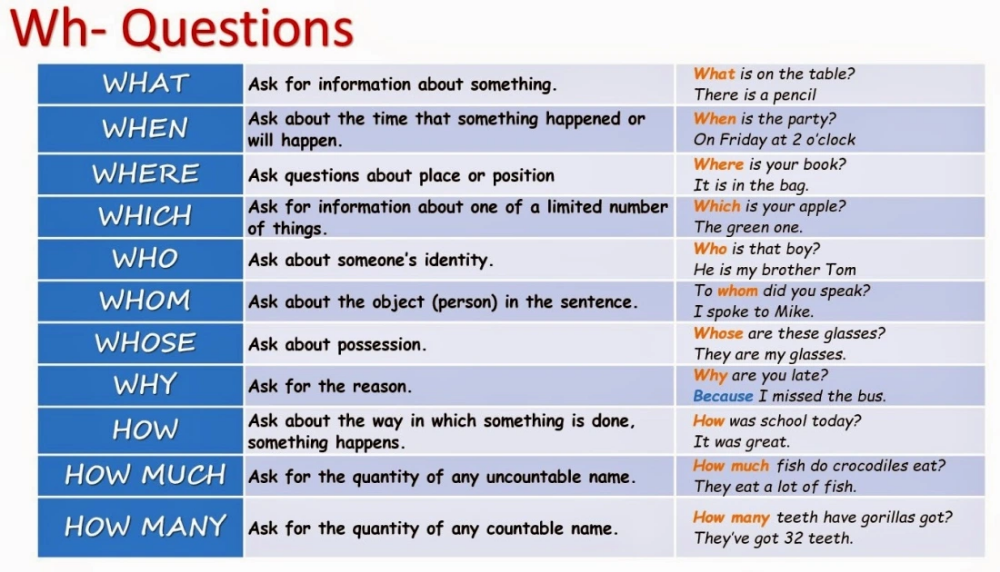
How to do the terminal reaction dance
CopperKnob - Terminal Reaction - Ray Boyd & Tony C
Transcribed by: Terence Ng
Phrasing: ABC AC*TagA
Intro: 18 Counts (Dance begins on lyrics, "I got money...")
Part A (102 Counts)
A [1 - 8] WEAVE R, L KNEE LIFTS, L TOE TOUCH, SLIDE L, R TOE TAP IN-OUT, HOLD, R TOE TAP, R STEP
1&2&Cross L over R, step R to the right, cross L behind R, step R to the right
3&4&Lift L knee up and touch L foot down, lift L knee up and touch L foot down
5&6Slide L to the left, touch R toe to L foot, touch R toe out to the right
7&8Hold, Touch R toe to L foot, step R foot to the right, taking weight
A [9 - 16] WEAVE R, L KNEE LIFTS, L TOE TOUCH, SLIDE L, R TOE TAPS, R KNEE LIFT
1&2&Cross L over R, step R to the right, cross L behind R, step R to the right
3&4&Lift L knee up and touch L foot down, lift L knee up and touch L foot down
5&6&Slide L to the left, touch R toe to L foot, touch R toe out to the right, touch R toe to L foot
7&8Touch R toe out to the right, touch R toe to L foot, lift R knee up
A [17 - 24] BACK ROCK RECOVER, SWEEP, ¼ TURN L W/R HITCH, FORWARD STEP, ROCKING CHAIR, ½ PIVOT, MAMBO
&1, 2&Step R back, recover onto L while sweeping R toe back and around into a ¼ turn left (9:00), hitching R knee up, step R forward
3&4&Rock forward on L, recover onto R, rock back on L, recover onto R
5, 6Step L forward, pivoting ½ turn right (3:00), transferring weight onto R
7&8Rock forward on L, recover onto R, step L together with R
A [25 - 32] L PUSH W/ L ½ SPIN, HITCH L, R PUSH W/ R ½ SPIN, HITCH R, L TOE POINT-HITCH, R TOE POINT-HITCH
&1, 2Step onto ball of R foot, step L down and push back, spinning ½ left on R (9:00), hitch L
&3, 4Step L down, step R down and push back, spinning ½ right on L (3:00), hitch R
&5, 6Step R down, point L toe to the left, hitch L knee
&7, 8Step L down, point R toe to the right, hitch R knee
A [33 - 40] BACK DIAGONAL SLIDE L, BACK LOCK STEP, BACK DIAGONAL SLIDE R, COASTER STOMP, HITCH-STOMP-HITCH
&1, 2&Step R down, take large left diagonal slide back with L, cross R behind L, lock L over R
3, 4&Take large right diagonal slide back with R, step L back, step R forward
5, 6Stomp L forward leaning body forward, hitch L, bringing body back up
7, 8Stomp L forward leaning body forward, hitch L, bringing body back up
A [41 - 48] L FORWARD SHUFFLES, L STOMP, HITCH STEPS BACK, L TOE POINT, ½ TURN L
1&2&Step L forward, step R forward to meet L, step L forward, step R forward to meet L
3&4Step L forward, step R forward to meet L, stomp L forward
5&6&Hitch L knee up, step L back, hitch R knee up, step R back
7, 8Point L toe back, ½ turn over L shoulder (9:00), sitting weight back onto R
A [49 - 56] HITCH STEPS BACK, L TOE POINT, ½ TURN L, REPEAT
1&2&Hitch L knee up, step L back, hitch R knee up, step R back
3, 4Point L toe back, ½ turn over L shoulder (3:00), sitting weight back onto R
5&6&Hitch L knee up, step L back, hitch R knee up, step R back
7, 8Point L toe back, ½ turn over L shoulder (9:00), sitting weight back onto R
A [57 - 64] HITCH STEPS BACK, L KICK BALL CHANGE
1&2&Hitch L knee up, step L back, hitch R knee up, step R back
3&4&Repeat
5&6&Repeat
7&8Kick L forward, bringing L back and taking weight while raising R, step R down
[65 - 72] L RUN, R TOE TOUCH, R HEEL TOUCH, R TOE TOUCH, STEP R, L CHASSE, R CHASSE
1&2(Small steps) Step L forward, R forward, L forward
&3&4Touch R toe next to L, touch R heel forward, touch R toe to L, step R to the right
5&6Step L to the left, step R together, step L to the left
7&8Step R to the right, step L together, step R to the right
A [73 - 80] REPEAT COUNTS [65 - 72]
A [81 - 88] L TRAVELING SHUFFLE W/ CLAPS, ¼ TURN L, KICKS, CROSS
1&2&Step L to the left while raising R hand, step R toward L, step L to the left while swinging R hand down to clap with L hand, step R toward L
3&4Step L to the left while raising R hand, step R toward L, step L to the left while swinging R hand down to clap with L hand
&5&6Step R forward into ¼ turn left (6:00), kick L heel out, bring L heel in, kick R heel out
&7&8Bring R heel in, kick L heel out, bring L heel in, cross R over L
A [89 - 96] REPEAT COUNTS [81 - 88] (ending facing 3:00)
A [97 - 102] L STOMP, HOLD, ¼ TURN BALL CROSS, L SLIDE, R STOMPS, L KICKS
1, 2Stomp L to left side, hold
&3, 4Quickly shift weight to R ball of foot while rocking L back with a ¼ turn left (12:00), and crossing R over L, slide L to the left dragging R together
5&6Hold, Stomp R twice, taking weight on the second stomp
Part B (56 Counts)
B [1 - 8] L KICKS, R KICKS, L KICK, L TOE TOUCH, R KICK, R TOE TOUCH
1&2&Kick L heel out, bring L toe in, kick L heel out, bring L in taking weight
3&4&Kick R heel out, bring R toe in, kick R heel out, bring R in taking weight
5&6&Kick L heel out, bring L toe in, point L toe to the left, bring L in taking weight
7&8&Kick R heel out, bring R toe in, point R toe to the right, bring R in taking weight
B [9 - 16] TOE TOUCHES, L TOE TOUCH, L HEEL TOUCH, BALL-DRAG, R HITCHES
1&2&Point L toe to the left, bring L in taking weight, point R toe to the right, bring R in taking weight
3&4Point L toe to the left, bring L in, touch L heel forward
&5, 6Quickly bring L in taking weight while sending R out to the right, slowly drag R in together over counts 5 - 6
7&8&Hitch R knee, touch R down, repeat
B [17 - 24] HITCH CROSS, SHOULDER SWITCHES, L ROCK RECOVER CROSS, R ROCK RECOVER CROSS
1, 2Hitch R knee, cross R over L
3&4&Holding in place, alternate R shoulder up, L shoulder up, repeat
5&6Rock L out to the left, recover onto R, cross L over R
7&8Rock R out to the right, recover onto L, cross R over L
B [25 - 32] ¾ UNWIND L, BALL CROSS, ½ UNWIND TURN L, L APPLEJACKS, R KICKS
1, 2Bounce while turning ½ turn left to unwind (6:00), bounce ¼ turn left (3:00)
&3, 4Quickly rock back on L ball of foot, cross R over L, ½ unwind turn left (9:00)
&5&6With weight on L heel and R toe, swivel L toe and R heel toward the left, return feet to center, repeat
7, 8Kick R heel forward twice
B [33 - 40] R STOMPS, SWEEPING ¼ TURN, R FORWARD, L TOE TOUCH, L BACK, R BACK, L FORWARD TAPS
1, 2Stomp R forward twice
&3, 4Shift weight to L and sweep ball of R foot around and back into ¼ turn right, placing R next to L over counts 3 - 4 (12:00)
5&6Step R forward rocking hips forward, touch L behind R, step L back
7&8Step R back, tap L foot forward twice
B [41 - 48] ½ PADDLE TURN L, L FORWARD, R TOE TOUCH, R BACK, L BACK, R FORWARD TAPS
1, 2Take weight on L and keep L stationary and push off of R foot two times, turning ⅛ left each time (9:00)
3, 4Continue pushing off R foot two more times, turning ⅛ left each time (6:00)
5&6Step L forward rocking hips forward, touch R behind L, step R back
7&8Step L back, tap R foot forward twice
B [49 - 56] ½ PADDLE TURN R
1, 2Take weight on R and keep R stationary and push off of L foot two times, turning 1/16th R each time (7:30)
3, 4Continue pushing off L foot two more times, turning 1/16th R each time (9:00)
5, 6Repeat [Counts 3 - 4] (10:30)
7, 8Repeat [Counts 3 - 4] (12:00)
Part C (66 Counts)
C [1 - 8] L KICKS, R KICKS, L KICK, L TOE TOUCH, R KICK, R TOE TOUCH
1&2&Kick L heel out, bring L toe in, kick L heel out, bring L in taking weight
3&4&Kick R heel out, bring R toe in, kick R heel out, bring R in taking weight
5&6&Kick L heel out, bring L toe in, point L toe to the left, bring L in taking weight
7&8&Kick R heel out, bring R toe in, point R toe to the right, bring R in taking weight
C [9 - 16] TOE TOUCHES, L TOE TOUCH, L HEEL TOUCH, R TOE TOUCHES, SHOULDER SWITCHES
1&2&Point L toe to the left, bring L in taking weight, point R toe to the right, bring R in taking weight
3&4&Point L toe to the left, bring L in, touch L heel forward, bring L in taking weight
5&6Tap R toe out to the right, tap in front, tap crossing R over L, taking weight on R
7&8&Holding in place, alternate R shoulder up, L shoulder up, repeat
C [17 - 24] L ROCK RECOVER CROSS, R ROCK RECOVER CROSS, ¾ UNWIND L, BALL CROSS, ½ UNWIND, TURN L
1&2Rock L out to the left, recover onto R, cross L over R
3&4Rock R out to the right, recover onto L, cross R over L
5, 6Bounce while turning ½ turn left to unwind (6:00), bounce ¼ turn left (3:00)
&7, 8Quickly rock back on L ball of foot, cross R over L, ½ unwind turn left (9:00)
C [25 - 32] L APPLEJACKS, R KICKS, R STOMPS, SWEEPING ¼ TURN
&1&2With weight on L heel and R toe, swivel L toe and R heel toward the left, return feet to center, repeat
3, 4Kick R heel forward twice
5, 6Stomp R forward twice
&7, 8Shift weight to L and sweep ball of R foot back and around into ¼ turn right (12:00), placing R next to L over counts 7 - 8
C [33 - 40] R FORWARD, L TOE TOUCH, L BACK, R BACK, L FORWARD TAPS, ½ PADDLE TURN L
1&2Step R forward rocking hips forward, touch L behind R, step L back
3&4Step R back, tap L foot forward twice
5, 6Take weight on L and keep L stationary and push off of R foot two times, turning ⅛ left each time (9:00)
7, 8Continue pushing off R foot two more times, turning ⅛ left each time (6:00)
C [41- 48] ½ PADDLE TURN R, BODY ROLLS
1, 2Take weight on R and keep R stationary and push off of L foot two times, turning ⅛ right each time (9:00)
3, 4Continue pushing off L foot two more times, turning ⅛ right each time (12:00)
5, 6Lean to the left looking right, stay squared to 12:00 and do body roll from right to left
7, 8Repeat body roll
C [49 - 56] BODY ROLLS, L FORWARD, R TOE TOUCH, R BACK, L BACK, R FORWARD TAPS
1, 2Lean to the right looking left, stay squared to 12:00 and do body roll from left to right
3, 4Repeat body roll
5&6Step L forward rocking hips forward, touch R behind L, step R back
7&8Step L back, tap R foot forward twice
C [57 - 64] FULL PADDLE R, BODY ROLL
1, 2Take weight on R and keep R stationary and push off of L foot two times, turning ¼ right each time (6:00)
3, 4Continue pushing off L foot two more times, turning ¼ right each time (12:00)
5, 6Lean to the left looking right, stay squared to 12:00 and do body roll from right to left
7, 8Repeat body roll
C [65 - 66] DIAGONAL LUNGE
1, 2Step R to right side diagonal (1:30) and lunge toward 1:30 on R, with L toe pointed and trailing behind, staying squared to 12:00
[Repeat Part A]
[Repeat Part C (for 40 Counts)]
[Tag]
[1 - 8] L FORWARD, R TOE TOUCH, R BACK, L BACK, R FORWARD TAPS, ¾ PADDLE R
1&2Step L forward rocking hips forward, touch R behind L, step R back
3&4Step L back, tap R foot forward twice
5, 6Take weight on R and keep R stationary and push off of L foot two times, turning 3/16ths left each time* (10:30)
7, 8Continue pushing off L foot two more times, turning 3/16ths left each time* (3:00)
[9 - 16] ¾ PADDLE R, SIDE TOUCHES
1, 2Continue pushing off L foot two more times, turning 3/16ths left each time* (7:30)
3, 4Continue pushing off L foot two more times, turning 3/16ths left each time* (12:00)
5&6&Step L out to the left, touch R to L, step R out to the right, touch L to R
7&8Step L out to the left, touch R to L, step R out to the right
[Repeat Part A until music ends]
Notes:
*Part C is a modified version of Part B with the following changes:
After B-[Count 12], an additional step is added to take weight on L and 3 R toe touches are added instead of the ball-drag and the dance skips immediately to B-[Count 19].
It proceeds as usual from B-[Counts 19 - 44], whereupon a new set of steps is added, ending on C-[Count 66].
Count numbering in Part C reflects the alteration caused by the change in steps, but C-[Counts 1 - 12] and [15 - 40] are the same as B-[Counts 1 - 12] and [19 - 44]
*The second time you do Part C, you only do 40 counts before doing the tag
*The final time you do Part A, you continue to dance it until the music ends, around A-[Count 64]
*The 3/16ths in the Tag may seem a little silly; essentially, you are dividing a 1½ turn evenly over 8 turns during 8 counts. 3/16ths is the even division, but do it however so long as you can go 1½ turns within the 8 turns/counts.
Last Update: 10 Nov. 2021
R&b Line Dance Songs | Popnable
Explore list of R&b Line Dance Songs. Discover music. R&b Line Dance Songs playlist.
Playlist created with sourceplcreated that lets you transfer your playlist to youtube from any.
Related to: songs Thursday, 29/12/2022, 2570 views
- 1. R&b Line Dance Songs 2019
- 2. R&b Line Dance Music
- 3. Popular R&b Line Dance Songs
- 4. Best R&b Line Dance Songs
- 5. 90S R&b Line Dance Songs
- 6. New R&b Line Dance Songs
- 7. Popular R&b Line Dance Songs 2018
- 8. R&b Hip Hop Line Dance Songs
- 9. Top 10 R&b Line Dance Songs
R&b Line Dance Songs 2019
Playlist created with sourceplcreated that lets you transfer your playlist to youtube from any.
2000s R&B Party Mix 🎊 Best R&B Dance Songs of the 2000s
Terminal Reaction
THE BIKERS SHUFFLE (MILWAUKEE VERSION)
R&B Talk Line Dance
OLD SCHOOL SUNDAY HIP HOP & R&B 803 316 4681
Muhneemix 2 - BEST MIX OF R&B SOUL DANCE FUNK FOR THE GYM ROAD TRIPS & COOKOUTS ( C. "Money" Rawlins
"Money" Rawlins
R&b Line Dance Music
Kenny J R&B Line Dance - Go Hard or Go Home
Drippin' Finesse Line Dance
DJ SkyWalker #27 | Old School Mix | R&B Hip Hop Classics | 90s 2000s Black Music Rap Songs
Best R&B Songs 2021 Doja Cat, Justin Bieber, Giveon, Bruno Mars, Pink Sweat$, The Weeknd, Khalid
r&b / hip-hop radio - chill live stream - 24/7 rnb
R&B and Deandre - Hip Hop Police Dance
Popular R&b Line Dance Songs
Can’t Get Enough Line Dance | Tamia | TMichelle Line Dance
💜💜STEADY LOVE LINE DANCE - NOLA💜💜
Soulful R&B Funky Disco House Mix (OLD SCHOOL)
★ R&B Cha ★Line Dance: Choreographer Unknown
Virtual Line Dancing with Kenny J: Beginners R&B/Soul Line Dancing 03. 30.2020
30.2020
Saturday Nights - Pop R&B Chill music mix - Khalid, Justin Bieber, Ali Gatie
Best R&b Line Dance Songs
Blurred Lines Line Dance
FROM R&B WITH LOVE - line dance
OLD SCHOOL POP & R&B (2000 - 2005) - DJ KENB [NELLY,KELLY ROWLAND, ASHANTI,DESTINY'S CHILD, BRITNEY]
2000s Hip Hop RnB Mashup | #1 | Best of R&B Hip Hop Party Mix
LDFF Class - R&B Hustle
Old School 2000's R&B Mix / Best Of 2000's R&B (by @DJDAYDAY_)
90S R&b Line Dance Songs
Beyoncé Before I Let Go Dance Challenge (Homecoming Live) Line Dance
The Line Dance Connection - Tucker
FAMILY DANCE MIX VOL. 1 & 2 ( LINE DANCE MUSIC ) R&B AND HIP-HOP
1 & 2 ( LINE DANCE MUSIC ) R&B AND HIP-HOP
Baby Shark (R&B Remix)
Various – Modernists - Modernism's Sharpest Cuts : 60's Mod R&B Soul Dance Music Songs Compilation
Playlist of songs that'll make you dance ~ Feeling good playlist ~ Songs to play in the party
New R&b Line Dance Songs
The New Easy Line Dance for 2020 "Backyard Sway" tutorial!
Come On! Merry Christmas Line Dance
Aretha, Queen of Soul (R&B Line Dance) - Dance & Teach
U4RIA HIP HOP DANCE- Chris Brown- Deuces
Best R&B Soul Playlist Mix - Chill Vibe
Popular R&b Line Dance Songs 2018
*NEW* Chris Brown- Fine China Line Dance
10 MIN R&B DANCE WORKOUT - a little sexy, a little gangster & for sure SWEATY! / Pamela Reif
R&B HIP HOP POLICE CHAMILLIONAIRE CHOREOGRAFI (DANCE#SENAM BY KAORIDILA)
WIZ KID | 2 Hours of Chill Songs | Afrobeats/R&B MUSIC PLAYLIST | Starboy
R&B Could It Be (This Could Be Love) Line Dance
R&b Hip Hop Line Dance Songs
Don’t Waste My Time Line Dance
SWMGA "BoxTrot" Line Dance (R&B Line Dance Movement)
One Night In Bangkok - FULL HD - REMIX DJ R&B
R&B CHA CHA LINE DANCE!!!
Top 10 R&b Line Dance Songs
Good Lovin Line Dance (Song change) R&B Groove!
80's R&B Soul Groove - Chaka Khan, Marvin Gaye, Al Green , Phylis Hyman, Ray Charles, Frank Sinatra
★ R&B Cha ★ Line Dance by Marva Black
Oldschool 2000s 90s Hip Hop R&B Classics Throwback Best Club Music Mix | DJ SkyWalker
R&B MASH UP MIX 2019
Popnable /Popnable Media
16.
 4. Mental disorders of an infectious nature
4. Mental disorders of an infectious nature Mental disorders can lead almost any brain and general infectious processes. Although for each of diseases, a number of characteristic manifestations and a special type of flow, It should be noted that the main set mental manifestations in general corresponds to the concept described above exogenous reactions. Specificity each individual infection is determined speed of progression, severity associated signs of intoxication (increase in body temperature, vascular permeability, tissue edema), direct involvement meninges and structures of the brain in pathological process. nine0003
The most well-studied manifestations syphilitic brain infection.
16.4.1. Neurosyphilis [A52.1, F02.8]
It should be noted that syphilitic psychoses are optional manifestation of chronic syphilitic infections. Even in the last century, when effective treatments for syphilis did not exist, syphilitic psychoses developed in only 5% of all infected. Usually psychiatric disorders occur quite late (after 4-15 years after initial infection), so timely data diagnostics disease is a significant difficulties. As a rule, the patient himself his relatives do not report past infection and quite often do not know that such an infection had place. There are 2 main forms syphilitic psychoses: brain syphilis and progressive paralysis. nine0003
Usually psychiatric disorders occur quite late (after 4-15 years after initial infection), so timely data diagnostics disease is a significant difficulties. As a rule, the patient himself his relatives do not report past infection and quite often do not know that such an infection had place. There are 2 main forms syphilitic psychoses: brain syphilis and progressive paralysis. nine0003
Syphilis brain (luescerebri) - specific inflammatory disease with predominant vascular disease and membranes of the brain. The sickness begins usually somewhat earlier than progressive paralysis, - 4-6 years after infections. Diffuse character brain damage corresponds to extremely polymorphic symptoms resembling non-specific vascular diseases, described in the previous section. The onset of the disease is gradual an increase in neurosis-like symptoms: fatigue, memory loss, irritability. However, compared with atherosclerosis turn on themselves attention relatively early start disease and faster progression without typical vascular disorders "flickering" symptoms. Characteristically early occurrence of seizures cerebral circulation. Although each from apoplexy episodes culminate in some improvement state and partial restoration lost functions (paresis, disorders speech), but soon there are repeated hemorrhages and rapidly developing picture of lacunar dementia. On different stages of manifestation of organic brain lesions may be Korsakov's syndrome, epileptiform seizures, long-term depressive states and psychoses with delusional and hallucinatory symptoms. plot delusions are usually ideas of persecution and jealousy, hypochondriacal delusions. hallucinosis (often auditory) threatening and accusatory statements. At an advanced stage of the disease, observed individual catatonic symptoms (negativism, stereotypes, impulsiveness). nine0003
Characteristically early occurrence of seizures cerebral circulation. Although each from apoplexy episodes culminate in some improvement state and partial restoration lost functions (paresis, disorders speech), but soon there are repeated hemorrhages and rapidly developing picture of lacunar dementia. On different stages of manifestation of organic brain lesions may be Korsakov's syndrome, epileptiform seizures, long-term depressive states and psychoses with delusional and hallucinatory symptoms. plot delusions are usually ideas of persecution and jealousy, hypochondriacal delusions. hallucinosis (often auditory) threatening and accusatory statements. At an advanced stage of the disease, observed individual catatonic symptoms (negativism, stereotypes, impulsiveness). nine0003
Almost always found diffuse nonspecific neurological symptomatology with asymmetric disturbances motility and sensitivity, anisocoria, pupillary irregularity, decreased their reactions to light. In diagnostics The main symptom of syphilis is positive serological tests (Wasserman reaction, RIF, RIBT). Wherein with syphilis of the brain, in contrast to progressive paralysis can more often see negative results blood samples. In this case, you should reactions with cerebrospinal fluid. When puncturing, you can find and other characteristic colloidal reactions (see section 2.2.4), in particular the specific "syphilitic prong" in the reaction Lange. nine0003
In diagnostics The main symptom of syphilis is positive serological tests (Wasserman reaction, RIF, RIBT). Wherein with syphilis of the brain, in contrast to progressive paralysis can more often see negative results blood samples. In this case, you should reactions with cerebrospinal fluid. When puncturing, you can find and other characteristic colloidal reactions (see section 2.2.4), in particular the specific "syphilitic prong" in the reaction Lange. nine0003
The course of syphilis of the brain is slow, mental disorders may increase for several years and even decades. Sometimes there is a sudden death after another stroke. Timely started specific treatment can not only stop disease progression, but be accompanied by a partial reverse the development of symptoms. On the later stages there is a persistent mental defect in the form of a lacunar (later total dementia.
Progressive paralysis (Bayle's disease, paralysis progressiva afenorum) - syphilitic severe meningoencephalitis intellectual-mnestic functions and various neurological symptoms. The difference of this disease is directly damage to the brain substance, accompanied by multiple withdrawal symptoms mental functions. Clinical manifestations of the disease have been described by A.JT. J. Baylem in 1822. Although in course of the 20th century repeatedly expressed assumption of a syphilitic nature this disease, directly detect spirochete pallidum in the brain patients succeeded only in 1911 year Japanese researcher H. Noguchi.
The difference of this disease is directly damage to the brain substance, accompanied by multiple withdrawal symptoms mental functions. Clinical manifestations of the disease have been described by A.JT. J. Baylem in 1822. Although in course of the 20th century repeatedly expressed assumption of a syphilitic nature this disease, directly detect spirochete pallidum in the brain patients succeeded only in 1911 year Japanese researcher H. Noguchi.
The disease occurs against the background of complete health 10-15 years after primary infections. The first sign of the beginning disease is non-specific pseudoneurasthenic symptoms in the form of irritability, fatigue, tearfulness, sleep disturbances. Careful examination allows already in this phase diseases to detect some neurological signs of illness (impaired pupillary response to light, anisocoria) and serological tests. Draws special attention behavior of patients with reduced criticism and inadequate attitude to existing violations. nine0003
nine0003
Quite quickly, the disease reaches full bloom phase. occasionally transition to this phase is accompanied by transient psychotic episodes with confusion consciousness, disorientation or delirium persecution. Main manifestation diseases at this stage are gross changes personality by organic type with loss criticism, absurdity, underestimation situations. Behavior is characterized disorder, on those around the patient makes an impression dissolved. It seems that a person acts in a state of intoxication. He leaves home, spends money thoughtlessly, loses them, leaves things anywhere. Often the patient starts random dating, getting in touch, often becomes a victim of dishonesty your friends, because it is different amazing gullibility and suggestibility. Patients do not notice a mess in clothes, can leave the house half-dressed. nine0003
The main content of the disease is severe mental disorder ( total dementia), with permanent the growth of intellectual-mnestic disorders. At first, it may no gross violation memorization, however, with aiming assessment of abstract thinking there is a lack of understanding essence of tasks, superficiality in judgments. However, patients never notice the mistakes they have made, benevolent, not embarrassed by others, strive demonstrate your abilities try to sing, dance. nine0003
At first, it may no gross violation memorization, however, with aiming assessment of abstract thinking there is a lack of understanding essence of tasks, superficiality in judgments. However, patients never notice the mistakes they have made, benevolent, not embarrassed by others, strive demonstrate your abilities try to sing, dance. nine0003
The typical manifestations described above diseases may be accompanied some optional symptoms, defining individual characteristics every patient. More often in the last century other disorders met delirium greatness with absurd ideas of the material wealth. In this case, always surprise grandiosity and apparent senselessness boasting of the sick. The patient is not only promises to make everyone around expensive gifts, but wants to "shower them diamonds", claims that he has “At home there are 500 boxes under the bed gold." A similar version of the progressive paralysis is indicated as expansive form. B In recent years, it has been found significantly less common - in 70% of cases observed predominance of intellectual disorders in the clinical picture without concomitant mood disorders ( dement- naya form). Quite rare there are variants of the disease with a decrease moods, ideas of self-abasement and hypochondriacal delirium ( depressive form) or distinct ideas of persecution and individual hallucinations ( paranoid form).
Quite rare there are variants of the disease with a decrease moods, ideas of self-abasement and hypochondriacal delirium ( depressive form) or distinct ideas of persecution and individual hallucinations ( paranoid form).
A variety of neurological symptoms. Almost always found Argyle Robertson's symptom (lack of pupillary response to light while maintaining reactions to convergence and accommodation). Quite often the pupils are narrow (like a pin prick), sometimes there is anisocoria or deformity pupils, decreased vision. Many patients have dysarthria. Often other disorders are observed speech (nasal, logoclonia, chanted speech). Asymmetry of the nasolabial folds, paresis of the facial nerve, masculinity face, tongue deviation, twitching facial muscles are optional symptoms, but may be observed. At letter is found to be a violation handwriting and rough spelling errors (omissions and repetition of letters). There is often asymmetry tendon reflexes, decreased or no knee or Achilles reflexes.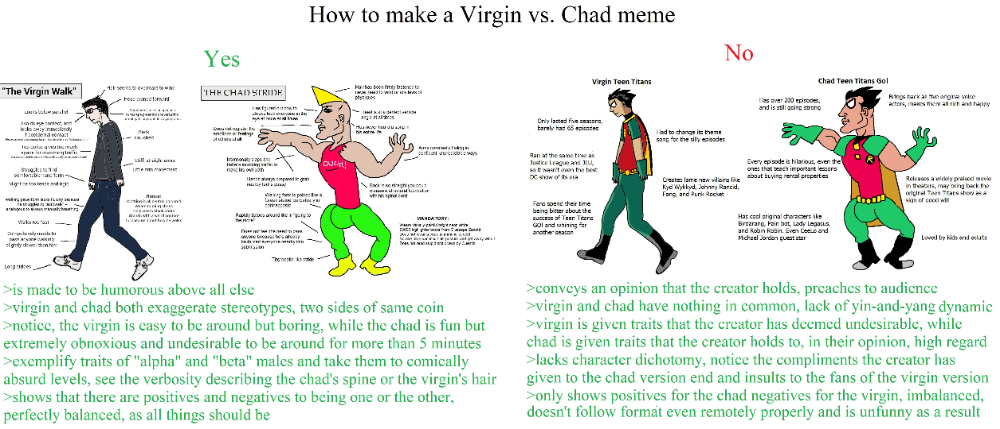 In the later stages of the course diseases often occur epileptiform seizures. Describe special forms of the disease with a predominance focal neurological symptoms: taboparalysis - combination dementia with manifestations of the dorsal tabes dorsalis is manifested by a violation of the superficial and deep sensitivity and disappearance tendon reflexes in the lower limbs combined with shooting pain), lissauer form - focal loss of mental functions with predominance of aphasia and apraxia.
In the later stages of the course diseases often occur epileptiform seizures. Describe special forms of the disease with a predominance focal neurological symptoms: taboparalysis - combination dementia with manifestations of the dorsal tabes dorsalis is manifested by a violation of the superficial and deep sensitivity and disappearance tendon reflexes in the lower limbs combined with shooting pain), lissauer form - focal loss of mental functions with predominance of aphasia and apraxia.
sick 45 years old, deputy director of a large department store, was sent to psychiatric clinic for misbehavior and helplessness at work. nine0003
Heredity not weighed down. The patient is the older of the two daughters. The patient's mother is healthy, father died of a heart attack. In childhood developed normally. Graduated from school and Institute of National Economy. Plekhanov. Always worked in trade was thoughtful and insight. Was not very beautiful, but possessed a light, mobile character, was a success with men. Married at 22 to a man who was 5 years older than her. Family life was going well. Has two sons. nine0003
Married at 22 to a man who was 5 years older than her. Family life was going well. Has two sons. nine0003
Approximately six months prior to present hospitalization became less diligent in work, a lot laughed. In the spring at the dacha there was an episode, when I couldn't sleep at night: I ran around home; didn't know where it was. In the morning, the husband asked the children to come. The patient did not recognize her eldest son, was afraid of him. Relatives turned to a private doctor. Treatment a number of drugs, including antibiotics.
State significantly improved: was completely oriented, tried to reach work. However, with their official did not cope, stupid joked, boasted to employees with their wealth. Once tried leave the house for work without wearing a skirt, did not react emotionally to the remark about this husband - just dressed appropriately. nine0003
At admission to the hospital does not show no complaints but also no objection hospitalizations. Names his own name, year of birth, but wrong when determining the present date. Does compliments to doctors, especially men. Looks at the interlocutor dressed in white coat, and can't identify it profession. Speaks indistinctly at times swallows individual syllables. laughing without hesitation declares that she is very rich: “I work in a store - whatever you want I can get. Money is trash." nine0003
Names his own name, year of birth, but wrong when determining the present date. Does compliments to doctors, especially men. Looks at the interlocutor dressed in white coat, and can't identify it profession. Speaks indistinctly at times swallows individual syllables. laughing without hesitation declares that she is very rich: “I work in a store - whatever you want I can get. Money is trash." nine0003
Allows gross errors in the simplest account, not can remember the name of the attending physician: "I'm so young charming young man serving. Writes without mistakes your name and address, however handwriting is unusual, with uneven pressure and crooked lines. characterizes himself as a cheerful, sociable person. Willingly sings songs, although not always can pronounce the words. Beats the beat palms, gets up, starts dancing.
Are celebrated miosis and lack of pupillary response to light. Tendon reflexes on the right and on the left are the same, the Achilles reflex is reduced at both sides.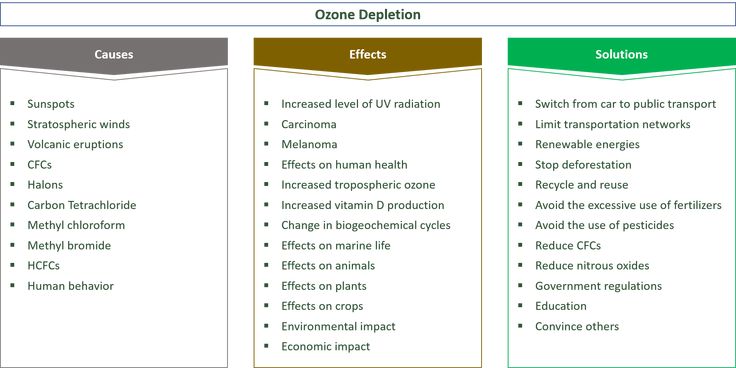 With laboratory examination revealed sharply positive wasserman reaction ("++++"), positive reactions RIF and RIBT. Liquor is transparent, its pressure is not increased, pleocytosis - 30 cells in 1 µl, globulin/albumin ratio — 1.0; Lange reaction - 4444332111111111.
With laboratory examination revealed sharply positive wasserman reaction ("++++"), positive reactions RIF and RIBT. Liquor is transparent, its pressure is not increased, pleocytosis - 30 cells in 1 µl, globulin/albumin ratio — 1.0; Lange reaction - 4444332111111111.
Conducted treatment with iodine salts, biyoquinol and penicillin. As a result of treatment became more calm, obedient, however significant improvement mnestic-intellectual processes was not observed. 2nd group completed disability.
Brightness mental and neurological disorders in typical cases progressive paralysis allows make a diagnosis of the disease clinical examination. However, in recent years have become more difficult for diagnosis of atypical cases diseases. In addition, due to the sharp reduce the incidence of this disease modern doctors do not always have enough clinical experience to detection. The most reliable method diagnostics are serological samples. Wassermann reaction at 95% of cases gives a sharply positive result; to rule out false positives cases always carry out RIF and RIBT. Although with a clear positive as a result of serological tests spinal puncture can be conduct, however, the study of liquor desirable as it allows check the level of activity painful process. Yes, for the presence inflammatory phenomena indicate an increase in the formed elements of the cerebrospinal fluid up to 100 in 1 µl, the predominance of globulin protein fractions, decolorization of colloidal gold in test tubes with the smallest dilution of cerebrospinal fluid ("paralytic type of curve" in the Lange reaction). nine0003
Although with a clear positive as a result of serological tests spinal puncture can be conduct, however, the study of liquor desirable as it allows check the level of activity painful process. Yes, for the presence inflammatory phenomena indicate an increase in the formed elements of the cerebrospinal fluid up to 100 in 1 µl, the predominance of globulin protein fractions, decolorization of colloidal gold in test tubes with the smallest dilution of cerebrospinal fluid ("paralytic type of curve" in the Lange reaction). nine0003
In the past century, the disease has been extremely malignant and most cases ended in death 3-8 years. In the terminal (senile) phase, gross violations were observed physiological functions (violation pelvic function, swallowing disorders and breathing), epileptic seizures, violation of tissue trophism (trophic leg ulcers, hair loss, bedsores). In recent years, timely treatment of the disease allows not only save the lives of the sick, but also in some cases to achieve a clear positive state dynamics. nine0003
nine0003
The treatment proposed at the beginning of the century progressive paralysis by vaccination malaria [Wagner-Yauregg Yu., 1917] in connection with introduction of antibiotics no longer applies. However, when antibiotic therapy should consider possible complications. So on late stages of syphilitic infections are very likely to occur gumm. In this case, antibiotics can lead to massive death pathogen and death as a result intoxication. Therefore, treatment is often start with the appointment of iodine preparations and bismuth. If you are allergic to means of the penicillin group prescribe erythromycin. Efficiency antibiotic therapy may be higher when combined with pyrotherapy. For correction of the behavior of patients is used mild neuroleptics. nine0003
16.4.2. Mental disorders in AIDS [F02.4]
The human immunodeficiency virus has pronounced tropism as to the lymphatic system and to the nervous tissue. Due with this mental disorder on different stages of the course of the disease observed in almost all patients. Quite difficult to differentiate disorders due to organic process, and mental psychogenic disorders, associated with the realization of the fact of incurable diseases.
Quite difficult to differentiate disorders due to organic process, and mental psychogenic disorders, associated with the realization of the fact of incurable diseases.
Mental disorders in AIDS in basically correspond to the reactions exogenous type. In the initial period persistent phenomena are often observed asthenia with a constant feeling of fatigue, excessive sweating, disorders sleep, loss of appetite. depression, melancholy, depression may occur before how the diagnosis is made. Changes personalities are growing irritability, irascibility, moodiness or disinhibition drives. Already at an early stage diseases often develop acute psychosis in the form of delirium, twilight confusion, hallucinosis, rarely acute paranoid psychosis, state of arousal with manic affect. Quite often there are epileptiform seizures. nine0003
Subsequently, quickly (within a few weeks or months) the negative symptoms of dementia. At 25% cases, signs of dementia are detected already in the initial phase of the disease. Symptoms of dementia are non-specific and depend on the nature of the brain process. With focal processes (cerebral lymphoma, hemorrhage) can be observed focal loss of individual functions (speech disorders, frontal symptoms, convulsive seizures, paresis and paralysis), diffuse lesion (diffuse sub- acute encephalitis, meningitis, cerebral arteritis) is manifested by a general increase passivity, lack of initiative, drowsiness, impaired attention, memory decline. Late stages disease, dementia reaches a degree total. Join violations pelvic organs functions, disorders respiration and cardiac activity. The cause of death in patients is usually intercurrent infections and malignant neoplasms. nine0003
Symptoms of dementia are non-specific and depend on the nature of the brain process. With focal processes (cerebral lymphoma, hemorrhage) can be observed focal loss of individual functions (speech disorders, frontal symptoms, convulsive seizures, paresis and paralysis), diffuse lesion (diffuse sub- acute encephalitis, meningitis, cerebral arteritis) is manifested by a general increase passivity, lack of initiative, drowsiness, impaired attention, memory decline. Late stages disease, dementia reaches a degree total. Join violations pelvic organs functions, disorders respiration and cardiac activity. The cause of death in patients is usually intercurrent infections and malignant neoplasms. nine0003
Organic mental disorders almost always accompanied psychologically understandable experiences sick. psychological reaction to the disease may manifest as clear depressive symptoms, and persistent denial of the fact diseases by type of defense mechanism (see section 1.1.4). Often patients require re-examination, blame doctors in incompetence, trying unleash your anger on others.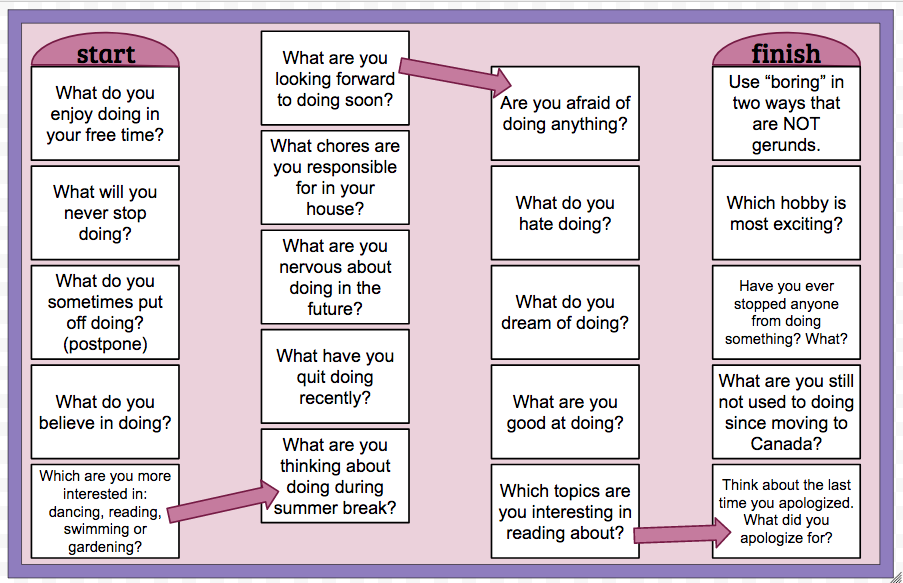 Sometimes, with hatred towards healthy people, trying to infect others. nine0003
Sometimes, with hatred towards healthy people, trying to infect others. nine0003
An important problem associated with HIV infection, is the danger of overdiagnosis AIDS by both doctors and HIV carriers. Thus, infected patients may accept any discomfort in the body for signs of manifestation disease and difficult to respond to examination as evidence its occurrence. In these cases it is possible desire to commit suicide.
There is no effective treatment for AIDS however, medical assistance may help prolong life patients and improve the quality life during the illness. In cases acute psychosis, neuroleptics are used (haloperidol, chlorpromazine, droperidol) and tranquilizers in doses reduced in accordance with the degree of expression organic defect. In the presence of signs of depression are prescribed antidepressants and their side effects effects. Correction of personal disorders are carried out with the help of tranquilizers and mild antipsychotics (such as thioridazine and neuleptil). The most important factor in maintaining psychological balance is properly organized psychotherapy. nine0003
The most important factor in maintaining psychological balance is properly organized psychotherapy. nine0003
16.4.3. Prion diseases
This group of diseases is associated with the discovery in 1983 of the prion protein, a natural human protein and animals (the gene encoding this protein, found on the short arm of the chromosome twenty). Established the possibility of infection mutant forms of this protein, its accumulation in brain tissues is shown. At present, out of the stipulated Prions have described 4 human diseases and 6 animal diseases. Among them are noted sporadic, infectious and hereditary diseases. However there is evidence that prion proteins produced by random mutations (sporadic cases of the disease), have the same degree of contagiousness, that are infectious. nine0003
An example of a typically infectious prion human disease is kuru — illness, found in one of the tribes of Papua New Guinea, where the ritual eating the brains of dead compatriots. Currently, with the change rituals this disease is practically disappeared. to hereditary prion diseases include the syndrome Gerstmann-Streussler-Scheinker, fatal familial insomnia and familial forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Family and infectious diseases account for less than 10% of all cases nine0% of cases are sporadic cases of the disease (sporadic form Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease).
Currently, with the change rituals this disease is practically disappeared. to hereditary prion diseases include the syndrome Gerstmann-Streussler-Scheinker, fatal familial insomnia and familial forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Family and infectious diseases account for less than 10% of all cases nine0% of cases are sporadic cases of the disease (sporadic form Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease).
Disease Creutzfeld-Jakob [F02.1] [Kreutzfeld X., 1920, Jacob A., 1921] - malignant rapidly progressive disease, characterized by spongy regeneration of the cerebral cortex, cerebellar cortex and gray matter subcortical nuclei. Main manifestation disease - dementia with severe brain dysfunction (agnosia, aphasia, alexia, apraxia) and motor disorders (myoclonus, ataxia, intention tremor, oculomotor disorders, seizures, pyramidal and extrapyramidal disorders). nine0003
In 30% of cases, the development of the disease is preceded by nonspecific prodromal symptoms in the form of asthenia, disorders sleep and appetite, memory impairment, behavioral changes, weight loss body. About the immediate debut of the disease evidence of visual disturbances headaches, dizziness, instability and paresthesia. Usually the disease occurs at the age of 50-65 years, men are slightly more often ill. No effective treatments have been found most patients die in during the first year, but sometimes the disease extended over 2 years or more. nine0003
About the immediate debut of the disease evidence of visual disturbances headaches, dizziness, instability and paresthesia. Usually the disease occurs at the age of 50-65 years, men are slightly more often ill. No effective treatments have been found most patients die in during the first year, but sometimes the disease extended over 2 years or more. nine0003
Timely diagnosis of the disease presents significant difficulties. Important diagnostic features are rapid progression symptoms, absence of inflammation changes in the blood and CSF (no fever, increased ESR, leukocytosis in the blood and pleocytosis in CSF), specific EEG changes (repetitive triphasic and polyphasic activity with an amplitude of at least 200 μV, the resulting every 1-2 s).
Special interest in prion diseases arose in connection with the epidemic of spongiform bovine encephalopathy in England and the emergence during the same period in England and France 11 cases of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with atypically early onset. nine0003
nine0003
Although clear evidence of a connection between these two facts is not found, but scientists have to take into account the data on the high persistence of prion proteins (formalin treatment of the tissues of the deceased does not reduce their contagiousness). AT documented cases of transmission Creutzfeld-Jakob disease from one person to another incubation period was 1.5-2 years.
16.4.4. Mental disorders in acute brain and extracerebral infections
Mental disorders can occur at almost any brain or general infection. To specific brain infections include epidemic encephalitis, tick-borne and mosquito encephalitis, rabies. Draw a clear line between brain and extracerebral processes not always possible, because encephalitis, meningitis and cerebrovascular disease may occur with such common infections like flu, measles, scarlet fever, rheumatism, mumps, chicken pox, tuberculosis, brucellosis, malaria, etc. In addition, indirect brain damage due to hyperthermia, general intoxication, hypoxia nonspecific pneumonia, purulent surgical lesions can also lead to psychoses similar in their manifestations with brain infections. nine0003
nine0003
In various infections often observed the same psychopathological syndromes. They are usually placed in concept of exogenous type of reactions. So, acute psychoses are manifested by switching off or clouding of consciousness (delirium, amentia, seizures are much less common, similar to oneiroid). Psychoses occur usually in the evening against the backdrop severe fever, accompanied signs of inflammation in blood tests and liquor. The factors that increase the risk of psychosis previous organic diseases of the central nervous system (injuries, disorders liquorodynamics), intoxication (alcoholism and substance abuse). More likely occurrence of psychosis in children. nine0003
For chronic sluggish infections sometimes there are hallucinatory and hallucinatory-delusional disorders. Debilitating diseases lead to prolonged asthenia. Like the outcome of a heavy infectious process may occur Korsakov's syndrome or dementia (psychoorganic syndrome). Highly common complication of severe infections disease is depression, which sometimes develops against a background of gradual resolution of acute manifestations of the disease. Manic episodes are much less common. and catatonic disorders. nine0003
Manic episodes are much less common. and catatonic disorders. nine0003
most specific clinical different picture epidemic encephalitis (lethargic encephalitis). The disease is described in 1917 by the Austrian psychiatrist K. Econo- mo during the pandemic of 1916-1922. In recent years of epidemics of this disease not observed - only described isolated sporadic cases.
The disease is markedly different variety of manifestations. Described as sharp, quickly leading to death cases that gradually develop asymptomatic options. Often after the resolution of the acute phase of the disease return of symptoms, less pronounced. In acute phase of the disease on the background of subfebrile condition (37.5–38.5°) there is a varied neurological symptoms: diplopia, ptosis, anisocoria, motor lethargy, amimia, rare flashing, violation of friendly movements of the arms and legs. With an acute onset may have severe headache and muscle pain, vomiting, impaired consciousness with hallucinations, delusions, hyperkinesis, sometimes epileptic seizures. An almost obligatory symptom is sleep disturbance either in the form of periods pathological hibernation, lasting for several days or weeks, or sleep-wake cycle disorders with pathological daytime sleepiness and insomnia at night. Sometimes in night time are observed excitement and hallucinations. nine0003
An almost obligatory symptom is sleep disturbance either in the form of periods pathological hibernation, lasting for several days or weeks, or sleep-wake cycle disorders with pathological daytime sleepiness and insomnia at night. Sometimes in night time are observed excitement and hallucinations. nine0003
In addition to the typical variants of the disease, often observed atypical forms with predominance of mental disorders - delirium, reminiscent of alcohol; depression with severe hypochondriasis ideas and desire for suicide; atypical manic states with chaotic unproductive excitement; phenomena apathy, adynamia, catatonia, hallucinatory-delusional states, that need to be differentiated from the onset of schizophrenia.
For previous epidemics '/ 3 patients died in acute phase of the disease. Many observed long persistent course diseases. In the remote period were especially pronounced motor disorders in the form of muscle stiffness, tremor, bradykinesia (parkinsonism). Rough intellectual-mnestic disorders were not usually observed. Often for a long time there were extremely unpleasant sensations in the head and all over the body (crawling, itching). Vote in the head, visual pseudohallucinatory images, violation of the sense of inner unity resembled schizophrenic symptoms. nine0003
Rough intellectual-mnestic disorders were not usually observed. Often for a long time there were extremely unpleasant sensations in the head and all over the body (crawling, itching). Vote in the head, visual pseudohallucinatory images, violation of the sense of inner unity resembled schizophrenic symptoms. nine0003
The diagnosis is confirmed by signs of sluggish inflammation in the cerebrospinal fluid - increased amount of protein and sugar, pathological Lange reaction (less distinct than with syphilis).
Treatment of infectious diseases in primarily based on etiotropic therapy. Unfortunately, in the case of viral infections chemotherapy is usually ineffective. Sometimes used serum of convalescents. Nonspecific anti-inflammatory therapy includes use of nonsteroidal drugs or corticosteroid hormones and ACTH. Antibiotics are used to prevent the connection of a secondary infections. In the case of a pronounced general intoxication (for example, with pneumonia) detoxification is of great importance measures in the form of polyionic infusions and colloidal solutions (hemodez, reo- polyglucin). To combat cerebral edema use diuretics, corticosteroids and oxygen, sometimes lum- ballpoint puncture. in acute psychosis need to prescribe antipsychotics and tranquilizers (usually in reduced doses). For a more complete recovery brain functions during convalescence prescribe nootropics (piracetam, pi- reditol) and mild stimulants-adaptogens (eleutherococcus, ginseng, pantocrine, Chinese Lemongrass). Treatment antidepressants are prescribed for persistent decrease in mood passing of the acute phase of the disease (in acute phase of TCA disease and other anticholinergic funds can provoke delirium occurs). nine0003
To combat cerebral edema use diuretics, corticosteroids and oxygen, sometimes lum- ballpoint puncture. in acute psychosis need to prescribe antipsychotics and tranquilizers (usually in reduced doses). For a more complete recovery brain functions during convalescence prescribe nootropics (piracetam, pi- reditol) and mild stimulants-adaptogens (eleutherococcus, ginseng, pantocrine, Chinese Lemongrass). Treatment antidepressants are prescribed for persistent decrease in mood passing of the acute phase of the disease (in acute phase of TCA disease and other anticholinergic funds can provoke delirium occurs). nine0003
Kavkazskiy Knot
Various sources inform about an anti-terrorist operation currently being carried out in the Khojavend region of Azerbaijan. At 11 o'clock today, the Ministry of Defense reported on the result of yesterday's battle - six attackers were killed, one was wounded and one Azerbaijani soldier died. At present, the illegal armed men are reportedly surrounded and the operation continues.
Society in Azerbaijan demands the withdrawal of the Russian army from Garabagh
After the Declaration on the cessation of hostilities signed by the three heads of state on November 9, 2020, all armed illegal formations on the territory of Azerbaijan were declared terrorists, martial law does not apply to them, since the war has officially ended. This explains the absence of prisoners.
The operation is carried out with the tacit consent of Russian peacekeepers, since the Azerbaijani army is now forced to ensure the safety of not only the Azerbaijani population returning to the region, the Armenian population remaining in Garabagh, but also the Russian peacekeepers serving in the military. nine0003
On the video: an Armenian in a characteristic form and expressions expresses his emotions when he sees a sign on the border (road) "Welcome to Azerbaijan"
are carried by the Russian Armed Forces, makes them responsible for peace in Garabagh. It can be seen that the Russians do not want to provide this world on their own. Then the path does not interfere, the Azerbaijani army knows its business. So far, that is exactly what is happening. Was this achieved as a result of the consent of Azerbaijan and Russia, or maybe Yerevan knows about the penetration of its armed citizens into Garabagh, but not being able to neutralize them, gives their fate to Azerbaijan? With Pashinyan, this is possible. nine0003
It can be seen that the Russians do not want to provide this world on their own. Then the path does not interfere, the Azerbaijani army knows its business. So far, that is exactly what is happening. Was this achieved as a result of the consent of Azerbaijan and Russia, or maybe Yerevan knows about the penetration of its armed citizens into Garabagh, but not being able to neutralize them, gives their fate to Azerbaijan? With Pashinyan, this is possible. nine0003
Today, the Azerbaijani army gave one hour, the last one, to the residents of the Armenian village of Vorotan in southern Armenia, so that the residents of houses built during the years of occupation on Azerbaijani soil should leave it. The hour is over. The remaining foreigners, if they are armed, will be punished. Peaceful people were deported as foreigners who illegally entered the territory of our country.
A complex process is going on in Garabagh, dangerous and fraught with various consequences. Armenians and Azerbaijanis have claims to the Armenian side, and it is clear that Russians cannot be nice to everyone.