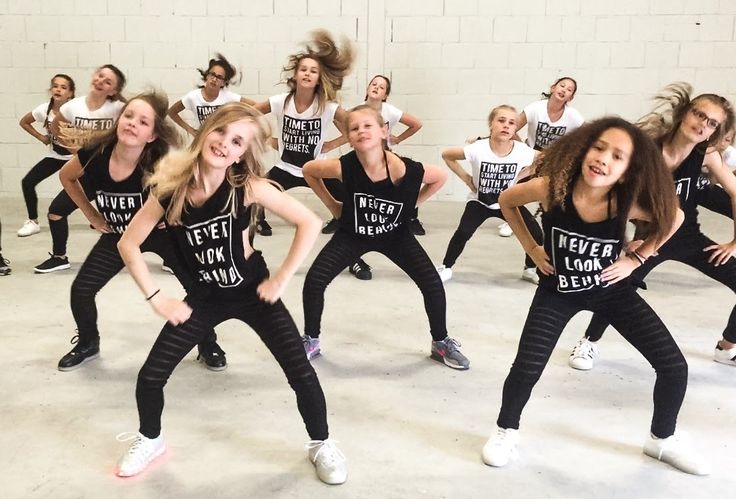
How to loosen up your body when dancing
How To Not Look AWKWARD When You Dance
Do you feel awkward when you dance??
It’s pretty normal to feel insecure about your dancing.
I mean, it’s your body. Your literal SELF that's being put out there!If you’re that person at the club swaying awkwardly or hanging out by the wall at a school dance…
We’re here to help make you feel more comfortable in your body.
Ready to stop being a wallflower?? Wanna get movin’ and groovin’??!?!
Let’s go!
1. Own your style
If you feel awkward when you dance, then you will look awkward when you dance. And if you keep telling yourself you're awkward, then you will stay awkward.
The first step to overcoming awkwardness is to stop that self-deprecating narrative.
You don’t have two left feet.
You do have rhythm.
You can be a good dancer.
Re-defining your view of yourself is the only way you allow yourself to grow.
And if you're truly convinced that you can't follow a beat or stop tripping over yourself... just take some time to practice those basic foundations!
STEEZY's online "Intro to Dance" program walks you through all of the fundamentals step-by-step, so it's the perfect place to start.
Click here to start the program for free!
2. Find your body’s natural groove
No two people in the world have the exact same bodies, music tastes, dance training, or life experiences. This means that no two people really dance the same.
Everyone dances like themselves. You, included! So find that groove that feels right to you.
When you take class, modify the choreography to fit your body. And when you freestyle, just start with a basic two-step.
That simple left-right, right-left skeleton leaves SO much room for you to build off of..jpg)
Feel the way your body reacts to the music...
Let yourself groove out...
3. And COMMIT to it
A lot of the time, dancers will look awkward because they PLAY THEMSELVES!!
That slight hesitation, that SMIDGEN of under-delivery, that look of “oh sh*t” on their faces…
Awkward.
Knowing and committing to yourself is the only way you won’t look awkward when you dance.
4. Loosen up!
Really, an instant fix. Most people look awkward when they dance because they are stiff. And they’re stiff because they aren’t moving.
Don’t lock your knees.
Free your neck to let your head bob.
Shake out your arms.
Relax your core.
You can even do some stretching or pilates to help your muscles get used to that relaxed, loose state!
This pilates class on STEEZY is perfect as it's literally designed to loosen the muscles you use when you dance.
So get LOOSE. No excuses.
5. LISTEN to the music
Maybe you look awkward when you dance because your body isn’t matching the tempo of the music.
Simply aligning the rhythm of your movements to the beat will make your dancing look a lot more put together.
Or, your vibe isn't matching the vibe of the song, making your dancing look off.
Follow Melvin Timtim's advice on this:
6. Have fun
I’ve never watched someone genuinely love what they’re doing and judged them.
Pure fun never looks or feels awkward.
So stop overthinking! Put on a soundtrack to a musical you love and lip sync it all the way through. Blast some dirty rap music in your car and go awff.
Play some sexy bedroom music and serenade your lover. At the end of the day, dance is something that lets you play.
You can be anyone you want, do anything you want, and escape from whatever stresses are plaguing your mind.
Dance is an escape, not another stressor.
So have fun with it :) and looking dope will happen on its own. Being a good dancer or a bad dancer, a dope one or an awkward one...
It depends on what you practice – both mentally and physically. Use these tips to make dancing look and feel like second nature.
You’ll be tearin’ it up on the dance floor in no time.
What are some things that helped you overcome looking awkward when you dance? Comment below and leave a tip!
Classes on STEEZY Studio help you loosen up to move more comfortably.
Take our beginner program to learn the essential grooves to start with!
Is Your Dancing Too Tense? 3 Ways To Loosen Up
When a dancer’s body has excess tension, their movement can lose its luster and flow. “What we see when we watch a spectacular performer is the precise application of effort,” says Peggy Gould, an associate professor at Sarah Lawrence College who teaches dance conditioning and kinesiology. “Not too much, not too little, but just the right amount.”
“What we see when we watch a spectacular performer is the precise application of effort,” says Peggy Gould, an associate professor at Sarah Lawrence College who teaches dance conditioning and kinesiology. “Not too much, not too little, but just the right amount.”
Yet even a dancer in top condition with strong technique can’t disguise the tension that builds up from overworking and imbalances. The solution does not lie simply in trying to “relax,” but in getting a better idea of where where the tension comes from.
Why We Need Some Tension
Tension refers to the action of muscles contracting. Dancing would be impossible without a certain amount of it. “We would be a puddle on the floor,” says Tom Welch, a professor of dance kinesiology at Florida State University. Gould defines it further. “Tension is muscle work that does not produce motion, but rather helps to maintain a stable or static situation. There is no change in muscle length, no change in relationship between the bones the muscle attaches to, no joint motion, no movement.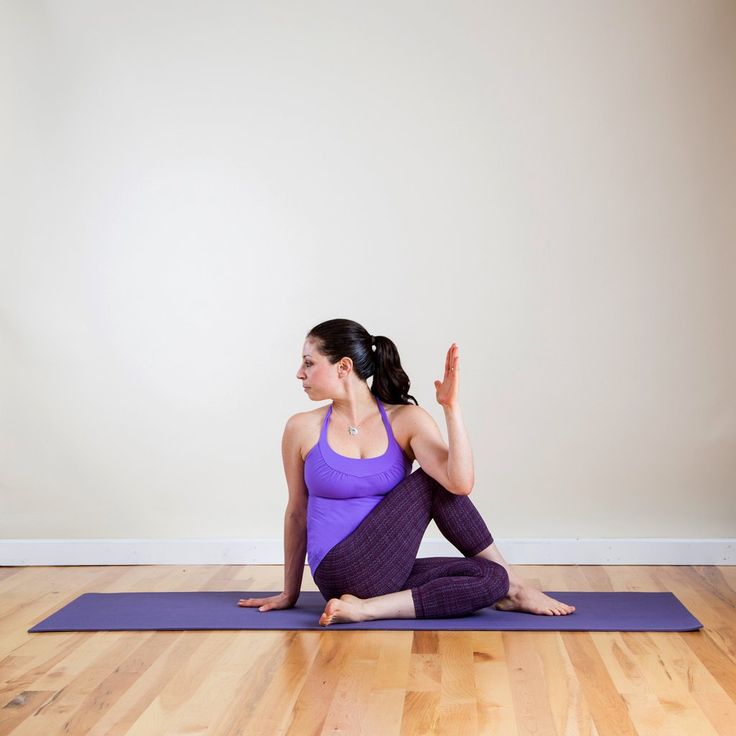 ”
”
Excess tension, which can make you look stiff, derives from the relationship between muscles and bones. “When we don’t make good use of our bony support structures, it’s often our muscles that wind up playing key roles in holding us up against gravity,” Gould says. “Treating a muscle like a bone generally leads to that muscle behaving more like bone, becoming stiffer and more resistant.”
Here’s the good news: There are numerous ways to relieve excess tension.
Work you do outside of technique class can help balance your body and build strength to help you dance with less tension. Photo via Unsplash
Start by Building Strong, Long Muscles
For Welch, the way you prepare your body for the job of dance can help release excess tension. “Muscles have to be strong and long,” he says. He teaches a special Pilates class devoted to reducing tension. “It’s a two-stage process involving activation and strengthening, then releasing and stretching,” he says.
Rub and Roll It Out
Jennifer Williams, of Chaddick Dance Company in Austin, Texas, has struggled with excess tension all her dancing life due to structural imbalances from scoliosis. “I’m a firm believer in rolling out muscles, whether it’s a tennis ball or a foam roller,” says Williams. These provide feedback to the neuromuscular system—a dancer can sense her body against it, and become more aware of where she is holding extra tension. Massage can also play a vital role in releasing tightness. “I see a massage therapist every other week,” Williams says. Heat and proper stretching can also help muscles relax.
Understand The Root of the Problem
Somatics training can help dancers get to the bottom of the tension cycle. “We must understand the origins of a tension pattern in order to let go of it,” says Gould. “I encourage students to think of this work as refinement in order to advance their technical capabilities.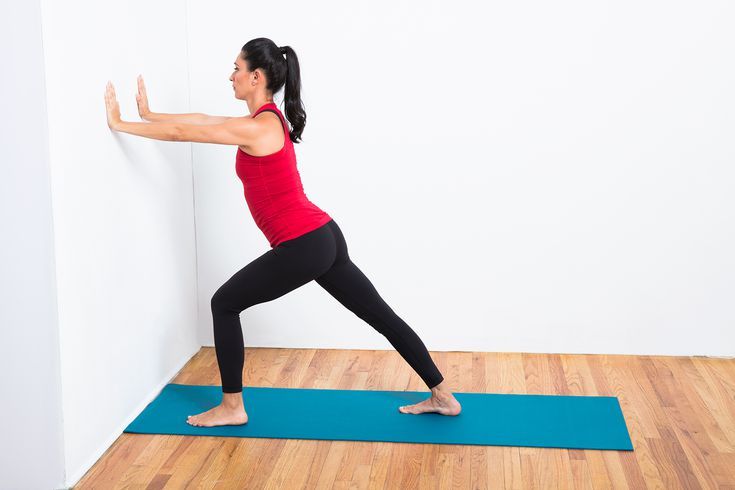 ”
”
Many somatic systems aim at freer movement. Methods like Feldenkrais, Alexander Technique and Ideokinesis allow students to slow down, make small changes and discover the differences in their posture without from the demands of dancing. Feldenkrais focuses on skeletal balance; Alexander, on the position of the skull; Ideokinesis enlists visualization and imagery to foster physical change.
The ease, length, balance and efficiency that these systems help dancers develop all lead to a reduction of unnecessary tension. Welch finds a multifaceted approach works best, one where a dancer can spend time exploring tension in a separate class. Then it can be useful to have the concepts reinforced in dance class through the verbal cues explored in somatic classes.
How to deal with tension while dancing
Many dancers, even very experienced ones, have such a problem as fear of the audience, excitement before going on stage or even during training, and the tightness that follows from this, which literally breaks the whole dance. Here you are standing on the floor, or even in an ordinary rehearsal room in front of the coach, and you start thinking that you are in the spotlight, that everyone is looking at you, how you look now, how not to forget the movements, get into the rhythm, etc. d. Bottom line: panic, stiffness, unnaturalness and nervousness. Familiar? Then this article is for you.
Here you are standing on the floor, or even in an ordinary rehearsal room in front of the coach, and you start thinking that you are in the spotlight, that everyone is looking at you, how you look now, how not to forget the movements, get into the rhythm, etc. d. Bottom line: panic, stiffness, unnaturalness and nervousness. Familiar? Then this article is for you.
So, what do you do to calm down, gain confidence and finally enjoy the dance itself, and maybe even the realization that everyone is looking at you and your great performance? There are several ways.
Relax
Try to learn (learn very well) the movements themselves first. Let it be a little "wooden", that's okay. And then, when the movements reach automatism, try to relax, treat the dance with calmness. Feel the music, immerse yourself in it. Movement will become much more relaxed and natural. The main thing is not to overdo it with "carelessness", you need to find a middle ground between ease and tension, which is also necessary in moderation.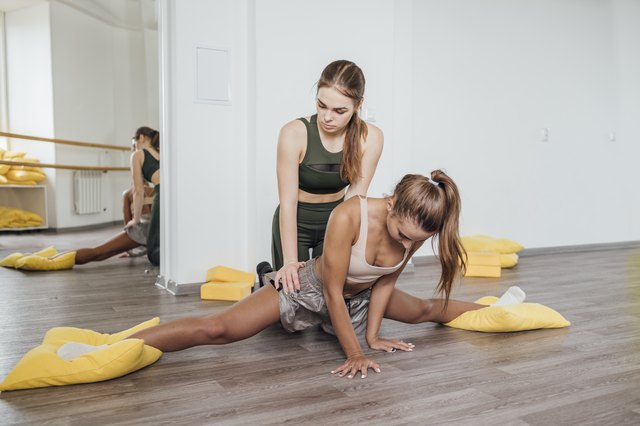
Go to dance parties, dance floors, discos
Go to discos more often, where there are many people like you, where you have the opportunity to relax and try dancing for yourself. Surely, when you dance, being alone, for example, at home, you do it easily and freely, and you get upset that it is much more difficult to do it in public. When you are at a disco, in a noisy crowd, among hundreds or dozens of people, no one will notice your mistakes, no one will correct and judge you, like in an exam. So you can just forget yourself and feel confident, as if no one is looking at you.
Improvise
Improvisation is a very rewarding experience. Turn on good, dynamic music and dance the way you want, the way you feel. Even if there are no such movements in a particular direction of dance, it does not matter. The important thing is that it relaxes well, helps to feel your body, establishes a dialogue between the mind, feelings and body. To know your body, to be able to fully - both physically and emotionally, to immerse yourself in music - is necessary for any dancer.
Dance for yourself
And finally, the main thing - dance for yourself, no matter how selfish it may sound. Learn to have fun, make it so that you are moved by music, so that during the dance the only thing that would be essential for you is the dance itself and nothing else: neither the reaction of the audience, judges, coach, nor your appearance - you can think about this after. As the hero of the film "Dandies" said: "Here you don't need faster, stronger, higher - here you need drive, energy." Let these words become your motto, and you will understand what happiness it is to dance.
Author:
More articles:
Dive into the depths of the dance. Structure and movement: zoukability — LiveJournal
Author: Murasheva NadezhdaThe article is a continuation of the first part: "Dive into the depth of dance. Muscles"
I met the concept of structure only in the last year of my active motor activity, which, as I think it's pretty weird right now. And at first I didn’t really understand what the meaning was in this concept in relation to the body and dance. It was only by delving deeper into the workings of the body and studying the physiology of movement in instructor courses that I began to understand what structure is and how it relates to our body and movement.
And at first I didn’t really understand what the meaning was in this concept in relation to the body and dance. It was only by delving deeper into the workings of the body and studying the physiology of movement in instructor courses that I began to understand what structure is and how it relates to our body and movement.
The phenomenon of structure is large and multifaceted, and I did not put everything at once in one huge article. Today I will share with you a general understanding of structure, the most comfortable, functional and safe body structure for dancing and the differences in structure in different workouts. About the secret of an interesting, varied, artistically filled dance.
WHAT IS STRUCTURE?
In the explanatory dictionaries, I found the two most suitable interpretations that apply to the structure of the body:
- "A certain interrelationship, mutual arrangement of components, structure, arrangement of something"
- "A set of internal connections"
That is, the structure of the body is what our body consists of (bones, muscles, nerves, vessels, etc.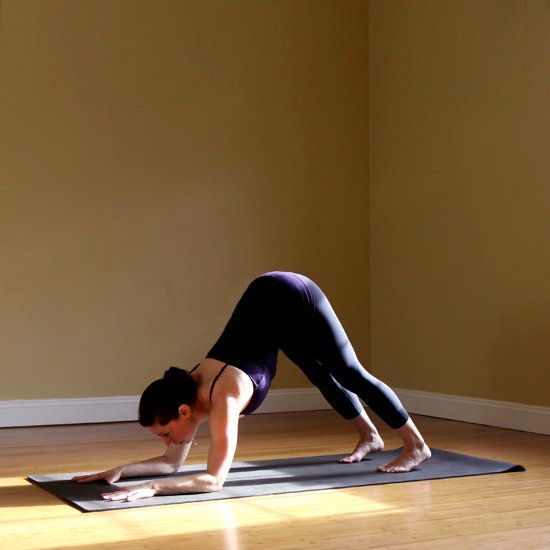 - their structure, location, functions), and also (which interests me much more) is the relationship of the components of the structure to each other. Today I will give you the basic idea of how it works and how it affects the dance, and next time I will continue on a deeper level.
- their structure, location, functions), and also (which interests me much more) is the relationship of the components of the structure to each other. Today I will give you the basic idea of how it works and how it affects the dance, and next time I will continue on a deeper level.
STATES OF MUSCLE TONE
In the context of this article, I will not analyze the structure of the muscle fiber as its structure, this is not necessary here. I am interested in the structure of different muscle states as a more global phenomenon that can be felt, touched, it can be consciously changed and used both in dance and in life.
So, there are three states available to any of our muscles: relaxation, tension, stretching.
Relax
Soft muscle, limp, feels like a piece of jelly. There is no tension in it, and, accordingly, there is no movement.
Unconscious relaxation of the muscle:
1) Normal healthy muscle: worked, got tired, after the completion of its work, it relaxed, since its further work is not required.
2) Weakened muscle (hypotonicity): does not work for some reason. Making it work at first is extremely difficult, all exercises feel very difficult and nasty (typical exercises for training the thoracic spine). Usually it is not felt in any way, as if it, in principle, is not in the body.
Mindful muscle relaxation:
We can adjust the speed of relaxation - in dance or in special slow exercises (Pilates, etc.) We can also consciously relax something that is chronically tense - for some this can be difficult, and this needs to be learned.
Tension
Rigid muscle contracted to perform some action. The greater the tension, the shorter and stiffer the muscle becomes. Tension can be dynamic (tightened up, performed an action - relaxed) and static (loads to hold a certain position, move a fixed support, etc.). Figuratively, tension can be compared to a spring compressed before a shot. After the shot, the spring should relax and return to its normal physiological state - relaxed, not compressed and not stretched. If this does not happen, then there is a dysfunction (hypertonicity) that must be dealt with, otherwise it will contribute to the development of more serious problems.
If this does not happen, then there is a dysfunction (hypertonicity) that must be dealt with, otherwise it will contribute to the development of more serious problems.
Unconscious muscle tension:
1) Healthy muscle: our nervous system controls the tension itself to perform any action (jump, bend, run, squat) - we do not need to think about the tension of all the necessary muscles in order to move It happened.
2) Muscle in hypertonicity: chronically tense, while not performing any action (lower back, upper trapezius, postural muscles of the spine). Rigid, immobile. At best, we feel its tension, stiffness, sometimes pain, we want to stretch and relax it. At worst, we live with this tension and are not aware of it until it leads to further problems. Here you need to spend extra time on learning to notice your tension, and then this will allow you to continue working on the problem. Chronic tension leads to infringement of nerve endings, to poor blood supply to muscles, connective tissues, internal organs, to the development of osteochondrosis, protrusions and diseases of the joints, to stretching of the tendons. I’ll tell you about the causes of chronic stress another time, I’ll tell you the great Secret ;))))
I’ll tell you about the causes of chronic stress another time, I’ll tell you the great Secret ;))))
Conscious muscle tension:
This is when we consciously perform any movements or exercises, tracking the technique and condition of our muscles. A necessary stage in order to develop muscle memory in oneself and then move correctly already unconsciously.
Traction
An elongated muscle that is in moderate tone and maintains this condition for some time. Not over-relaxed and not over-stressed. It can be compared to a stretched string or a bowstring. An important condition necessary for the correct execution of many movements, maintaining balance, for the health of the spine, and even just for plastic surgery. You need to learn how to move forward. If a person does not know how to do this, then he will perform all movements through tension, because he cannot do otherwise. Then his body will be rigid, movements angular and sharp. If you are not completely sure that you understand the essence of stretching and do not know for sure whether you can do it, then you do not know how. When you master stretching, there is no doubt what it is and how to do it. This is a real physical sensation that you cannot confuse with something else.
When you master stretching, there is no doubt what it is and how to do it. This is a real physical sensation that you cannot confuse with something else.
Unconscious stretching : yawned, stretched.
Conscious stretching: intentionally stretching our body in exercises, in dance. Ballet, Pilates, yoga will help you.
For harmonious control of one's body and technical dance it is important to be able to control all three states, switch them, combine several states at the same time.
Structure as a combination of states of muscle tone
In the dance there is a constant alternation of these states. Usually everything is built on traction. This allows you to keep a good balance, makes movements soft, flexible and strong at the same time, protects the joints from compression. By the way, all joint gymnastics and all Pilates are performed in traction.
In Zouk (with proper technique) we clearly see the constant alternation of stretching and relaxation. The same thing happens in contemporary and jazz-modern. In ballet, ballroom and more static styles, there is much less relaxation, and all movements are done on the stretch of the body, arms and legs. In contact improvisation and qigong, on the contrary, there is much more relaxation. But tension in all dances and many bodily practices is present only occasionally when performing some more complex elements and tricks: jumps, lifts, squats. If you are constantly tense in the dance, then you are clearly doing something wrong. Tension is the essence of strength training, not dance.
The same thing happens in contemporary and jazz-modern. In ballet, ballroom and more static styles, there is much less relaxation, and all movements are done on the stretch of the body, arms and legs. In contact improvisation and qigong, on the contrary, there is much more relaxation. But tension in all dances and many bodily practices is present only occasionally when performing some more complex elements and tricks: jumps, lifts, squats. If you are constantly tense in the dance, then you are clearly doing something wrong. Tension is the essence of strength training, not dance.
I think you yourself understand that in dance there will rarely be tension or relaxation in the whole body at once. Tension - in general, still happens - in ballet, etc. But complete relaxation can only be in contact improvisation, when we completely give our weight to the floor or partner. However, the zouk appears to be a very relaxed dance. Why?
In fact, in dance there is a simultaneous combination of states in constant dynamics. In Zouk, the most important thing is to stretch the body and relax the shoulder girdle. This is what allows you to make movements so plastic and flying. Only with a relaxed chest and a relaxed top of the trapezoid will it be possible to make beautiful, soft bones, waves, headworks, and so on. To prevent the body from falling apart and losing balance from this relaxation, the taut structure must be maintained in the center. If your center is something else (jelly or one big strain), then you will not have the physical ability to normally relax the top, and then you will move through tension in the chest, shoulders and neck. Visually, it may even seem flexible and beautiful, but physically you get very tired and feel badly leading / following a partner through your tension. In addition, this tension indicates the absence of a frame.
In Zouk, the most important thing is to stretch the body and relax the shoulder girdle. This is what allows you to make movements so plastic and flying. Only with a relaxed chest and a relaxed top of the trapezoid will it be possible to make beautiful, soft bones, waves, headworks, and so on. To prevent the body from falling apart and losing balance from this relaxation, the taut structure must be maintained in the center. If your center is something else (jelly or one big strain), then you will not have the physical ability to normally relax the top, and then you will move through tension in the chest, shoulders and neck. Visually, it may even seem flexible and beautiful, but physically you get very tired and feel badly leading / following a partner through your tension. In addition, this tension indicates the absence of a frame.
Spoiler for the next article: if your shoulders rise, then you do not and cannot have a frame. If you are a partner, then you lead with your hands, if you are a partner, then following goes through guessing.
What about the legs? The legs should be soft, this is important for balance, for even distribution of the load throughout the body and for good depreciation - then it does not burden the joints. If the legs are too sluggish, tangled, or, on the contrary, too stiff, then they do not perform this function, and you get an increased load on the spine and knees, as well as a constant overstrain of the muscles of the body.
Let's get back to understanding structure. What will be the structure of the body in the dance?
The whole pattern of tension and relaxation.
Long spine, soft legs, light top is an example of structure. A tense wooden body is also a structure, just uncomfortable and non-functional. A weak center and raised shoulders are also structure. I perceive the structure as a set of different materials and qualities of these materials, from which the building of our body and our dance is built. One builds with rubber bands and strong flexible bases, the other with cardboard and snot.
FRAME is also a structure. And in different styles of dance, the structure of the frame is different. The position of the hands, the degree of tension, the manner of touching, the tone of the shoulders, and so on - all this matters.
Grounding and overestimation of the center are also nuances of the structure. In some dances we gravitate more towards the floor (west coast, contempo, improvisation), in some we rush upwards more (ballet, lambazook). Zouk, in my opinion, is universal and allows you to play with the height of the center, which, in turn, will affect the manner of movements and the nature of the interaction of partners. The height of the center will depend on the height of the frame, on the degree of relaxation, on the structure of the bodies of both partners, and on each specific movement and point of contact. Even from shoes. Like it or not, heeled shoes raise the center higher.
Structure and interaction of partners
Rigid body poorly transmits movement and impulses. A tense partner will feel badly leading. A tense partner will lead the partner at the “volume level” available to him, conditionally, yell in her ear. Even if it is a very soft, sensitive partner. He cannot be quieter, simply because then he himself will not hear his words. He does not realize that "quieter" exists, and that this is actually the norm, and not a whim of a partner ("how picky you are"). For him, the norm is to yell in the ear. That's where the problem is.
A tense partner will feel badly leading. A tense partner will lead the partner at the “volume level” available to him, conditionally, yell in her ear. Even if it is a very soft, sensitive partner. He cannot be quieter, simply because then he himself will not hear his words. He does not realize that "quieter" exists, and that this is actually the norm, and not a whim of a partner ("how picky you are"). For him, the norm is to yell in the ear. That's where the problem is.
An over-relaxed, shapeless structure also distorts the interaction, the movement loses control and manageability. In this state, it is easy to get injured, sprained by negligence and inattention.
Only the state of soft tone on the stretch makes the dance sensitive, pleasant and well controlled.
If we imagine the interaction of partners as a pair structure, then it is also heterogeneous. In an interesting dance, this structure will change: it will become softer or denser, tighter or more airy from movement to movement, depending on what is happening in the dance, on the music and the feelings of the partners. Contrabalances and supports require more stretch and tone. Fingertip contact requires a subtle air pull (in the tooth), which can then go into counterbalance or support. Bodyworks can be very soft and gentle or active and rhythmic. A good dancer is not subject to the same structure (because he doesn't know how to do it differently), he manages his own structure as an artist. This makes the dances exciting, expressive and different from each other, perfectly keeps the attention of the dancers in sensitive contact with each other.
Contrabalances and supports require more stretch and tone. Fingertip contact requires a subtle air pull (in the tooth), which can then go into counterbalance or support. Bodyworks can be very soft and gentle or active and rhythmic. A good dancer is not subject to the same structure (because he doesn't know how to do it differently), he manages his own structure as an artist. This makes the dances exciting, expressive and different from each other, perfectly keeps the attention of the dancers in sensitive contact with each other.
An example of playing with structure in a dance. If you want a deeper understanding of what I'm writing about here, find moments in the video where relaxation, grounding, stretching up and to the side, interaction with the partner's weight, changing dynamics are used. Think about where Anderson and Brenda use their core muscles to move, and where they relax and give their body to gravity and momentum.
Structure and internal state
The structure of your body, the nature of movement and the internal state are closely interconnected and mutually influence each other. Your mood and mental characteristics affect the structure of your body both at the moment and in general (psychosomatics), which in turn affects how you dance and how you want to move. From the dance and movement of a person, you can tell a lot about him and his model of interaction with the world. And, on the other hand, work on the manner of movement, relaxation and stretching exercises will affect your mental state and mood, can even lift layers of old traumas and memories and serve as light therapy for the experience, and this will change the way you feel, how you move and what decisions you make. This is the basis of body-oriented and dance-movement psychotherapy.
Your mood and mental characteristics affect the structure of your body both at the moment and in general (psychosomatics), which in turn affects how you dance and how you want to move. From the dance and movement of a person, you can tell a lot about him and his model of interaction with the world. And, on the other hand, work on the manner of movement, relaxation and stretching exercises will affect your mental state and mood, can even lift layers of old traumas and memories and serve as light therapy for the experience, and this will change the way you feel, how you move and what decisions you make. This is the basis of body-oriented and dance-movement psychotherapy.
This is where I wrap up today. To begin with, I wanted to convey a general idea of \u200b\u200bthe structure and its influence on movement. Think about what structure you usually dance with, do you know how to manage it? What works and what doesn't and why, in your opinion? Have you noticed how your structure changes with your mood?
Next time I will share the knowledge about the structural relationships in our body, which I received only in instructor courses.