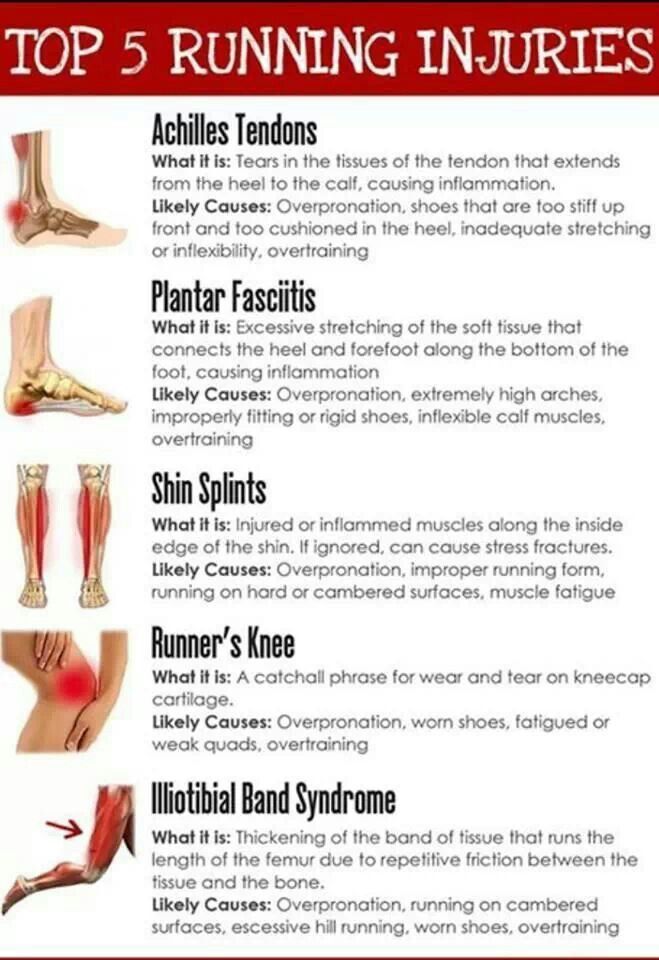
Teach people how to dance
Effective dance teaching methods » Ausdance
by Ausdance National originally published on in Australian guidelines for teaching danceIn This Article
Use effective and safe teaching methods
Consider:
- the type of class (community, social, school, studio, professional etc)
- participants' age, stage and needs
- the dance style/genre
- class size and venue.
Lesson planning
Consider:
- the aim of class or teaching program
- pre-testing for prior knowledge/understanding
- skill levels and age
- logical, suitable and safe progression beginning with warm-up and stretching
- students’ emotional, physical and intellectual development and/or limitations
- a graduated workload, i.
e. frequency, intensity, duration and type of dance.
Create a positive learning/teaching environment
Make sure that the:
- teaching is supportive, encouraging and non-threatening
- goals are clearly stated
- students respect the rights of others to be taught and to learn
- students are given equal opportunities to learn and develop their dance skills
- teachers encourage students to accept reasonable challenges and to take risks with teacher support
- students support each other in challenging or risk-taking activity
- cultural, gender and age differences and different physical and learning abilities are reflected in fair and inclusive teaching/learning practices.
Demonstrate positive communication skills
- Discuss your goals and expectations of a class, program or course.
- Give clear instructions, explanations and demonstrations in verbal, non-verbal, audiovisual and written forms.

- Create a safe, friendly and positive atmosphere.
- Adapt your language to suit the age and experience of students
- Give regular verbal feedback that respects students and helps them develop as independent learners.
- Help students to reflect, evaluate and share knowledge.
Be a positive role model
- Show your love for dance with energy and enthusiasm.
- Set clear goals and expectations.
- Use language that shows respect for students and staff.
- Teach safe dance principles; non-judgmental attitudes; positive body image; punctuality, planning and preparation.
Pedagogy—develop and use dance teaching practices
Level 1
- Respect students’ personal space.
- Encourage a healthy awareness and understanding of the physical nature of dance.
- Use verbal explanations and show correct stance/movement.
- Before any physical contact, tell the student why and how contact is needed.
- Show different approaches to a task, movement or problem solving exercise.
- Allow exploratory learning by encouraging students to talk about ideas and processes.
- Use positive approaches that give students information, confidence, encouragement and a willingness and desire to practice and improve their dance skills.
- Be sensitive to social, economic and cultural contexts, expectations, language and themes.
Level 2
- Recognise and be sensitive to the external lives/pressures that students (particularly adolescents) are experiencing.
- Monitor issues that relate to dance training and talk with a student about concerning symptoms.
- If needed, discuss issues with colleagues, parents and carers, while being sensitive to a student’s right to privacy.
- Be aware and adhere to teacher responsibility to Mandatory Reporting regulations (check your state legislation).
- Refer students and parents/carers to other dance and health professionals with sensitivity.
- Use terminology and explanations which are understood by students.
- Include assessment as an informal or formal gauge of progress.
- Place dance as an art form in its historical, social and cultural contexts according to the style taught, and the training level.
- Help students learn to relate dance practice and theory.
- Give students learning opportunities which develop and recognise different learning styles.
- Use various teaching resources and modes of learning.
Self-development and career development
Level 1
- Invite and welcome honest feedback from parents, students and colleagues.
- Make time to talk with students, course leaders, school or institution leaders and parents or carers about issues affecting individual students, classes or groups.
- Find opportunities for learning and development.
- Find opportunities for learning and certification as a dance educator.
- Learn about lifelong learning practices.

Professional development
Maintain knowledge and expertise in your chosen genre and style of dance; develop a broad knowledge of dance; enrich your qualifications.
Level 1
- Attend performances and read dance-related material.
- Develop your awareness and knowledge of different stage crafts.
- Enroll in teaching, stage craft, health, fitness and business management courses.
- Encourage employed staff to do professional development.
Level 2
- Make sure your professional knowledge is current and qualifications are upgraded through a teaching or syllabus organisation.
- Attend professional development workshops or short courses.
- Maintain or subscribe to a professional journal or library.
Encourage self-expression and creativity
Level 1
- Include regular times for students to use imagination, expressive skills and creativity.
- Teach students the elements of composition using the relevant style or genre.

- Use different creative stimuli and models of self expression.
- Use a developmental approach (creative scaffolding) to build creative skills along with technique development.
- Include time to develop performance skills.
- Give students access to other teachers or artists (workshops, summer schools and special events) to stimulate creativity through new ways of thinking about dance.
- Recognise the subjective nature of creativity.
Level 2
- Help students develop independence, problem-solving and decision-making skills.
- Recognise individual learning styles and offer choices so each student has practice with problem solving and decision-making.
- Make sure that programs/curriculum let students choose class tasks, projects or electives that allow creative growth.
- Use technical training as a tool for expressive development and creative growth.
- Give students tools to assess their expressive and creative development.

- Give students opportunities and support their interest in dance experiences beyond their educational setting
- Encourage use, review and criticism of dance-related material
- Facilitate or encourage attendance at rehearsals, performances, exhibitions and performances in dance and other art forms
- Support students to audition for events or performances or take part in activities/workshops where they can work with other teachers, choreographers or directors to enhance their
- Understanding of creative processes, performance and professional expectations.
Use assessment and reporting procedures
Note: There are teaching situations such as community and recreational dance instruction which do not require or expect formal assessment and reporting.
Assess the work of students against criteria
Level 1
- Give students regular verbal or written feedback that includes praise and identifies areas for improvement.

- Let students discuss and receive feedback about work in development (technique, creative work and theory).
- Give progress reports to parents and students.
- Before assessment, make sure students understand the assessment measures.
- Use external standards or assessors to moderate your assessment process.
- Deal privately with sensitive assessment and achievement issues.
Give parents and students an accurate assessment of dance potential
Level 2
- Give regular verbal and written descriptive assessment (which includes marks or grades), and some independent assessment.
- Give honest opinions about a dancer’s potential or readiness to pass an exam or succeed in an audition.
- Use criterion-based assessment which can be complemented by subjective opinions, references and statements.
Provide vocational support for training and careers
Level 2
- Encourage students to complete their school education and to develop interests both within and outside dance.

- Give students resources, structures, educational counselling that helps them complete Year 12 and receive university admission ranking.
- Encourage students to gain experience in dance and theatre related work.
- Give students access to professional career counselling.
- Give students work, career and transition planning tools.
Author
Ausdance National
We lead a network of Ausdance organisations that deliver integrated programs across the country, anticipating industry issues and providing innovative and inclusive responses.
Ausdance National now operates as a voluntary organisation, and continues its work through its own National projects and programs. Read about our contributions to the Australian dance sector.
Through advocacy, Ausdance National aims to:
- Lead and shape dance policy development and debate.
- Provide a national voice for dance and dance education.

- Identify and promote diverse forms of dance and dance practice.
- Encourage access to and understanding of dance.
- Foster national and international links with dance and dance-related organisations.
View more from Ausdance National
Colophon
© Ausdance National 2011
This is the second edition of The Australian Guidelines for Teaching Dance which was orignally published in 1998. The content has been updated by Jane Pamenter and edited by Rachael Jennings and Leanne Craig in consultation with selected professionals from different sectors of the dance education industry.
The original guidelines were based on draft competency standards developed in 1994 and 1995 by Arts Training ACT and Ausdance ACT in response to community demand. They support the Code of Ethics developed by the teaching profession in 1986 and 1987 and the Safe Dance Project Report 1990, which increased community awareness of the need for dance teachers to maintain and upgrade their qualifications in injury prevention and management.
Thanks to Ruth Osborne, Maggi Phillips, Kylie Hunter, Irene Lind, Charmaine Hallam, Jacqui Simmonds and Fresh Funk.
Posted under: Teaching dance, Teaching methods, Factsheets + guides
Colophon
A 4-Step Method to Help Your Dancers Learn Choreography Faster
Todd Rosenlieb, left, of The Governor's School for the Arts. Photo by Victor Frailing, courtesy of Todd Rosenlieb<span></span>
A 4-Step Method to Help Your Dancers Learn Choreography Faster
You’re setting choreography on your class and most of the students are picking it up. One dancer, though, is having difficulty remembering the steps. You review the material several times, but you fear that this is starting to hold back your more advanced students. Still, you’re worried the struggling dancer will be left behind. What is the best way to proceed?
Memorizing choreography is an essential skill for dancers. Fast learners have more time to work on the technique and artistry within a combination, and they are often the first to catch the eyes of directors. Like most skills, learning pace can be improved. Encouraging students to develop their own memorization methods will help them approach choreography with confidence.
Like most skills, learning pace can be improved. Encouraging students to develop their own memorization methods will help them approach choreography with confidence.
Teaching the Steps
The traditional way for dancers to learn choreography is to mimic movement as you teach it. But some students may benefit from first watching you show the phrase. The mirror-neuron theory, a component of ideokinesis (a movement-science visualization method), says that dancers’ own movements are better informed after seeing someone else perform. This means that having students sit and watch you demonstrate a full phrase may actually help their muscles pick up choreography more efficiently.
Some students become stressed out by the amount of information being taught. It may be less intimidating for them to break the movement down into sections of the body. Todd Rosenlieb, chair of the dance department at The Governor’s School for the Arts in Virginia, has these dancers first tackle the feet. “Once they get the rhythm of it, add the upper body,” he says. Rosenlieb also asks dancers to think of the choreography in stage terms. For instance, moving upstage or downstage instead of forward and back can help them understand the space if they get lost or have to reverse the material.
“Once they get the rhythm of it, add the upper body,” he says. Rosenlieb also asks dancers to think of the choreography in stage terms. For instance, moving upstage or downstage instead of forward and back can help them understand the space if they get lost or have to reverse the material.
Don’t hesitate to take an extra moment with struggling students in class or rehearsal, but be sensitive to embarrassment and frustration. Singling a dancer out in front of their classmates can undermine their confidence. Having an advanced student take the other aside removes some of the pressure and allows you to continue teaching the rest of the group.
Walnut Hill’s Denise Lewis. Photo by Sharyn Peavey, courtesy of Walnut Hill School
On Their Own
Dancers can create landmarks in the choreography by connecting steps with musical cues. “Students need to see the connection between the music and the physical parts,” says Denise Lewis, associate director of dance at Walnut Hill School for the Arts in Massachusetts. She finds that particularly detailed sections of choreography are retained best when broken down into smaller beats (like “one-e-and-a-two”). “I get a really good result using counts, especially with younger children,” says Lewis. “That kind of clarity eliminates any confusion.”
She finds that particularly detailed sections of choreography are retained best when broken down into smaller beats (like “one-e-and-a-two”). “I get a really good result using counts, especially with younger children,” says Lewis. “That kind of clarity eliminates any confusion.”
Dancers can also create their own keywords, creative names or sounds associated with the movement. For instance, “If you cross your legs and swirl to the floor, call it a swizzlestick,” says Rosenlieb. Singing the word or sound in their heads through the time it takes to complete the step will help them learn the musicality and rhythm. (For similar techniques, see the sidebar “Building Off Imagery.”)
Keeping a notebook to journal a difficult sequence of choreography, as well as corrections given during class and rehearsal, will allow dancers to review what they learned without your help. It also forces them to clearly articulate each movement as they write it down. Give them copies of the music so they can physically or mentally practice the phrases during downtime, like car rides to the studio, before bed or in the shower. “When they have a quiet moment,” says Rosenlieb, “students can close their eyes and visualize the dance and the way they want to dance it.”
“When they have a quiet moment,” says Rosenlieb, “students can close their eyes and visualize the dance and the way they want to dance it.”
Building Off Imagery
Sometimes a vivid mental picture is all it takes to remember steps, says Eric Franklin, creator of the Franklin Method (franklinmethod.com).
1. Create metaphors: Dancers of all levels respond well to vivid images. Instead of putting your arm out and reaching, identify it as “reaching for an apple.”
2. Chain images together: Reach for the apple, kick a ball, open a curtain and jump over a stream. “Dancers who couldn’t remember anything suddenly can remember a very long series of steps,” says Franklin.
3. Identify transitions: The in-between moments are where dancers often struggle the most. Create specific qualities, like “Your shoulder blades are melting down your back like ice cream on a warm day.”
4. Share strategies: Ask students to come up with their own imagery and then teach it to another group of dancers. “Kids love it and they learn a lot more, a lot faster,” says Franklin. This helps them develop new ways of remembering the same choreography.
“Kids love it and they learn a lot more, a lot faster,” says Franklin. This helps them develop new ways of remembering the same choreography.
Dances
Author: Pavel Gather
Psychologist, Lecturer Salsa and Tango
Dances
Author: Pavel Pavel
Psychologist, Lecturer Salsa
on At the start, you always want to get a quick result. When it doesn't happen, the hypothesis arises that everything takes time. After a conditionally acceptable time, humility comes to mastering pair dances, which, perhaps, is not given, and I will just do what I learned somehow.
This is the most common story of those who believe that the mere act of attending a pair dance class is enough to learn how to dance.
Absolutely not. If you want to really dance well, you have to make an effort outside of the dance class. A good teacher will definitely be needed, but the initiative should be on your side.
1. Listen to music
The most common and accessible advice that is given already in the first lessons. And it definitely works. Music creates a certain atmosphere of the dance and intuitively you want to move to it. It doesn't matter where you listen to music - in the car, on headphones while walking or doing household chores.
An addition that will help you dance better is your active participation in the music. Sing along, dance or simply beat musical accents with any free parts of the body. In the subway, for example, it is enough to tap out bright moments with your fingers, in the car to sing along with sounds, and at home you can jump for pleasure.
2. Watch videos of good dancers
It's complicated, but also obvious. It’s more difficult, because without recommendations from more experienced dancers, unfortunately, it’s not so easy to find a good quality video on the net (I mean not the resolution quality, but the content itself).
Meaningful video viewing is about building an understanding of HOW dancers make a particular impression on a partner or viewer. Technology is at the heart of everything. Understanding how the pros do it is a big step forward.
It is important to distinguish a show from a disco dance, a staged performance from an improvisation, a stylized dance from an authentic one, etc. Ask for recommendations and dance teachers will always throw off a couple of videos of worthy landmarks.
Tango Z. Showreel.
Online modern tango courses
Tango nuevo is the most advanced version of tango. We can quickly learn to dance from zero to a steep level.
| View details |
3. Dance in salsatecas/milongas/discotheques
A very delicate moment when it is worth coming to the first party. From a technical point of view, most students in 1-3 months have a sufficient set of figures and techniques to come and dance calmly. Psychologically, the same moment can be stretched out for an indefinite time. After all, it is imperative to “not lose face”, “learn more figures” and be sure what to do in case “there is an unfamiliar movement”.
Psychologically, the same moment can be stretched out for an indefinite time. After all, it is imperative to “not lose face”, “learn more figures” and be sure what to do in case “there is an unfamiliar movement”.
In fact, the partygoers don't really care (except for a small layer of non-professional teachers who want to help inexperienced dancers by treating them as customers in the future). It is important to come and try dancing after a month of classes. You can only with friends or guys from your group. This will be enough to feel the adrenaline and inspiration from the dance.
4. Dance with partners or partners not of your level
The conventional wisdom that you need to practice in groups of your level does not withstand the test of experience. Perhaps now your eyes widened in surprise, and you want to meaningfully read the phrase again. Yes, you saw everything correctly: when you dance with a partner of your level, you don’t grow anywhere.
It's important to understand that not only does it work one way and you have to dance with cooler dancers, but it works even more effectively the other way. It is no coincidence that teaching pair dances dramatically raises the level of the teacher himself. You have an endless stream of very beginner dancers.
How it works. A more experienced partner needs to be "stretched". It's easy and obvious. With beginners, you need to take more initiative on yourself, see the general pattern of the dance more widely, turn on and insure more, try to be an example and be more careful. The quality of interaction begins to grow significantly. And wonderful partners too.
Dancing with partners of your level doesn't make you grow. Dance with both beginners and more advanced dancers
Dominican Bachata Women's Style Online Course
Want to learn how to hypnotize those around you with the most appetizing part of your body? On the course we will tell you all the secrets.
| Interesting |
5. Learn to dance for a partner and for a partner
Turks and Argentines are one of the best partners in the world. In Russia, partners are highly valued. Why? The answer is simple. In Argentina and Turkey, it is not questionable for men to ask another man to lead in one piece or another and give feedback on the quality of the lead. For them, it will be a great shame to hear moralizing from a partner, or even more so to be known in the community as an insecure partner.
In Russia, due to the constant, often far-fetched, opinion that there are more women in pair dances, partners calmly get up and study their partner's part. Such partners then grow into very cool dancers and teachers. In no case do this at parties, only in class. Here we are talking only about the learning strategy. At parties, be yourself.
6. Do not memorize the links
Always try to look deeper and understand the through principle and idea of movement. Understanding what and how is done will make it possible to independently generate any sequences and chips.
Understanding what and how is done will make it possible to independently generate any sequences and chips.
Human memory is limited and there will always be a moment when something will escape and your repertoire will be limited by the size of RAM.
In Argentine tango, for example, there are seven levels of movement construction that, when mastered, will allow you to make millions of combinations. And how many dance sequences can you really remember? In rueda, more than 150 figures dance in a rare circle. It's hard to keep more in mind.
7. Develop your body
Many years of experience in teaching couple dance shows that as soon as everyone pairs up in a class, any progress in individual style ends. But it is the individual style that distinguishes everyone at the disco: partners change, and style is always with you.
The body as the main instrument of dance must be very plastic, responsive and emotional. Surprisingly, not all pair dance schools have a general physical warm-up. It is vital to tune the body and understand how it works.
It is vital to tune the body and understand how it works.
You can always train extra and concentrate more on the basic steps, as their true value is as body work. The sequence of steps is, in fact, the simplest thing that can be in pair dancing. The quality of individual performance determines the craftsmanship.
8. Try on the images of inspiring dancers
A psychological life hack for those who have already mastered the steps, but still feel that there is not enough brightness and drive. Most are terribly afraid of being someone else's "clone". Here the action is the same as under the influence of hypnosis - the more you resist, the more you plunge into an altered state of consciousness.
With a high degree of probability, you are already dancing like someone else's "clone". A meaningful fitting of someone else's image is that you mentally take the image of the one who inspires you (inspiration is critical in this case) and "put on" yourself. Then you start dancing and trying to feel in general how it is to be able, for example, to be the best partner or the sexiest partner in a disco. This is much more difficult than it seems. But it works extremely efficiently.
Then you start dancing and trying to feel in general how it is to be able, for example, to be the best partner or the sexiest partner in a disco. This is much more difficult than it seems. But it works extremely efficiently.
9. Dance to offbeat music
Habitual rhythms keep you tight. Tango salon or speedy timba leave little room for experimentation and fantasy. Pattern dancing is always noticeable and is reserved for beginners.
The truly new is born outside of the usual. Look for places to experiment. If there is no place, organize self-training. The main thing is not to get carried away, because music determines the style. We bring something new to pair dances, rather than trying to change them.
Search, improvise, don’t be afraid to go beyond, develop in different directions, be inspired by music atypical for the style
10. Try your hand at basic dance directions
dances exist according to their own non-choreographic laws.
This is the deepest delusion, which has turned into a ceiling for the qualitative development of partner dances. After all, all professional dancers, for example, in salsa or bachata, build their ideas on the basic choreographic principles.
Do not think that choreography is only applicable on stage. Any meaningful movement of the body can be choreographic. In general, try classical or modern choreography. Basically, hip-hop can work too.
11. Look for battle sensations
Pair dances return us to an active position of manifestation of our body. As in the days of our ancient ancestors, we impress the members of the opposite sex by how dexterous, hardy, sexy, etc. we are. Modern laws of the jungle in the entourage of large cities.
If you look around the dance floor, it becomes clear that the majority are clearly herbivores (not in the sense of vegetarians, but in relation to those around them). I am sure that predators are always more interesting in terms of the attractiveness of the image - try to find a counterbalance among herbivores, for example, a cat woman or a lion man.
I am sure that predators are always more interesting in terms of the attractiveness of the image - try to find a counterbalance among herbivores, for example, a cat woman or a lion man.
The conversation is about an internal position, not about aggressiveness. Lability and lack of control are inherent in adolescents, and not in adult self-sufficient people.
Accordingly, even a training or friendly battle gives, on the one hand, practical skills - to make a bright sequence of movements, bring an idea to a climax, show a spectacular feature, on the other hand, develops the psychological basis of the dance - self-confidence, resistance to extraneous attention, self-control and self-control in complex elements.
12. Communicate with professionals
The environment shapes the internal position. Basically, real passionaries of the dance community are ready to openly talk, discuss and support the development of dance in every possible way. Universal principles and the ideas they articulate have a much longer and more practical perspective than meets the eye.
Universal principles and the ideas they articulate have a much longer and more practical perspective than meets the eye.
Accept that, for example, behind the words "listen to your partner" is not only a beautiful metaphor, but also a practical skill to literally listen to your partner. At the same time, always treat every thought, even the most respected teacher, as a private opinion.
Your skill will lie in finding the scope of the idea even in conflicting opinions. Most often, the contradiction is speculative and the truth lies in the angle of perception or situationality.
Your dancing growth will stop sooner or later. This can happen at the level of three basic steps or years of experience in teaching and show performances. Regardless of your level, the suggested 12 life hacks can get you off the ground and greatly accelerate your dance growth. There is no way here without your motivation and activity. Take your dance development into your own hands. 9Ol000 Dangerous sexuality
Salsa: destroyers of stereotypes
Couple dancing as a source of strength.
Self-destruction of the couple dance community
The Salsa series as a mirror of the community
Mamita Fridays: salsa, bachata
Destroying the myths about leading pair dances
Does dancing make us better?
The seven deadly sins of teachers
Why we will never dance bachata like the Dominicans
Why tango?
Dispute over musicality
Selection of dances according to alcohol preferences
Where to find inspiration for dancing?
Terrible tango nuevo
Distribution of roles in a salsa party
Argentinean tango through the eyes of a salsa dancer
Is there a predisposition to dancing?
Which is more effective: individual or group lessons?
Sexual overtones in partner dancing
I want to dance. 10 misconceptions about dancing
The desire to learn to dance is natural and natural in the modern world. You can list the reasons, starting with obvious and popular pragmatic desires, for example, to start moving or losing weight, ending with unconscious and even existential ones.
This is due to the fact that dancing is at the subtle intersection of the inner and outer worlds, physical and spiritual. Above this, music becomes a driver that cannot leave anyone indifferent.
In dancing there is magic inside a person, which is not always noticeable when observed from the side. At the initial stage, it is the external picture that attracts to dances, and sometimes repels, as it seems too frivolous and superficial.
But there are even stronger obstacles that stop many people from starting dancing. These illusions and delusions roam the minds of the majority, and are often afraid to ask about them directly, or they ask the question about it so often that they are no longer ready to hear an honest direct answer. I will try to do it in this article.
There are many examples of contemporary dance instructors sharing their thoughts about not expecting to be in the dance industry. Once upon a time there was a man and was engaged in adult, serious business. Sometimes even very serious. A person could have children and even grandchildren. I saw dances only on stage or on TV. For reasons unknown to himself, he ended up in dances. At first, everything seemed like entertainment and a useful pastime. But time has passed, and a person catches himself thinking that he thinks about dancing not just every day, but really all the time. A couple of years pass, and he already becomes a teacher or organizer of some event.
Sometimes even very serious. A person could have children and even grandchildren. I saw dances only on stage or on TV. For reasons unknown to himself, he ended up in dances. At first, everything seemed like entertainment and a useful pastime. But time has passed, and a person catches himself thinking that he thinks about dancing not just every day, but really all the time. A couple of years pass, and he already becomes a teacher or organizer of some event.
A similar path can start at 15 or 55 years old. The only difference will be in the self-perception of the starting stage, that it’s too late to dance. In fact, for each age there is its own dance direction, which can reveal it to the greatest extent at this stage. Hip-hop or breaking is closer to children and teenagers, and Argentine tango is closer to adults. It's never too late to start dancing. You need to make the right choice of dance style based on several parameters: age, gender, music, goal. There is a dance direction for any arrangement.
Misconception 2: men don't dance
Our culture has a number of restrictions related to dancing. Most of these causes are psychological and lie outside the realm of rational reasoning.
First, in our culture, in principle, dancing for pleasure or self-expression appeared relatively recently. 20-30 years ago dance clubs were only for children. To start dancing even in adolescence was considered exotic.
Secondly, the aesthetics of the body in our country for men is not in the focus of attention. In general, this can be attributed to the fact that Russian men try hard not to draw attention to their appearance and clothing. Men in our country use other tools for this.
Third, dancing is associated with entertainment and alcohol. If a man feels serious and respectable, then he either does not have time or desire for this.
Nowadays the general cultural background has changed and the result is that men are learning to dance. It becomes as much a sign of masculinity as clothing, hair or beard.
It becomes as much a sign of masculinity as clothing, hair or beard.
Unfortunately, many misconceptions remain even among those who have already started dancing. Dance teachers do not always pay attention to this, as it seems to them that this is a matter of course.
Fallacy 3: special training is needed
For an outside observer, there is always a cognitive dissonance about what dance is. What he sees on the big stage in the form of a show with sweeping movements and splits is obviously dancing. Breakers doing unimaginable elements in the air and on their hands, competing with each other, also seem to be dancing. Pensioners in the park waltz. Dancing again, but for some reason everyone is so different. How to understand that this is a dance, and what physical criteria should be in the body.
In fact, any self-expression through the body to music can be attributed to dance. There are a number of reservations, but they are not essential. For self-expression, a person uses the set of plastics that he has. Subtlety and technique do not depend on extreme ways of self-expression, and it often happens that splits and somersaults interfere with a meaningful dance. The development of plasticity and the expansion of the body's capabilities are part of the preparation of the dancer, but not an end in itself.
For self-expression, a person uses the set of plastics that he has. Subtlety and technique do not depend on extreme ways of self-expression, and it often happens that splits and somersaults interfere with a meaningful dance. The development of plasticity and the expansion of the body's capabilities are part of the preparation of the dancer, but not an end in itself.
Misconception 4: You must learn to dance in pairs
In couple dancing, the final learning outcome is that the couple dances at a party. It would seem that you should always train together to get the desired result. This is not true. Let's take an example from boxing. An indicator of a boxer's skill is a fight with an opponent, but this does not mean that he constantly has to fight. Also, the ability to dance is built on the possession of one's own body and the ability to interact.
The skill of the teacher is the correct selection of methods so that the student masters the skill. Based on the skill, you can engage in creativity and self-expression in dance. Not everyone knows, but it is no coincidence that almost all social dance dancers have a serious dance background, which is based on the development of individual techniques.
Based on the skill, you can engage in creativity and self-expression in dance. Not everyone knows, but it is no coincidence that almost all social dance dancers have a serious dance background, which is based on the development of individual techniques.
The same can be attributed to the interaction in a pair. The ability to separate in oneself the one who leads and the one who follows the lead is impossible within the framework of studying the sequence of movements in pairs. For this, there are special exercises that make the skill more versatile. For this, the presence of a permanent couple is not necessary, as well as the regular presence of a partner in general.
IMPORTANT! You can’t experiment at a party, and everything should be in its place there: men dance with women.
Getting rid of illusions is a complex internal process. If you leave them to yourself, you can even get the opposite result.
Misconception 5: plastique and stretching are obligatory attributes of dance
Much depends on the genre of dance that you want to master. In previous articles, I have already mentioned that different dance styles are suitable for different ages. It is appropriate to dance hip-hop in adolescence or youth, Argentine tango is a more adult dance, it is important to enter classical choreography at a young age.
In previous articles, I have already mentioned that different dance styles are suitable for different ages. It is appropriate to dance hip-hop in adolescence or youth, Argentine tango is a more adult dance, it is important to enter classical choreography at a young age.
The degree of necessary plasticity and sensitivity to the dance direction also correlates. For example, breaking requires great physical effort and dexterity. Elements are built on acrobatics and high speed of execution. Who are they more suitable for? Obviously young people.
There is a lot of interaction in salsa. It is necessary to feel the partner subtly, to be able to show a variety of figures and elements. Twine or acrobatics are completely inappropriate here. However, a variety of ways to show oneself are required. Accordingly, the dance is youthful, but not at all childish.
The older the dance, the less stretching or acrobatics is required. The main emphasis is on the quality of technology, the variety of ideas and the ability to show plasticity.
Misconception 6: Mirrors are necessary for learning
There is a set of instruments that dancers use to learn how to dance. The fact is that the dancer needs to receive feedback on how his movements look from the side. It is impossible to dance and see yourself from the side at the same time. The most common tool is a mirror. But not the only one.
Like any auxiliary tool, mirrors have positive and negative effects. The positive is that they can receive feedback in real time and technically it is not very difficult. The downside can be dependence on mirrors. A situation where a dancer cannot capture the feeling of dancing, such as on stage or at a party. For these purposes, you can use, among other things, video filming or proper preparation.
In many countries in Latin America, dance classrooms are not equipped with mirrors. Classes are held in bars or large halls. The dancers initially form the skill of focusing on the inner sensation, and not the habit of looking for their reflection in the mirror with their eyes.
Misconception 7: there is a lot of obsceneness in dancing
A common question from novice dancers who are taking their first steps in more contact couple dances is “in order to dance cool, there must be passion inside the couple?”. I immediately answer that no, not necessarily. Kizomba, bachata and Argentine tango attract many with their close contact. Like any other contact in our everyday life, in dances, contact can be different. We hug friends, parents, children. These hugs can wear many different shades. Sexual overtones are one of many.
The culture of dance also includes the boundaries of what is acceptable. A compliment from a well-mannered person is different from a statement about female sexuality by a gopnik. Usually, those who study at a dance school already have an idea of what boundaries should not be crossed. A good dance from a technical point of view will never look vulgar or vulgar.
Dancers always have a choice about the boundaries of contact. Most prefer to leave a good impression of themselves, as word spreads just as fast in the dance world.
Most prefer to leave a good impression of themselves, as word spreads just as fast in the dance world.
Misconception 8: the best dancers are the bearers of culture
Even the very question of the origin of a particular dance can be paradoxical and ambiguous, especially when it comes to its development and performance.
For example, the Viennese waltz did not originate in Vienna, but in Germany. Salsa has its main roots in the USA, not in Cuba. The famous Greek folk dance sirtaki was invented for the film "Zorba the Greek" and appeared only in 1964.
The same can be attributed to the development of modern dance styles. Korea is known for its world-leading break dancers. People go to Turkey for Argentine tango, Spain is strong with excellent salsa and bachata dancers, in Egypt, Russians are considered the best belly-dance performers.
A good dance is based on quality training and diligence. Skin color, place of birth and age are secondary. Exotic appearance, unfortunately, is often a reason to be more superficial about one's own professional development. This becomes the reason for the low level of teaching among the bearers of culture. I am sure that few readers of this post will be ready to conduct a master class in Russian folk dance outside of Russia.
Exotic appearance, unfortunately, is often a reason to be more superficial about one's own professional development. This becomes the reason for the low level of teaching among the bearers of culture. I am sure that few readers of this post will be ready to conduct a master class in Russian folk dance outside of Russia.
The mastery of mastering and teaching a particular style does not depend on the dancer's homeland. And "they absorbed the dance with their mother's milk" is nothing more than a common misconception.
Misconception 9: You have to know a lot of moves to learn to dance
Focusing on learning a lot of moves often detracts from the essence of dance. Of course, the sequence of figures is important. Especially at the start. Over time, the dancer should have an understanding of how movements can be generated independently. Accordingly, instead of memorizing millions of figures, you can understand how to create them.
From every system of improvisation that a dancer can use as an instrument, dozens, hundreds or thousands of variations are derived. This frees the head from trying to reproduce the exact sequence and definitely adds freedom in the performance of the dance.
This frees the head from trying to reproduce the exact sequence and definitely adds freedom in the performance of the dance.
The huge theme of musicality can be attributed to the same question. Not every pre-conceived or learned sequence will fit specific music. The dance should give freedom, and not drive the dancer into the shell of the ropes.
Misconception 10: dancing is homosexual
The unusually high attention to the body and the flair from stories about professional ballet led to the spread of this myth, among other things. Unfortunately, such an idea still exists in the minds of our fellow citizens.
The dance industry is now very broad and is represented by many dance styles. Some of them can even be called homophobic. Dances reflect the general attitude to the world and it is different depending on the life position and worldview of a person.
In many dances there is contact between the dancers. In Russia, dance contact between men has always been perceived very intensely. In most other countries it is different. An example of the fact that this tension is associated only with the dance theme and does not apply to other areas is, for example, wrestling. When practicing techniques, men are in much closer contact with each other. Sometimes lying on the floor and holding each other tightly. The historical roots of Greco-Roman wrestling are also ambiguous from a sexual point of view. But in our country, unlike dance, they are perceived as acceptable and brutal.
In most other countries it is different. An example of the fact that this tension is associated only with the dance theme and does not apply to other areas is, for example, wrestling. When practicing techniques, men are in much closer contact with each other. Sometimes lying on the floor and holding each other tightly. The historical roots of Greco-Roman wrestling are also ambiguous from a sexual point of view. But in our country, unlike dance, they are perceived as acceptable and brutal.
Dance, like the culture of speech, makes a modern person more successful and self-confident. The ability to control one's body, tune in to another person and the ability to be aesthetic in the plasticity of movement is valuable in the modern world. If we add here the pleasure of the process and the availability of dance as such, then the possibilities of this activity can hardly be overestimated.
It's sad when interested people are stopped by prejudices and myths that have nothing to do with dancing.