teach you new things and will help you become a better dancer.
You’ll find that dancing with different people can teach you new things and will help you become a better dancer.
- Record yourself
Record yourself dancing so you can watch the footage back and see what you’re doing right and what you’re doing wrong.
- Listen to swing music (lots of it)
When you’re just starting out, listen to a lot of swing music. It will help you with rhythm and breaks.
- Take dance lessons
By taking swing dance lessons, you can improve your technique and your style. You can learn from other swing dancers and see how they move.
- Watch other dancers
While you want to get as much practice as possible, watching other dancers, especially those who have mastered professional swing dancing, will help your craft. As you watch them and learn the basics, you can begin to learn other swing dances as well.
- Don’t be afraid to make mistakes
When you first start out, you’re going to make mistakes. Instead of being afraid of making mistakes, learn from them so you can become a better swing dancer.
Instead of being afraid of making mistakes, learn from them so you can become a better swing dancer.
- Attend a swing camp
It may be a little intense, but attending a swing camp, Lindy Hop exchange, or workshop can really help you learn how to swing dance. These are like swing dance boot camps. There are usually dances at night that have advanced swing dancers or professional dancers to inspire you to continue to swing dance and get better at your craft. There is a huge event in Southern California known as Camp Hollywood. But, you don’t have to go to Southern California. There are plenty all over the country year-round.
FAQ About Swing Dancing
If you’re thinking of learning how to swing dance, you may still have some questions before you get started.
Do I need a steady dance partner?
Not at all! When you’re just learning how to swing dance, you’ll learn moves that can be used with all partners.
Do I have to be a certain age to swing dance?
No! Swing dancing is for people of all ages.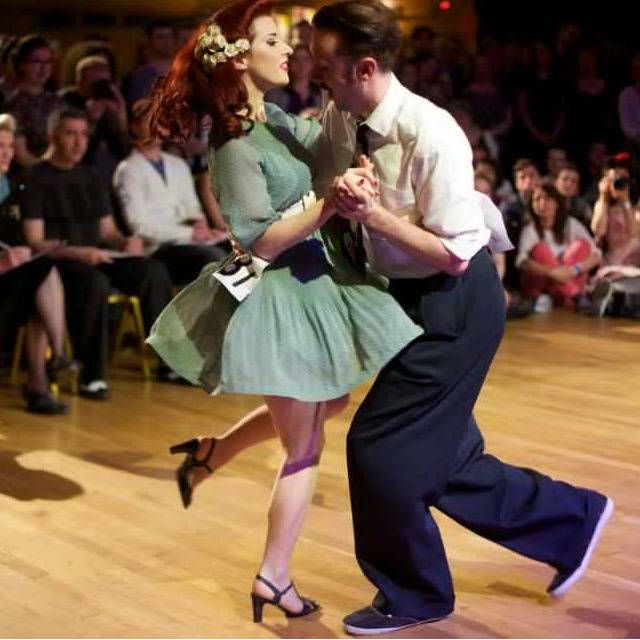 Whether you’re learning the Lindy Hop or Jive, you can learn any type of social dancing at any age.
Whether you’re learning the Lindy Hop or Jive, you can learn any type of social dancing at any age.
Do I need to be coordinated to learn to swing dance?
If you are willing to learn, you will learn to be more coordinated as you learn to swing dance.
Is previous swing dancing experience required?
No, you don’t need to have experience to take swing dance lessons.
What do I wear to learn how to swing dance?
When you’re just starting to learn how to swing dance, you want to wear comfortable clothes like a t-shirt, and leggings. You also want to wear shoes with hard leather soles or very hard rubber or plastic soles.
Where Can you Learn To Swing Dance?
You can learn to swing dance at the Fred Astaire Dance Studio in Durham. We love to teach beginners the art of swing dancing and can help you learn the swing dance style you choose. Call us today at 919-489-4313 or reach out to us online to learn more about dance lessons in Durham.
Schedule Your Lesson Today
No Partner Necessary
Swing, concepts of hands, steps, HIP-HOP mechanics (practice)
In this topic, it is important to analyze - the strength of the swing - types of swing (by direction, by accent, by condition) - swing in separate parts of the body - swing in positions and planes
- swing for musical elements
Power of swing.
Everything is simple here. We train with the guys different variations of the swing in terms of strength: weak, normal, strong.
First, we work in each of the options. We pay special attention to a strong and clear swing, because. this option is more complex and requires some control of the body. But also such a swing is a powerful freestyle component and adds energy to the whole dance.
Then we combine different types of swing in freestyle, change the strength depending on the track or musical moment.
Types of quality.
In this subtopic, we analyze all possible swing variations, moving away from the basic one (with an accent down)
In the direction of the swing, it can be:
-forward -backward -sideways -obliquely -upward -circular
-down -up -impact (blow) -impulse (emphasis on the initial jerk) -double -torn
Status. In this case, we take different states and modify the quality relative to it. For example, a swing in a "curtain" or "water" state will be softer than a swing in a "rock" or "ball" state.
For example, a swing in a "curtain" or "water" state will be softer than a swing in a "rock" or "ball" state.
To consolidate the material covered, you can complete the task: Freestyle exclusively on the quality, changing its strength, accents, state.
Next, you can go a little “deep” into the body and develop in more detail the feeling of swing in each part of the body.
It is worth noting that in each part of the body all the above-mentioned swing variations work (strength, directions, accents, states)
In this format, the work is built according to the scheme already known to us:
We take one part of the body and try to apply to it all the knowledge of the swing that we already have. We select parts of the body: head, shoulders (one at a time and together), chest, body, pelvis, knees).
Quality in different parts of the body.
After the dancer has more or less figured out the swing, felt it and became able to modify it, it's time to learn how to hold the swing in difficult dance positions.
This stage is very important for the dance to be a hip-hop freestyle, and not just a flow of movements. In this case, it is very important to develop a feeling of swing in absolutely any difficult position.
How do we build the training process? Very simple and creative.
We came up with a position, gave it to the students, they picked it up and begin to swing in it, using the knowledge that they had already received earlier.
They stood, shook, came up with a new position, changed, shook again. The logic, I think, is clear.
Next, you can go to the ground and analyze the concepts and positions that took place earlier and apply the same quality to them.
Having figured out a little how to swing in different difficult positions, you can fix the theme with freestyle. The task of the guys is to move between positions, but not to lose a constant quality.
Quality and music.
At the last stage, when the student's body is already “uploaded”, you can move on to the relationship between download and music.
i.e. we offer students to work with music, but only with music. All sound elements need to be beaten only through the swing, changing its strength, speed, state, accent, and so on.
As an example, you can demonstrate that under a smooth melody, the swing can be slowed down, and under the “tsik-tsik-tsik” the swing can be accelerated and made less. You can take a rhythmic pattern and beat it with a swing.
I recommend stretching the entire stage of studying step 9 over a large number of workouts. The more your students are in the state of pumping, the faster they will develop its automatism and feeling.
Some of the master classes of visiting dancers consisted entirely in the analysis of different types of bounca’a and the “buildup” of the participants. This proves that a highly developed fundamental basis in the form of a swing plays an important role. Don't be afraid to put a lot of time and practice into it.
Dive into the depths of the dance. Muscles: zoukability — LiveJournal
Author: Murasheva Nadezhda Friends, I am starting a block of articles about the "underwater" part of the dance. We will explore the topic in more depth, how to learn to move beautifully and plastically and hear your partner. If you don't go to some third-party classes and master classes outside of social dances, then these topics are almost not covered in the lessons. In good classes, the correct work of the muscles is sorted out, but this still does not add up to a comprehensive picture.
We will explore the topic in more depth, how to learn to move beautifully and plastically and hear your partner. If you don't go to some third-party classes and master classes outside of social dances, then these topics are almost not covered in the lessons. In good classes, the correct work of the muscles is sorted out, but this still does not add up to a comprehensive picture.
In one of my previous articles, I likened dance to a big iceberg, the main part of which is hidden under water and opens up to us as we deepen into the knowledge of dance, movement, our body. When a non-dancing person looks at the dance from the side, he sees the tip of the iceberg - its external manifestation. A beginner dancer continues to see only this top for a long time (and sometimes it ends with this), because the dance for him still remains a set of movements - an external form. Even if these are movements from an advanced lesson. Beautiful, cool, complex, spectacular. "I want that too." Growing dancers begin to master all these complex movements, go into narcissism and show off through figures. When I look at dancers at parties it's 90% of the time I see exactly this - chasing the outer form. Sometimes tops dance like that. Dancers think in figures. But this is only the surface ABOVE the water! All the most interesting is deeper.
When I look at dancers at parties it's 90% of the time I see exactly this - chasing the outer form. Sometimes tops dance like that. Dancers think in figures. But this is only the surface ABOVE the water! All the most interesting is deeper.
And what is there, in the depths, "under water"?
- The world of connection with a partner. What does it depend on? From connecting with yourself. How to feel a partner if you don't feel your own body?..
- Control of your body: muscle tone, ability to relax, control of your body structure, general feeling and awareness of your body.
- Feeling and awareness of oneself as a whole. After all, our body and consciousness are interconnected, and the state of one is reflected in the state of the other. By acting on one, we have an effect on the other, and vice versa. Both in a positive and negative way. What a person has inside is how he moves.
 It is impossible to briefly and simply cover the topic of connection and ownership of your body in one article, one master class or one individual. I will try to outline the entire layer of independent and internal work that is open and accessible to every enthusiastic dancer. But this is only one quarter of the way, theoretical. Everyone must overcome three-quarters on their own, studying their movement, their body, developing awareness in themselves, training their control of muscles, relaxation, feeling "up" and "down", feeling a partner ...
It is impossible to briefly and simply cover the topic of connection and ownership of your body in one article, one master class or one individual. I will try to outline the entire layer of independent and internal work that is open and accessible to every enthusiastic dancer. But this is only one quarter of the way, theoretical. Everyone must overcome three-quarters on their own, studying their movement, their body, developing awareness in themselves, training their control of muscles, relaxation, feeling "up" and "down", feeling a partner ...
So, today we will begin to consider the level closest to the surface of the iceberg - muscle control . It is also the easiest to understand and use. When you better understand what muscles are performing movements, what to follow, your movements will become clearer, cleaner, more conscious. The movements that you learned by visually copying after the teacher will become clear from the inside: what works, why it works and what you need to make it even better.
Why is this level closest to the surface? Because muscle ownership determines how your movements will look (but not only from this), because your balance, rotations, cambrai and much more depend on muscle tone.
And it is the simplest because it is much easier to pump up muscles than to learn isolation, relaxation and finer sensations. Muscle training is just a physical activity, albeit hard sometimes. Any dancer can pump up the press, which, however, will not teach him plasticity and connection with a partner.
Muscles not only help us perform movements correctly and beautifully, but also protect us from injuries, which is why it is so important to develop our physical form.
One of my favorite themes is that if you just go to the gym and pump something there, it doesn't help you dance properly at all. In addition to having a pumped up muscle, you must learn how to use it in dance movements, keep it in good shape on the machine, without flying out of your attention from the dance and connection, otherwise your work in the gym is useless.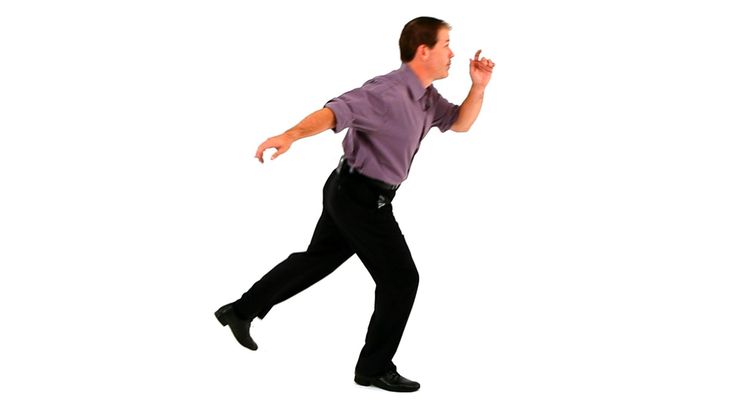 This is a characteristic feature of the dance. In the gym, we learn to tense our muscles strongly and relax 10-50 times. We leave the room and forget about them.
This is a characteristic feature of the dance. In the gym, we learn to tense our muscles strongly and relax 10-50 times. We leave the room and forget about them.
In dancing, you need to constantly keep in good shape and control many different muscles at once. This is a lot less tension than in the gym, but getting used to this state of constant soft tone can be very difficult. The dancer must have good control over his entire body in dynamics and statics, must be able to control tension and relaxation (stability and plasticity), feel his individual muscles (isolation), must have acquired the skill of holding passive attention at several points at once (back, abs, feet as minimum), which should not distract from the dance itself, connection, music and the surrounding space.
Note: The article does not take into account physical limitations due to injuries, hernia, protrusions, etc.
PRESS
Upper, lower and oblique abdominal muscles.
From an anatomical point of view, the abdominal muscles give stability to our spine (in fact, this is somewhere around 50% of success). - Balance, rotation, stability, yes, yes
Using the press greatly reduces the load on the back when bending and tilting, helps to build the axis on rotations. And therefore, a non-working press creates an overload of the lower back and other parts of the spine, which is fraught with muscle and nerve clamps, displacement of the spinal discs, hernia and chronic back pain, especially among zuckers. And with a broken press, you will be chatting on all rotations.
The oblique muscles of the abdomen give us plasticity, beautiful tilts to the sides, light soft work of the body in a circle and, of course, additional stability in difficult positions of the body.
If we talk about the zouk, then we actively use the press in all movements with body inclinations (cambrai, headworks, bones, etc.), on rotations, on counterbalances. Wherever we need stability, a strong body, a straight back (in particular, the lower back).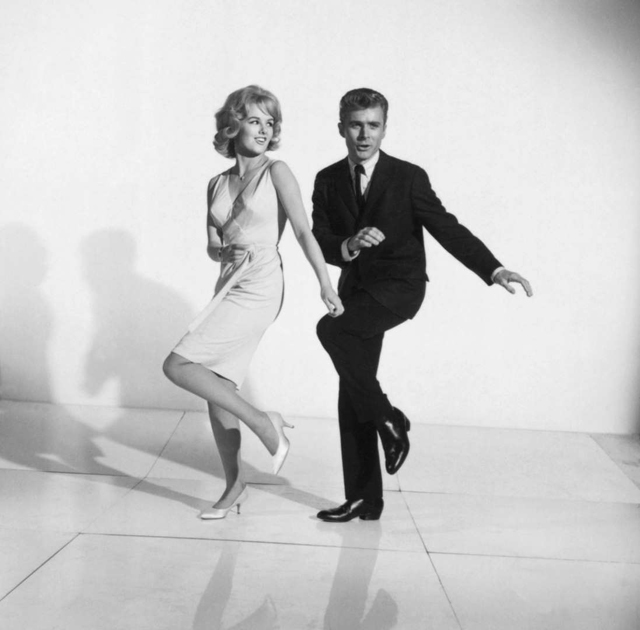 The press is collected on all supports and "falls" on a plank-type partner so that the body does not fall through. Sometimes, for even greater stability and inclusion of the press, you need to twist the pelvis forward even more (a la Michael Jackson) to fix the body even more strongly. I use it on cambra preps, bone necks, long spins. But you need to understand that the press does not tense up in the dance with an impenetrable shield as before the opponent's blow (then the dance would be too hard and exhausting). The work of the press is rather similar to what happens in Pilates: the navel is pulled up to the spine and remains there in a passive tone always. If necessary, the lower or upper press is additionally strengthened.
The press is collected on all supports and "falls" on a plank-type partner so that the body does not fall through. Sometimes, for even greater stability and inclusion of the press, you need to twist the pelvis forward even more (a la Michael Jackson) to fix the body even more strongly. I use it on cambra preps, bone necks, long spins. But you need to understand that the press does not tense up in the dance with an impenetrable shield as before the opponent's blow (then the dance would be too hard and exhausting). The work of the press is rather similar to what happens in Pilates: the navel is pulled up to the spine and remains there in a passive tone always. If necessary, the lower or upper press is additionally strengthened.
Interestingly, in zouk, a number of common movements require isolated possession of the upper and lower press. So, for example, when working with the chest (headworks, etc.), we weaken the upper press, but firmly hold the lower one - for stability, balance, so as not to fall apart.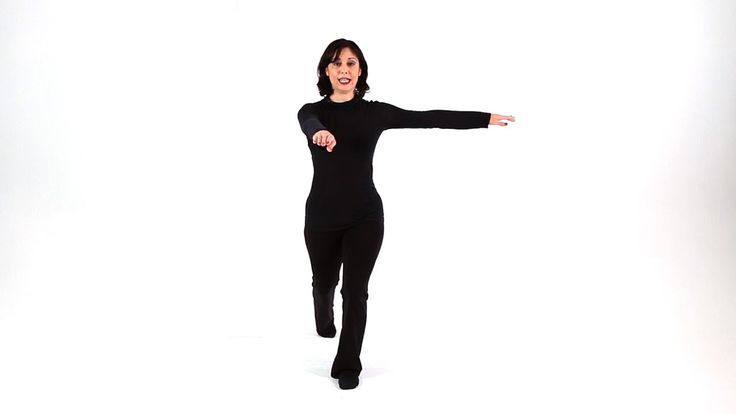
Alas, even with trained abs, many dancers do not use them. They make movements with a relaxed stomach, which is why they fall apart, lose structure in the body. Using the abdominal muscles should be a habit. Spent, automatic. However, like all other muscles, which will be discussed further. In order not to think every time about all the muscles that need to be included.
It is common to see dancers in a position of constant arching in the lower back even just standing still. This is an indicator that they do not use the press at all;) In the position of the lumbar deflection, it is possible to draw in the stomach a little, but it is impossible to fully use the press. Which is logical, because when in one place there is contraction, tension (in the lower back), then on the other side there is stretching and relaxation.
Another common mistake is the constant deflection under the shoulder blades, which is what they say "remove the ribs" in ballet lessons. This is a deflection above the waist, which means that in this case the upper press does not turn on and, as a rule, the back muscles in the thoracic region and sometimes between the shoulder blades are strongly clamped. It is very difficult to get rid of this habit. Usually combined with a lumbar deflection. Ribs stick out in front, buttocks in the back, and somewhere in the middle in a bend, a poor, clamped spine.
It is very difficult to get rid of this habit. Usually combined with a lumbar deflection. Ribs stick out in front, buttocks in the back, and somewhere in the middle in a bend, a poor, clamped spine.
Basicly everyone knows how to pump the upper and lower press. There are a lot of options. I will only add that, firstly, you should not put your hands on your neck and try to lift yourself with a jerk of your arms or head - this is technically incorrect and dangerous, hypertension is created in the neck, and in fact you lift yourself with your neck, not with a press. It is better to keep your hands on your chest or on your stomach. If the press is weak, then it will be more difficult, yes. But now you do not deceive yourself. And secondly, if you swing the lower press by raising your legs, then there should be no deflection in the lower back. If the lower back sags, it means that you do not have enough strength and abs and back, and instead of the lower press, you again overload your back. Press your back completely to the floor and bend your knees - this will be better. And yet, given the peculiarities of the dance work of the muscles, it is better to do all exercises slowly. No need to chase the number of movements. Let them be only 10, but each stretched into 10 accounts, for example.
Press your back completely to the floor and bend your knees - this will be better. And yet, given the peculiarities of the dance work of the muscles, it is better to do all exercises slowly. No need to chase the number of movements. Let them be only 10, but each stretched into 10 accounts, for example.
The oblique abdominal muscles are trained with various twists and side bends. Twisting should be smooth, on the muscles, not jerky. Turns are carried out from the waist, the hips should not turn anywhere - this is important and a common mistake. So that the hips do not exactly spin, you can do twists while sitting on the priest (and at the same time keep a straight back). Still tilts to the sides - both fast (strength training) and slow (stretching, endurance). On tilts to the side, both of your shoulders should look into the mirror, and not at the floor - otherwise you train other muscles, and the obliques remain undeveloped. The chin on the side slopes also looks into the mirror, and not at the floor.
I would like to draw attention to the following points in the photo:
See how evenly she holds her neck. The head does not move forward and does not throw back. That's right, that's the way it should be.
This position can be made easier by bending your knees and rounding your back a little (the press still works, it will be easier). But the option in the photo with a straight back is more complicated and better because the back muscles will also work this way. And the legs extended at the knees are heavier, more difficult to hold them.
BUTTOCKS
There are quite a lot of gluteal muscles, and they will work differently depending on the movements. Therefore, the expression "swing ass" is somewhat abstract. But if you dance only social dances, then you should be primarily interested in the gluteus maximus muscle and the ability, if necessary, to keep (!) It in suspense during dance movements.
The effect of using the gluteal muscle is about the same as that of the press - stabilization of the core.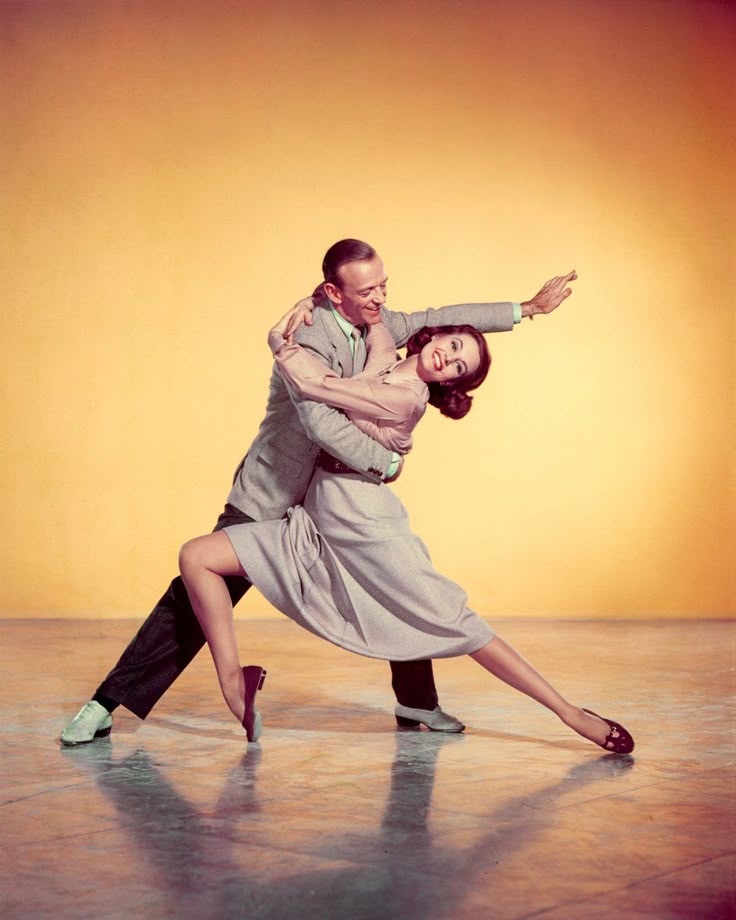 Here it is only necessary to understand that the press directly stabilizes our top (spine), and the buttocks stabilize the pelvis, that is, the bottom (legs, hips, lower back). A retracted buttock limits the mobility and rotation of the hip joint, and the position of the hip joint affects the position of the lower back as well - everything is interconnected. By pulling your butt in, you limit the stride length available to you, this helps to fight drifts in the dance, especially on turns and spins.
Here it is only necessary to understand that the press directly stabilizes our top (spine), and the buttocks stabilize the pelvis, that is, the bottom (legs, hips, lower back). A retracted buttock limits the mobility and rotation of the hip joint, and the position of the hip joint affects the position of the lower back as well - everything is interconnected. By pulling your butt in, you limit the stride length available to you, this helps to fight drifts in the dance, especially on turns and spins.
What do you need to remember? The fact that if you pumped up a big beautiful ass in the gym, and in the dance she is always relaxed, then there is zero sense in her! Amen.
To dance, you just need to be able to pull it in strongly, "squeeze a coin" between the buttocks. Well, to maintain this position for a while - it's easier here than with the press.
Regular squats won't do very well here, they just increase the volume of the buttocks and thighs. Much better are leg raises while lying on your stomach, and even better are real bodily tasks in dance: ballet exercises in which you always need to keep your butt. For example, ballet plies with toned buttocks, tandu and all other happiness. The bar is still very good, if done correctly, retract and twist the pelvis forward.
For example, ballet plies with toned buttocks, tandu and all other happiness. The bar is still very good, if done correctly, retract and twist the pelvis forward.
But this is the wrong plank! There should not be such a bend in the lower back, the pelvis needs to be scrolled forward more.
Correct bar . Compare body lines.
LONG BACK MUSCLES
In fact, this is a whole group of closely spaced muscles. It doesn't matter to us now. If you put your thumbs on your spine and step back a little, you will feel such powerful thick seals from the lower back and along the entire spine, passing into the muscles of the neck. It's them.
Muscles are potentially very strong and useful, and therefore sad if they are not working. You have no idea how much you are missing if you don't own them! And often they are non-working and at the same time they are still heavily clogged with incorrect operation of the case in principle. Then they have overstressed painful areas that you do not know how to control, you cannot relax them and strain them at will. Then it's even more difficult, but it's fixable.
Then they have overstressed painful areas that you do not know how to control, you cannot relax them and strain them at will. Then it's even more difficult, but it's fixable.
The long back muscles pull the spine up and help keep it in a straight, straight position. Just as the abs keep the spine stable on one side, the long back muscles support it on the other side. When the teacher says "we stretch the top of the head up", then the activation of these particular muscles is meant. When you feel and control them, you feel a real physical upward pull. These same muscles keep the spine in good shape and when tilting the body, they also greatly affect your posture and body structure in the dance, the pattern of relaxation and tension, and this affects how absolutely all your movements look and feel.
An ordinary untrained person does not feel these muscles and does not understand what it means to stretch upwards. "How to stretch, what?". Or maybe these muscles are even pumped up by boats, but it's still not clear how to reach up.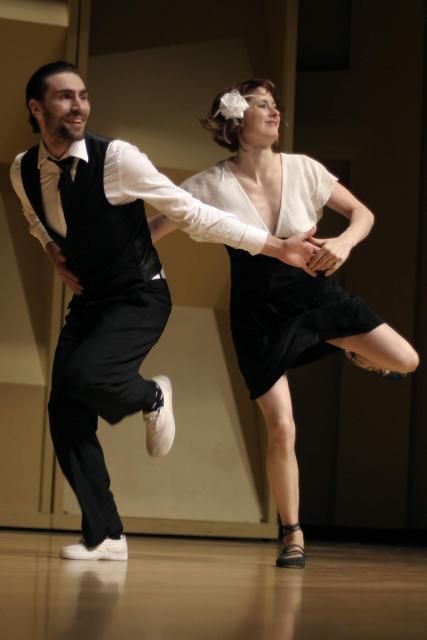 This is fine. If you are working on yourself, then it is very important to learn how to master them. The technique of your rotations, centering, a smooth, stable exit from any rotations, without blockages, distortions, even with poor partner guidance, will depend on this, and in general your well-being and health will be better. When female partners fall heavily on their side in slopes and fall in turns - they do not work, there is nothing to build an axis with.
This is fine. If you are working on yourself, then it is very important to learn how to master them. The technique of your rotations, centering, a smooth, stable exit from any rotations, without blockages, distortions, even with poor partner guidance, will depend on this, and in general your well-being and health will be better. When female partners fall heavily on their side in slopes and fall in turns - they do not work, there is nothing to build an axis with.
Learning to control the long back muscles is more difficult than mastering the abs or buttocks. First you need to remove the interference of posture, which prevent these muscles from being included in the work. Namely, you need to tighten your stomach, remove the deflections in the lower back and under the shoulder blades, remove the ribs sticking out forward. If your ribs stick out, then you a priori cannot use your back muscles normally. They are chronically tight and shortened. Stand up to the wall and try to press against the wall with your whole back as much as possible, hold the position without the wall. And strive to press the lower back, even if it doesn’t work out completely.
And strive to press the lower back, even if it doesn’t work out completely.
The strength of the long back muscles is well trained by boats and tilt-ups with a straight back, but this does not teach you to reach up. For training the stretch itself, I have not yet come across anything more effective than ballet exercises in the middle of the hall. When you balance on one foot without the support of the barre, your body finds this stretch on its own, it gives stability. That's exactly what happened to me, and pretty quickly.
NECK
I wrote an article about headwork rules. You need to know these rules!
Headworks are not done with the neck muscles. But the muscles of the neck must be in a passive tone so that the cervical vertebrae are safe, so that they are not subjected to sudden traumatic movements, are not clamped or overextended. The exercises are very simple: tilt the head up and down, turn left and right, tilt the ear to the shoulder. Exercises are best done slowly and with effort. It is also very useful to work with an isometric load: press your head through the resistance of your hands. All this at the same time is the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis, strengthens muscles and promotes the health of our cervical discs.
Exercises are best done slowly and with effort. It is also very useful to work with an isometric load: press your head through the resistance of your hands. All this at the same time is the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis, strengthens muscles and promotes the health of our cervical discs.
Typical mistakes of the zouk : throwing the head back, throwing the head back on a relaxed neck, headwork through the neck muscles, asymmetrical position of the head relative to the work of the body (the head falls forward or back and outweighs).
But besides this, there is a posture error that few people talk about, and it is inherent in many. This error is chin up. We know to reach up with the top of our head. That's just the muscles of the top of the head physically can not pull us up and have completely different functions. The crown is a purely visual landmark (just not everyone is aware). But we don’t even know where the top of our head is and how it should feel. And so we raise our chin and stretch our foreheads up. In this position, the front muscles of the neck stretch upward, and the back muscles, which should work, are compressed. This is exactly the opposite of what the teacher wants from you. In addition to the physiological harm to your neck, this also prevents you from dancing: the stable position of the head is disturbed, the head begins to outweigh and fills you back. This is especially problematic on spins.
And so we raise our chin and stretch our foreheads up. In this position, the front muscles of the neck stretch upward, and the back muscles, which should work, are compressed. This is exactly the opposite of what the teacher wants from you. In addition to the physiological harm to your neck, this also prevents you from dancing: the stable position of the head is disturbed, the head begins to outweigh and fills you back. This is especially problematic on spins.
It is better to correct the position of the head at the mirror and through the same exercises, carefully monitoring the position of the head. The simplest and most effective: put your hands on the back of your head. Feel for two bones at the base of the skull with your thumbs and grab them as well. Press your head on your hands and your hands on your head. Holding these bones and maintaining pressure, stretch your head with your hands a couple of centimeters up.
LOIN
Dancers! The lower back in the dance should be straight! (Well, almost straight, - for the most meticulous) No deflections just like that in every movement. Deflection is not styling! Chronic backbend is a lump of tension that you live with, and hit it even more in all amplitude movements. Then it can turn into a hernia of the lumbar and pinched nerve endings.
Deflection is not styling! Chronic backbend is a lump of tension that you live with, and hit it even more in all amplitude movements. Then it can turn into a hernia of the lumbar and pinched nerve endings.
As I wrote above, you need to pump the lower press more, and activate the abdominal muscles to align the lower back and hip joint. In addition to this, it is very necessary to learn how to sit on the sitting bones with a flat back. This is generally a mandatory minimum for the normal posture of any non-dancing person. When you can just sit straight, then we go into the fold to the legs, be sure to stretch the lower back. It will be very gross. This is not a leg stretch, no need to dive head first. It is important to start folding towards the legs from the hip, trying to put the stomach and ribs on the legs. At the same time, you can stretch your arms forward, this helps to stretch yourself.
The muscles of the lower back are also trained in different inclinations with a straight back.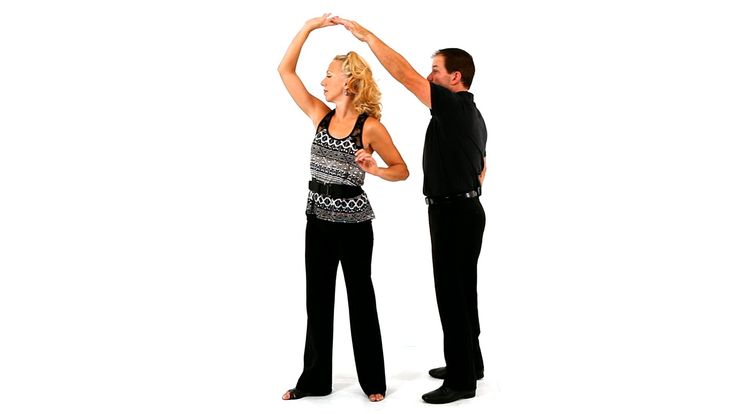 Also, be sure to keep your lower back pressed to the floor in all pumping exercises when you are lying on your back. Especially when it comes to abdominal exercises. And standing against the wall, we press the lower back into the wall! Out of habit, it will seem that you are hunched over, but in fact, sleeping muscles just turn on, and your back becomes straighter. Try to maintain this position yourself by checking yourself in the mirror.
Also, be sure to keep your lower back pressed to the floor in all pumping exercises when you are lying on your back. Especially when it comes to abdominal exercises. And standing against the wall, we press the lower back into the wall! Out of habit, it will seem that you are hunched over, but in fact, sleeping muscles just turn on, and your back becomes straighter. Try to maintain this position yourself by checking yourself in the mirror.
serratus anterior
Depressor of the scapula. If your shoulders often rise, it means that she is not in good shape, and at the same time, the muscles of the neck and trapezium are probably clamped. If this muscle does not work, the female partners do not understand the lead well, and the partners do not know how to frame and twitch their arms a lot. If the serratus anterior muscle is not in good shape, then the shoulder and shoulder blade are not the connecting link between the body and arms. The body moves by itself, and the arms and shoulders move by themselves, without coordination with the body. Connection without anterior dentate is snotty and twitchy (because with hands).
Connection without anterior dentate is snotty and twitchy (because with hands).
In the dance, you literally need to weld the shoulder blade to the ribs and leave it there forever. Difficult? Possibly)
You can come up with quite a few exercises to strengthen the anterior serratus. Mandatory condition: through "I can not" lower the shoulder blades. You can slowly raise and lower straight arms with a small weight, do rotations in the shoulder joint, you can stretch the elastic in different positions. The slats also pump the front gear well, just do not forget to press the shoulder blades down. All sorts of positions are good with an emphasis on the floor with your hands (I want to relax my shoulder, and then it will climb into my ear).
Rhomboid muscle
Muscle that brings the shoulder blades to the center. It affects the spread of the shoulders and the tone of the frame as well.
It is important that the muscle is in good shape, but not overstressed (!). Attempts to dance with the shoulder blades constantly gathered towards the center will kill all the plasticity in the thoracic region, and at the same time you will no longer feel the physical connection with the partner (where it is clamped, energy and subtle sensations do not pass there).
Attempts to dance with the shoulder blades constantly gathered towards the center will kill all the plasticity in the thoracic region, and at the same time you will no longer feel the physical connection with the partner (where it is clamped, energy and subtle sensations do not pass there).
Actively activated by spreading the arms to the sides with the institution far behind the back, you can use weights, you can lie on your stomach. On your stomach, simply spread your straight arms to the sides and tear them off the floor as high as possible. If you wish, you can find many more options on the Internet.
When training the rhomboid muscle, watch the ribs, do not bend in the chest. It can be difficult)
LEGS
The fact that any dancer needs strong, trained legs is obvious. And it would be strange to single out some individual muscles and say that they are the most necessary for social dances. All the muscles of the legs are somehow involved in performing various movements and maintaining balance. Everything is important here. Legs need to be trained in a complex and varied way. The health of your joints, especially your knees, depends on the condition of your legs (strength and stretching of the muscles). About them a little further.
Everything is important here. Legs need to be trained in a complex and varied way. The health of your joints, especially your knees, depends on the condition of your legs (strength and stretching of the muscles). About them a little further.
It usually happens that dancers perform some kind of monotonous set of exercises that does not fully load their legs. This is not good, as you will be left with undeveloped areas, the weakness of which will affect the quality of your movements and may even negatively affect the condition of your joints. For example, the most common leg exercises (lunges, squats, swings, half-toes, etc. - the basic set) usually do not pump the inner thigh muscles in any way. Ballet exercises, on the contrary, perfectly pump the back muscle group and adductor muscles of the thigh, but load the muscles of the front and outer sides a little. Pilates works very complex with the muscles of the legs (and the whole body).
Conclusion: you need to train your legs in a complex way.
Do not ignore any "heavy" unusual exercises, because "in dance I don't need it." Use both the non-reversible position of the feet in the exercises (feet parallel) and the reversible position (heels together, toes apart, knee joint over the toes, between the thighs "clamped piece of paper"). Stand on your toes and on your heels. Remember that you need to evenly pump muscles and stretch. Pumped, unstretched legs are stiff, clogged, prone to accidental sprains. Poorly pumped, but well stretched - very weak, prone to joint injuries, dislocations.
THIGH MUSCLES
The anterior and posterior thigh muscles are usually more or less trained even just in dance, without any additional effort. Although it is better, of course, to attach them and practice more. And if you often go in for some kinds of sports, then most likely they are already well developed in you.
The typical weaknesses of an ill-trained dancer are the muscles of the inner and outer sides of the thigh. And in vain, they perform important functions.
And in vain, they perform important functions.
Adductors of the thigh - a bundle of internal muscles that bring the legs to the center. The tension of these muscles allows us to maintain balance very well, literally grow to a point in the floor. They help with balance even in tilted postures when the pelvis is turned back and it can be difficult to keep the tension in the gluteal muscles. And the legs in such positions continue to hold us, if they are strongly reduced to the center (at the same time, it is not at all necessary that the legs should stand close to each other). The adductors are best pumped with ballet and scissor exercises. At the same time, different internal muscles work in the reversible / non-reversible positions.
It's also very ugly when girls have a non-closing hole between their thighs.
About the outer surface of the thigh I would like to say that if you are not going to permanently raise your legs to the sides (it is not necessary in the soush), then their main purpose is to keep the knee joint in a stable position.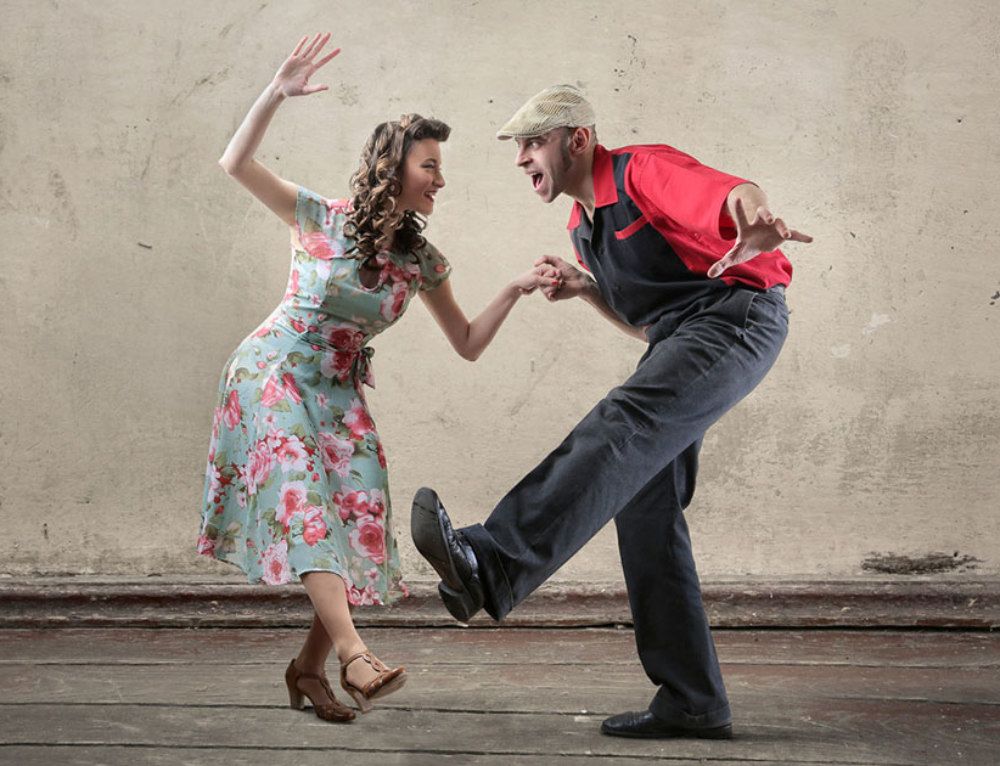 What's the matter here? If the thigh muscles are weak, then the knee joint can fall inward (X legs), and over time, from this position, you will have big problems with the knee ligaments. If in the neutral position your legs are straight, not an X, then this is good, but not enough.
What's the matter here? If the thigh muscles are weak, then the knee joint can fall inward (X legs), and over time, from this position, you will have big problems with the knee ligaments. If in the neutral position your legs are straight, not an X, then this is good, but not enough.
I just wrote that the hip adductors help us balance. If two legs stand together, and through effort we press them against each other, then everything is fine, there should be no mistakes here. What if your feet are a little wider? This is the most common position for female partners when performing boneques and other things. Bring them together here, don't bring them together, all the same, 8 out of 10 girls' knees will come together to the center. This happens because the external thigh muscles are turned off, and there is also no habit and understanding. In fact, when we stand with our legs parallel, we need to carefully monitor the position of the knee. If we bring the adductors to the center to better hold ourselves, then the outer group of muscles should remain in good shape and “push” the knees a little to the sides.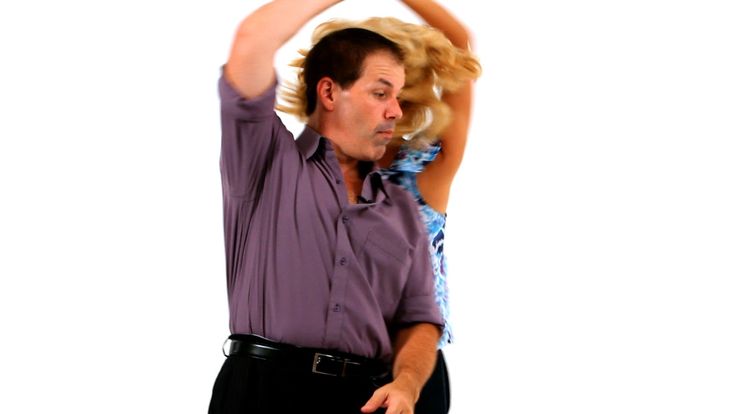 This is necessary so that the knee remains exactly above the foot and does not fall inward.
This is necessary so that the knee remains exactly above the foot and does not fall inward.
That's what I'm talking about. Not a very bright example, but my own))) Feet at a distance, knees together.
It is very important, when performing any squat (plie) in any position of the legs, to ensure that the knee is clearly above the foot and does not fall either in or out.
SHIN MUSCLES
Shank = caviar, caviar = shank, strengthen the shins = pump calves? No, nifiga) This is a very limited perception.
Caviar needed. Calves help to confidently rise to the half-toes and stand on them for a long time, help to run, jump and land. But you won't get far with them.
Other muscles also influence the position of the foot, the names of which the ordinary dancer does not know and has never heard of. The position of your ankle will depend on the condition of all the muscles of the lower leg, the balance both on the half-toes and on the full foot. And the health of your knees will also depend on the position of your ankle. If the foot is turned inward or outward, or collapses on the outer or inner rib, and the knee is not above the foot (a typical social worker mistake: toes apart - knees forward), the cruciate ligaments of the knee joint will suffer, then pain will appear. By the way, the weakness of the calf muscles is the reason why the feet of the dancers in motion accidentally come into a clubfoot position.
And the health of your knees will also depend on the position of your ankle. If the foot is turned inward or outward, or collapses on the outer or inner rib, and the knee is not above the foot (a typical social worker mistake: toes apart - knees forward), the cruciate ligaments of the knee joint will suffer, then pain will appear. By the way, the weakness of the calf muscles is the reason why the feet of the dancers in motion accidentally come into a clubfoot position.
Therefore, it is necessary to additionally strengthen the stabilizing muscles. located in the lower part of the lower leg and affecting the position and stability of the foot. Stretch and shorten the foot, rotate the feet in a circle, roll the feet on the inner and outer ribs, stand on the toes and on the heels (no one allowed me to stand on the heels in class, and by the way, this is quite difficult and includes the front of the lower leg), through resistance to turning the foot in and out. There are many exercises, they are all simple and just require method and perseverance.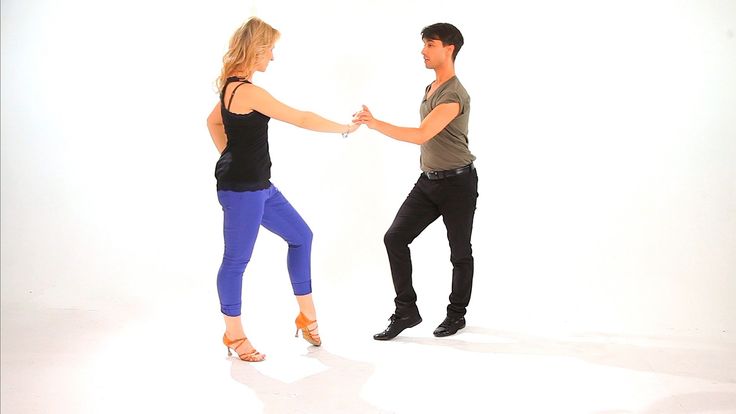
A very effective exercise for the muscles from the foot to the thigh is to stand on one leg for a long time, just on a full foot. 5 minutes or more. At the same time, try not to sag on your hip and not substitute your free leg. It also helps a lot to stand on one leg on a balance circle (a round disk that staggers).
Mandatory rule for standing on half toes : the weight must be over the big and forefinger of the foot and in no case should it fall on the little toes. It also depends on the stabilizing muscles of the lower leg.
FOOT
The structure of the foot is very similar to that of the palm. She can be just as sensitive and mobile. Some professional dancers achieve this. An ordinary person hardly uses the muscles of the foot. Then the brain begins to perceive the muscles of the foot as one whole, the foot becomes like an iron shovel, rigid and inactive.
Due to the undeveloped feet, the position of the ankle is disturbed, the softness of movements is lost (the knees also suffer from this, yes), other muscles begin to clog, which try to compensate for the weakness of the feet (usually calves, thighs).
Feet are the foundation on which our whole building stands. If something is wrong with the foundation, it will inevitably cause distortions in other parts of the body: in the knees, hips, back, it can even affect the position of the head. And therefore it is important to develop the feet, increase their mobility, strength, plasticity and sensitivity.
Dancers' feet are often very clogged, especially those dancing in heels. Attempts to maintain balance on poorly trained legs lead to the fact that the dancers try to “grab the floor” with their feet - they overstrain the muscles of the foot, squeeze their fingers. From this foot can reduce. This is especially evident in the training exercises of ballet and jazz-modern: we get so used to straining our feet that where they need to be relaxed, we generally forget to do it, and our feet start to feel pain right in the exercises. On the one hand, this comes from the wrong technique of the foot, on the other hand, from the underdeveloped muscles. Developed feet do not reduce. Well, the reasons may also be the lack of some microelements, etc. In social dance, a vivid example of tightness of the feet is when girls constantly dance on half-toes (in any shoes), practically without lowering their heels, and at the same time on bent knees. Looks ugly. This is how I dance here, it is very clearly visible: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lzpFeYB8nHc
Developed feet do not reduce. Well, the reasons may also be the lack of some microelements, etc. In social dance, a vivid example of tightness of the feet is when girls constantly dance on half-toes (in any shoes), practically without lowering their heels, and at the same time on bent knees. Looks ugly. This is how I dance here, it is very clearly visible: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lzpFeYB8nHc
Foot development exercises are far more than calf raises. It is necessary to move the fingers up, down and to the sides in isolation, lift the napkin with the toes of the foot, stretch the outer and inner surfaces. Foot massage is very useful, and for this purpose I really like a massage ball with spikes (it should be elastic, a wooden massage roller will also work). At first, I roll the ball lightly, until I feel a pleasant tickle and tingle from contact with the skin. This relaxes the tissues of the foot and stimulates blood circulation, relieving chronic tension. When the foot relaxes a little, the sensations are dulled, I start pushing the ball through the foot in different places in order to act on a deeper level. So you can find especially painful areas and suppress them longer. After such a foot massage, the balance becomes better and the legs become softer.
So you can find especially painful areas and suppress them longer. After such a foot massage, the balance becomes better and the legs become softer.
Here is an example of how to wake up dormant foot muscles. I made up my own mind based on what I read. I was not given this in any class. Someone will not succeed at all, someone will feel new sensations in a couple of minutes.
That's all for this article. This is a review article. Train, study your body, ask questions.
On VK you can send me your dance video for analysis, I will make a storyboard with errors and detailed comments, where you have technical errors in the sound, and where there are crookedness and obliqueness associated with the work of your body. I'll tell you what to do, how to work. I can record a detailed video answer with exercises for you. I wrote about it here: https://vk.com/wall599099_11435
I wrote this article for a very long time. I got a lot of different classes, I began to conduct thematic seminars about the work of the body in dance.