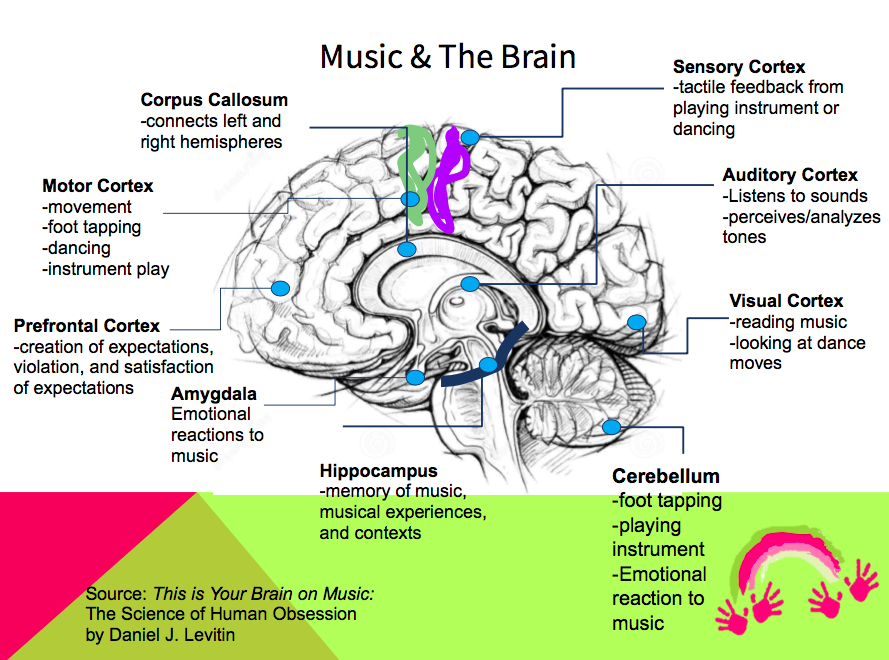
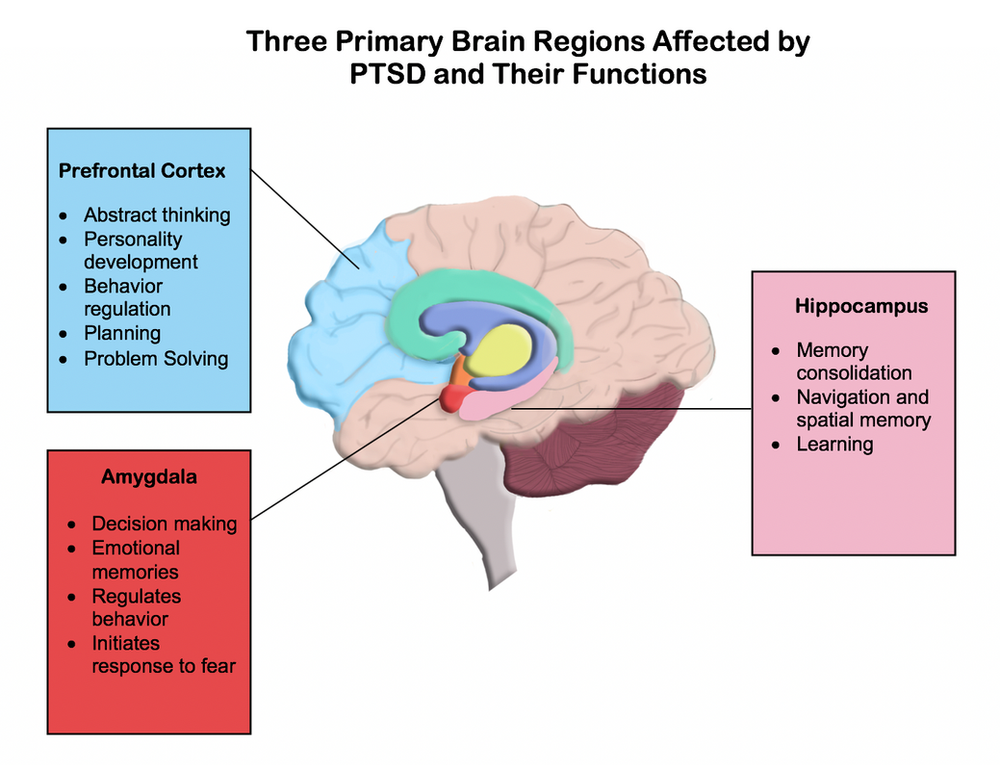
How dance affects the brain
Is Dancing Good for the Brain?
- Download PDF Copy
By Angela Betsaida B. Laguipo, BSNReviewed by Dr. Liji Thomas, MD
Dance is a form of performing art wherein the body moves in a rhythmic way, usually to express feelings or ideas. Dancing has shown many health benefits, including boosting brain power and function.
Dancing can provide various physical benefits. Image Credit: goodluz / Shutterstock
What benefits does dancing have for the brain?
Dancing reduces depression symptoms
Dancing can provide various physical benefits but now, researches show promising results that it can also benefit the mind, with a growing body of evidence that suggests that dancing is good for mental health.
Depression is a disabling mental illness as evidenced by feelings of sadness, problems with emotion regulation, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Depression affects more than 350 million people worldwide. Today, the most common and effective treatment for depression is medication in combination with counseling and psychotherapy.
In a study, the researchers examined whether dancing was a good treatment therapy for depression. Dancing focuses on body movement and emotional expression, that helps alleviate the symptoms of depression. At the same time, it helps reduce the levels of depression as shown by psychometric measures.
Dancing supports motor, emotional, and intellectual brain functions
Dance/Movement Therapy (DMT), also called movement psychotherapy, is the psychotherapeutic use of body movements to maintain and improve intellectual, motor, and emotional abilities of the body.
DMT is based on the conception that movement is a language, movement can be communicative and expressive, movement can be both an assessment tool and a primary mode of intervention, and the mind, body, and spirit are interconnected. Furthermore, dance movement therapists can look at a person’s movements to assess and intervene, thus enabling it to contribute to the treatment of mental health problems.
Furthermore, dance movement therapists can look at a person’s movements to assess and intervene, thus enabling it to contribute to the treatment of mental health problems.
DMT has also been found to have a positive effect on children’s cognitive development. Dance can use spirituality, intelligence, spontaneity, and discovery while the body is producing movements, which is a form of art. Dance therapy can create a good environment for cognitive development.
Dance As Therapy: Natalia Duong at TEDxStanford
Dance boosts memory
Dancing improves brain function and boosts memory. Several studies have shown that dancing is linked to a reduced risk of dementia. In a study by researchers at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, they found that dancing is associated with 76% reduced risk of dementia among the participants.
Another study published on the Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience shows that dancing improves cerebral health. Dancing improves one of the cognitive domains, which is spatial memory.
The study also suggests that maintaining an active lifestyle into old age can preserve motor, cognitive, and perceptual abilities.
Dancing stimulates nerve growth factors
Dancing has many positive effects on the brain. The driving force behind its inhibition of aging relates to its ability to stimulate nerve growth factors. Nerve growth factors are proteins important for maintaining sensory neuron health.
In a study published in the Journal of Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, the researchers concluded that dancing can boost the connectivity between both cerebral hemispheres, and long-term dance practice positively affects brain activity. All these are linked to neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections to change and adapt.
The combination of exercise and sensory enrichment during a dance can improve neuroplasticity. Hence, dancing can be used as an intervention for many neurological diseases, like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and cerebral palsy.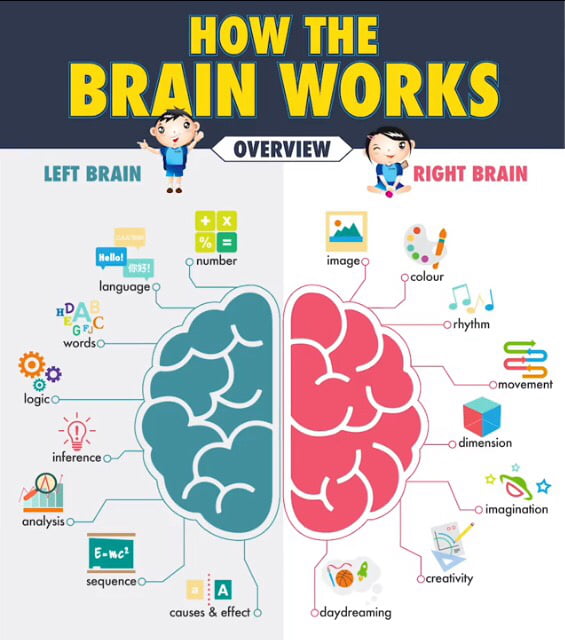
Sources
- Punkanen, M., et al., (2017). Emotions in motion: depression in dance-movement and dance-movement in treatment of depression. Oxford Handbooks Online. DOI: 10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199949298.013.58
- Goodill, S. (2016). Dance/movement therapy and the arts in healthcare: the first 50 years. American Journal of Dance Therapy. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs10465-016-9235-z Balgaonkar, AV. (2010). Effect of dance/ motor therapy on the cognitive development of children. International Journal of Arts and Sciences. www.openaccesslibrary.org/images/XEW191_Asmita_Vilas_Balgaonkar.pdf
- Verghese, J. et al., (2003). Leisure activities and the risk of dementia in the elderly. New England Journal of Medicine. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa022252
- Merom, D. et al., (2016). Cognitive benefits of social dancing and walking in old age: the dancing mind randomized controlled trial. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.
 https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00026
https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00026 - Machado L. T. et al.,(2018). Dance for neuroplasticity: A descriptive systematic review. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.12.010
Further Reading
- All Dancing Content
- Can Dancing Improve your Mental Health?
Last Updated: Jun 26, 2019
- Download PDF Copy
Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report:
APA
Laguipo, Angela. (2019, June 26). Is Dancing Good for the Brain?. News-Medical. Retrieved on December 23, 2022 from https://www.news-medical.net/health/Is-Dancing-Good-for-the-Brain.aspx.
MLA
Laguipo, Angela. "Is Dancing Good for the Brain?". News-Medical. 23 December 2022. <https://www.news-medical.net/health/Is-Dancing-Good-for-the-Brain.
 aspx>.
aspx>.Chicago
Laguipo, Angela. "Is Dancing Good for the Brain?". News-Medical. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Is-Dancing-Good-for-the-Brain.aspx. (accessed December 23, 2022).
Harvard
Laguipo, Angela. 2019. Is Dancing Good for the Brain?. News-Medical, viewed 23 December 2022, https://www.news-medical.net/health/Is-Dancing-Good-for-the-Brain.aspx.
This Is How Dancing Helps Your Brain
Dancing is fantastic for fitness, but it is even better for what it does to your brain. We did some research, and here is what we found.
Does dancing help your brain? Yes, dancing and taking dance classes frequently can help your brain in a few ways. A study had shown that dancing frequently reduced the risk of dementia by 76%!
- It can be a great way to maintain and improve many of the brain functions.
- Dancing has also shown to increase your neural connectivity.
- Dance has also led to enhancing neuroplasticity
- Increase intelligence
- Improve muscle memory
- Slow down aging
- Boost memory
- Prevent dizziness.
If you want to get a little deeper, speed up your online research time, and see what our research has shown. Read on; we promise you won't be disappointed.
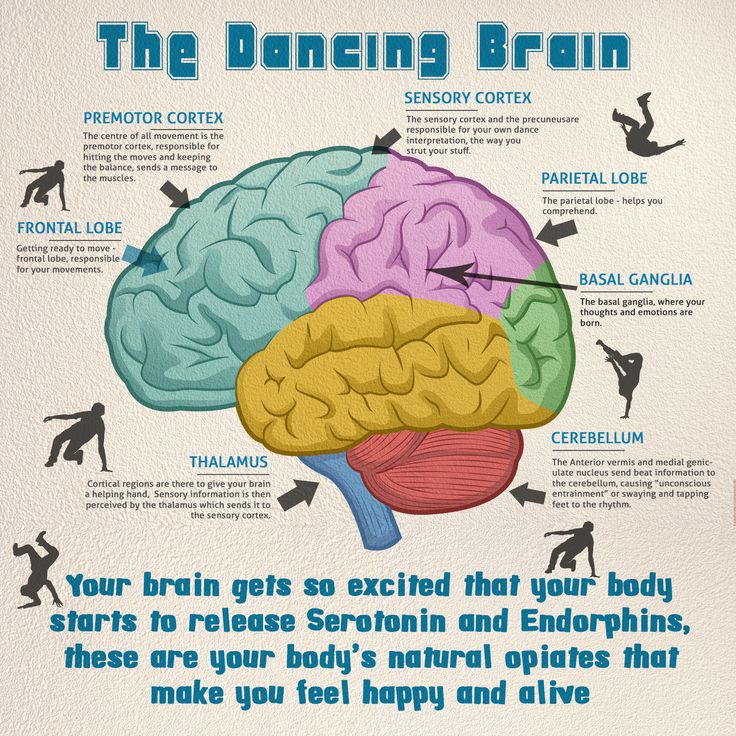
Since dance requires you to integrate several brain functions at once like; rational, musical, kinesthetic, and emotional, it makes your brain fire up and gets stronger.
Also, because of the nature of dance, it improves neural connectivity. The increase in neural connectivity can be of great benefit to your brain as it ages. It is allowing your brain to engage and activate each of its parts.
via GIPHY
According to Psychology Today and Science Daily, In 2013, researchers from ICL (Imperial College London) published research that showed specific differences in the brain structure of ballet dancers that help them avoid feeling dizzy when they perform pirouettes. Furthermore, the research suggests that years of training can enable dancers to suppress signals from the balance organs in the inner ear linked to the cerebellum. (psychologytoday.com and Sciencedaily.com)
via GIPHY
At the University of Illinois at Chicago, through a CDC-funded program, some researchers designed a dance program for older adults. Participants in the program reported improvements in attention, focus, and of course.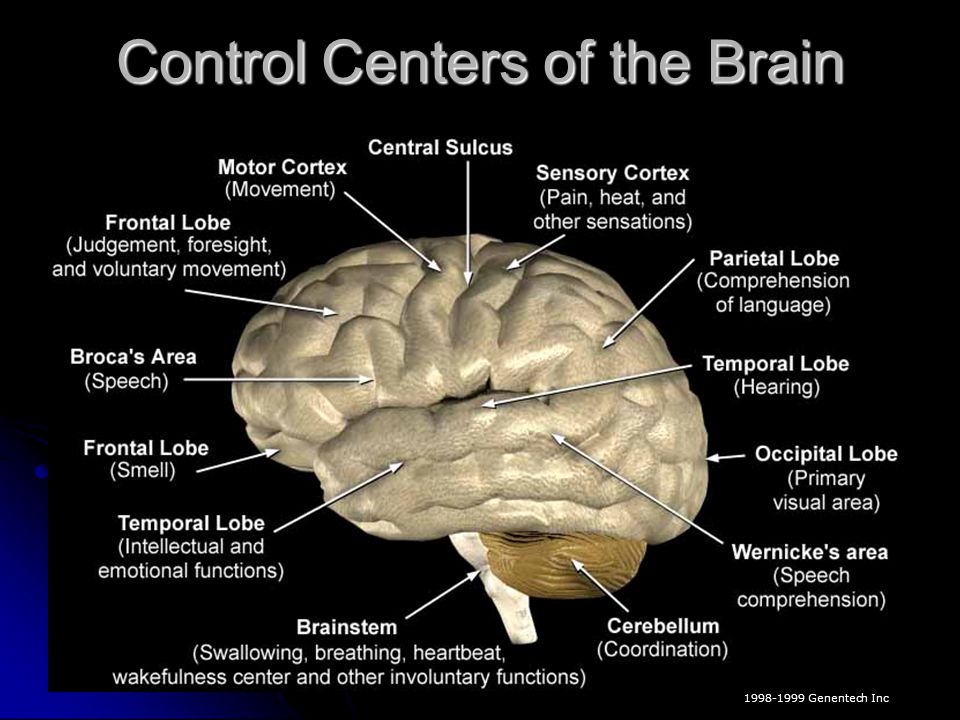 Also, in another separate dance program, older people experiencing mild cognitive impairment improved their thinking and memory after a 10-month-long of dance class. (cdc.gov) As dancers, we kind of already knew that, right, having to remember all those choreographies and corrections.
Also, in another separate dance program, older people experiencing mild cognitive impairment improved their thinking and memory after a 10-month-long of dance class. (cdc.gov) As dancers, we kind of already knew that, right, having to remember all those choreographies and corrections.
via GIPHY
Research led by the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City published 21-year research that studies senior citizens 75 years and older. The researchers tracked/measured mental acuity in aging by monitoring rates of dementia. The goal was to see if any physical or cognitive recreational activities had an effect on mental acuity.
What they found was just WOW; almost none of the physical activities had had any effect. The one exception was frequent dancing. Some findings of the studies were:
- Bicycling and swimming – 0% reduced risk of dementia
- Playing golf – 0% reduced risk of dementia.
- Reading – 35% reduced risk of dementia.
- Doing crossword puzzles at least four days a week – 47% reduced risk of dementia.
- Dancing frequently – 76% reduced risk of dementia (Let's go dancing!!!)
To see the full study click here (stanford.edu).
via GIPHY
Okay, we can already hear the skeptics when mentioning that dance increases intelligence. If this is you, read on to put it simply, the basis of "intelligence" is making decisions. There are other definitions of intelligence, like "the ability to apply knowledge to manipulate one's environment or to think in abstractly as measured by objective criteria (such as tests) - Merriam-Webster."
To get your mental acuity better, it is best to get yourself in an activity that demands quick, rapid decision making. Dancing is an example of a fast-paced activity that demands speedy decision making.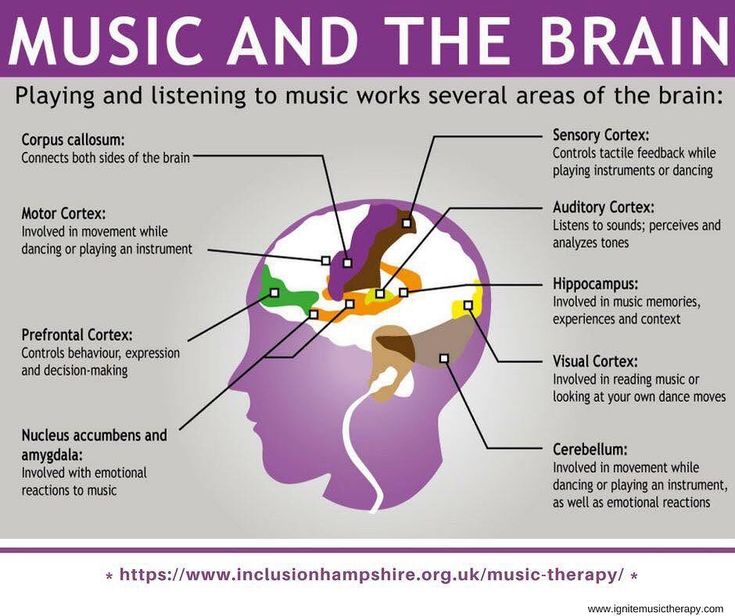 \It requires instant physical responses to questions like What speed to move your body? How to react to your partner's movements in social dancing? And Which way to turn or not to turn? lol (lifehack.org)
\It requires instant physical responses to questions like What speed to move your body? How to react to your partner's movements in social dancing? And Which way to turn or not to turn? lol (lifehack.org)
via GIPHY
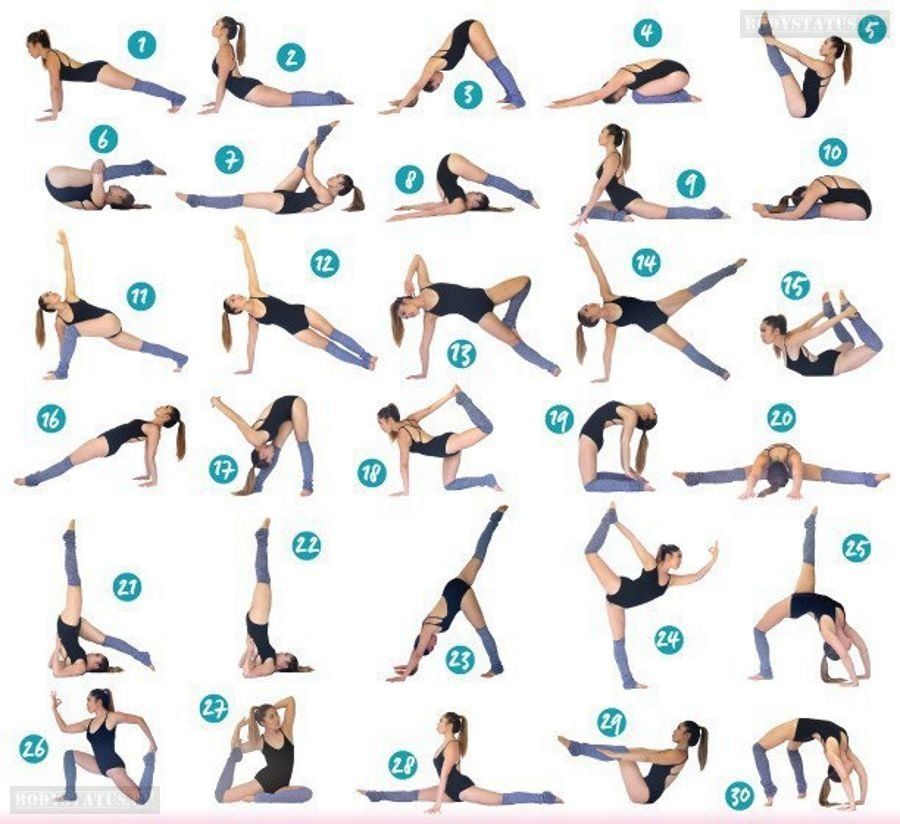
Hasn't your teachers told you a million gazillion times? Practice makes perfect, or we are working on muscle memories, or perfect practice makes perfect. As dancers, we physically engage our body, which requires strength and stamina, and we remember choreography; okay, most times, we remember choreography. Choreography, when done enough, becomes muscle memory, the connection between physical and mental. In fact, the process of "marking" a routine—walking through the movements—is an effective method of encoding choreography. This allows you (the dancer) to repeat the moves with greater fluidity once they perform them full-out.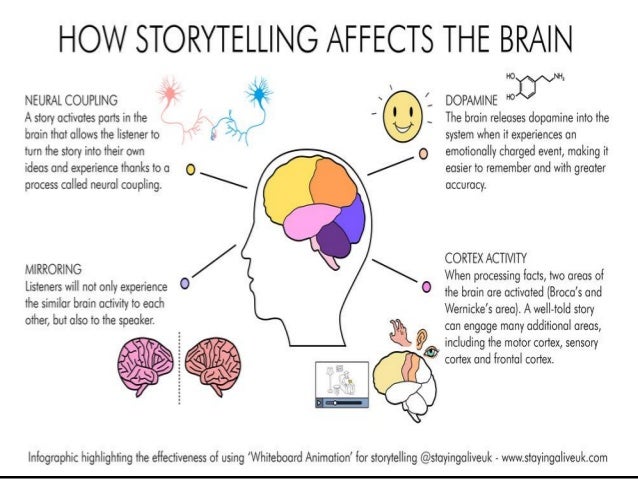 (DanceAcademyUsa)
(DanceAcademyUsa)
Bonus
Dancing - Why dancing is good - How to improve brain function - Health / HB
From the point of view of protection against neurodegenerative diseases, dancing is more effective than any other physical training
It is precisely proven: to be smart, you need to ... dance! Preferably in different styles. Ideal - since childhood. And definitely with pleasure.
There are many studies of the neuroevolution of the human psyche, and they all show that brain development in children depends not only on the study of languages and mathematics, but also on motor activity. nine0003
Video of the day
How does it work?
Dance is one of the most ancient forms of human self-expression. It developed along with music. In essence, dance is a sign language. This suggests that dance plays the role of an early form of speech.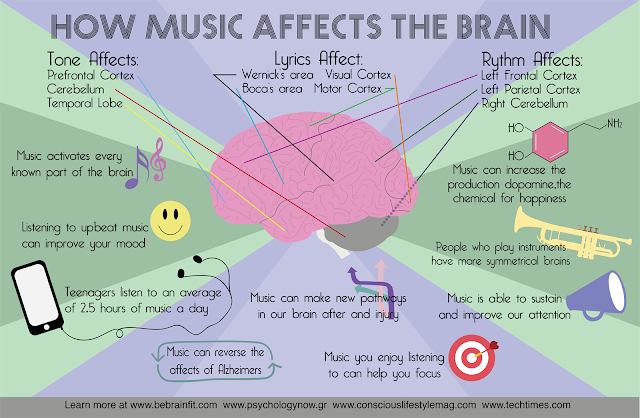 And helps to master it.
And helps to master it.
During dance movements, the same area is activated in the brain as when pronouncing words. But not only.
In order for a person to jump on one foot, his brain must instantly perform calculations in the sensorimotor system, taking into account the surrounding space, the force of gravity, maintaining balance and many other factors. nine0003
People who do aerobic exercise grow their brains
Music, rhythm, body vibration activate all brain structures and nervous system. There is a lot of work going on in the brain.
Therefore, dancing for an adult or an elderly person is also very useful, and not only to improve the figure and mood.
Experts from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases in Magdeburg found that dancing is more effective than any other physical training. And slow down the aging of the brain. nine0003
Conducted an experiment (mean age of participants 68 years). The people were divided into two groups. Some attended different sports training. Others were dancing. Moreover, they danced jazz dances, and Latin American, and a quadrille, and a waltz. In general, dances that are different in rhythm, combinations of movements and speed.
Some attended different sports training. Others were dancing. Moreover, they danced jazz dances, and Latin American, and a quadrille, and a waltz. In general, dances that are different in rhythm, combinations of movements and speed.
Read also:
So, both groups showed an improvement in the functioning of the hippocampus - the area of the brain that is most susceptible to age-related changes (for example, Alzheimer's disease). However, in the dance group, positive changes in the hippocampus were more pronounced. That is, the brains of those who danced developed much better. nine0003
American neuroscience star, author of The Weird Girl Who Fell in Love with the Brain, Wendy Suzuki, Ph.D., wrote: “When you do aerobic exercise, your heart rate increases, and this stimulates the production of new cells in the hippocampus. Accordingly, people who engage in aerobic exercise grow their brains. And it improves long-term memory. It turns out that I can create as many new cells as I want.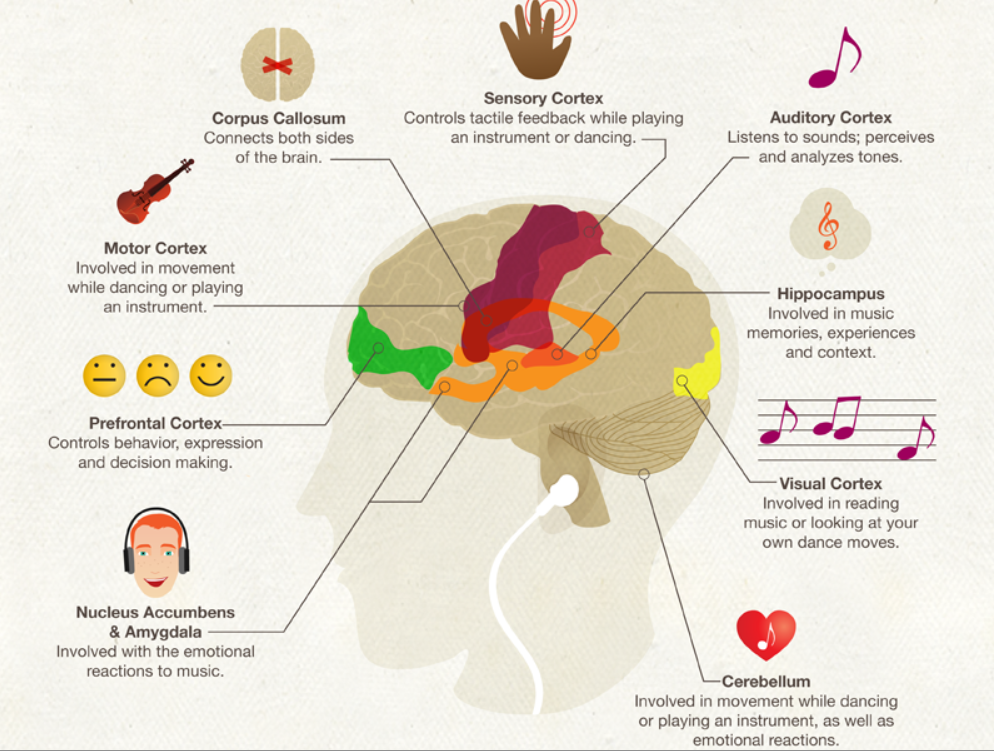 ”
”
Even if this forecast seems too optimistic, all the same, after these words, you already want to run to the dance. And you? nine0003
Main news digest
Free email newsletter of only the best materials from editors NV
Sending is sent from Monday to Friday
The text is published with the permission of the author
9005 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 Telegram channel Opinions HB
More blogs here
Tags: Health Dance Brain
How does dancing develop the brain? Scientists' arguments: matveychev_oleg — LiveJournal
Do you already know that physical activity has a beneficial effect on mood and well-being? Scientists have long found out that during training, the level of serotonin in the brain rises, and endorphins cannot do without endorphins. Today, science has gone much further, trying to understand whether dance can improve brain function, and not just improve mood. It became clear that any physical activity affects our mental abilities, but dancing is the most effective. And that's why. nine0003
Today, science has gone much further, trying to understand whether dance can improve brain function, and not just improve mood. It became clear that any physical activity affects our mental abilities, but dancing is the most effective. And that's why. nine0003
The brain is the most complex human organ
Neuroscientists have even suggested that the phrase “my brain” is incorrect. According to Tatyana Chernigovskaya, a well-known Russian neurolinguist, it is more likely that we are 100% dependent on him.
He himself formulates the decision and gives a signal to action to other bodies. He knows how to study. What's more, the brain is learning at any given time, whether we're reading a book or washing dishes.
The most important thing that scientists have proven over the past decades is that the brain is plastic, it can change. An interesting experiment conducted with rats proved that a life filled with impressions, interesting events and constant action (in their case, this is the presence of games with and without comrades), allows you to "grow" a brain that is larger than the brain of those who led a calm everyday life. a life. nine0003
a life. nine0003
A brain that receives more impressions can receive and process more information, learn better, and remember more.
What do you need?
Enriched environment. A world that is filled with colors in the form of new smells, delicious food, intellectual knowledge and, of course, dances, gives rise to more emotions.
Emotions enhance and strengthen memory. These impressions are processed by the part of the brain that is responsible for long memories and, like any regular exercise, trains the organ. It is not by chance that we remember the days when we were very bad and very good, but we remember our first dance lesson even when we lost all our knowledge of mathematics. nine0003
Why dancing?
1) Dancing is not just movement, it is movement to music
When a person listens to his favorite music, the centers responsible for encouragement are activated in his head, we experience inspiration and a feeling of happiness. At the same time, we enjoy physical activity.
At the same time, we enjoy physical activity.
When this happens at the same time, a person experiences an unprecedented emotional upsurge and is completely immersed in the movement, dissolving in it. Therefore, we can make absolutely any physical exercise effective by adding a positive attitude to it - music, a smile and an inner mantra. nine0003
Wendy Suzuki, neuroscientist and author of The Girl Who Fell in Love with the Brain, calls it goal-directed exercise.
2) Dancing is a gentle exercise
It improves blood circulation throughout the body, and the brain is better supplied with oxygen and nutrients.
3) Dancing reduces the risk of developing dementia
This is a complex disease, as a result of which a person loses memories and is almost unable to learn new things. 13 years ago, Albert Einstein College researchers studied the effects of eleven types of physical activity, and it was the choreographic art that showed the best results. nine0003
nine0003
4) The brain develops by adapting to loads
Have you ever wondered why ballerinas do not experience discomfort during endless fouettes? Such turns, sooner or later, were bound to lead to dizziness.
Scientists have studied the perception of turns of ballerinas and ordinary women of the same age and size and have come to the conclusion that training suppresses the very signals that go from the vestibular organs in the inner ear to the brain.
Did you know that you don't have to dance with conscious memory? nine0003
The dance class left neuroscientist Wendy Suzuki feeling dissatisfied for a long time, as she was the worst student in the group. She tried to remember exactly the movements that the trainer showed, using the hippocampus (it is responsible for conscious memory).
Only after a while she realized and tested on herself, and then on her students, that movements involve completely different parts of the brain and it is impossible to control this with consciousness.
“When you hit a golf ball, you don't think about what muscle movements you need to do it. You learn punches by practice, without the participation of consciousness ... I just used the WRONG part of the brain, memorizing the dance! Now all I had to do was to use the basal ganglia instead of the hippocampus - and that's it, you can enter the troupe of Alvin Ailey! I no longer tried to remember the movements of the dance and just tried to focus on making my body move, as the coach showed. I “surrendered to the flow”, which greatly improved my ability to master the choreography.” nine0035
What does this mean?
To develop the brain and stimulate memory, it is not necessary to visit 52 countries in a year and study mathematics intensively. You can daily load the brain with new impressions, emotions and knowledge.
Dancing classes give a particularly strong and varied load.
Neuroscientist Wendy Suzuki advises to learn at least one movement a day and repeat it for four minutes to your favorite track.